Abstract
Prosthodontic decision-making process is done through analysis of clinical information and mutual communication between patient and dentist. When opposing teeth are extruded due to missing tooth or tooth defects, selection of appropriate treatment plan and predictory prognosis can be complicated in functional rehabilitation. In case of severely disharmonious occlusal plane result from extruded teeth, re-establishment of the occlusal plane is required, if necessary via prudent evaluation. In this case, class III patient had unesthetic appearance and mastication discomfort caused by disharmonious occlusal plane due to severe extrusion. Through a structured diagnostic process, appropriate treatment plan was selected. Esthetic and functional results were obtained through from full mouth rehabilitation with re-establishment of the occlusal plane. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2016;54:451-7)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Hulley SB., Cummings SR., Browner WS., Grady D., Newman TB. Designing clinical research. 3th ed.Philadelphia: Li ppincott; Williams & Wilkins;2007. p. 23.
2.Rosenstiel SF., Land MF., Fujimoto J. Comtemporary fixed prosthodontics. 4th ed.Elsevier;2008. p. 12–5.
3.McGuire MK., Nunn ME. Prognosis versus actual outcome. II. The effectiveness of clinical parameters in developing an accurate prognosis. J Periodontol. 1996. 67:658–65.

4.McGuire MK., Nunn ME. Prognosis versus actual outcome. III. The effectiveness of clinical parameters in accurately predicting tooth survival. J Periodontol. 1996. 67:666–74.

5.Faggion CM Jr., Petersilka G., Lange DE., Gerss J., Flemmig TF. Prognostic model for tooth survival in patients treated for periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2007. 34:226–31.

6.Fayz F., Eslami A. Determination of occlusal vertical dimension: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 1988. 59:321–3.

7.Turner KA., Missirlian DM. Restoration of the extremely worn dentition. J Prosthet Dent. 1984. 52:467–74.

8.Dawson PE. Functional occlusion from TMJ to smile design. Elsevier;2007. p. 58–68.
9.el-Sheikh MM., Powers JM. Tensile bond strength of porcelain teeth to denture resin before and after aging. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:16–20.
Go to : 
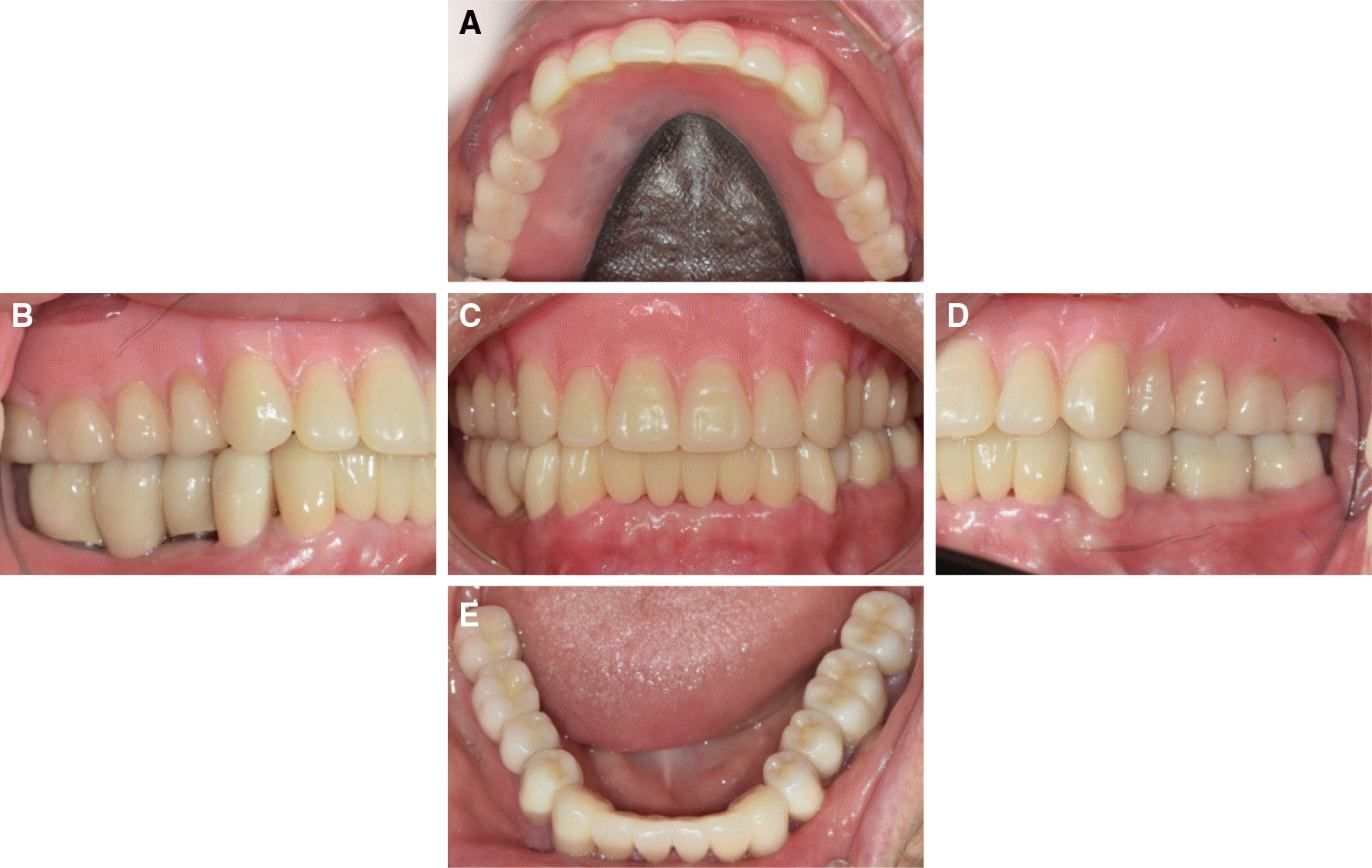
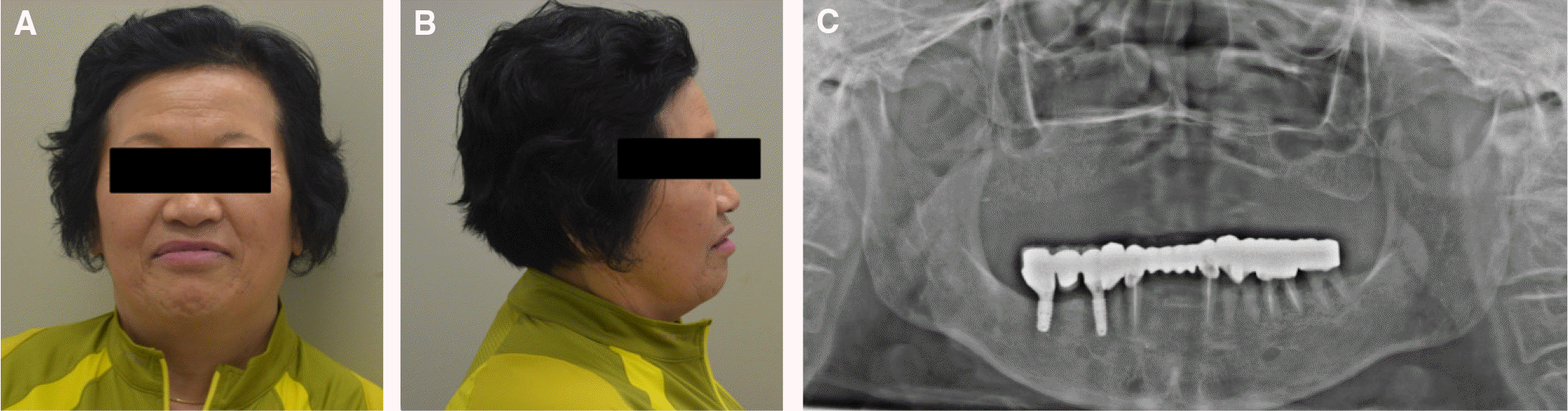
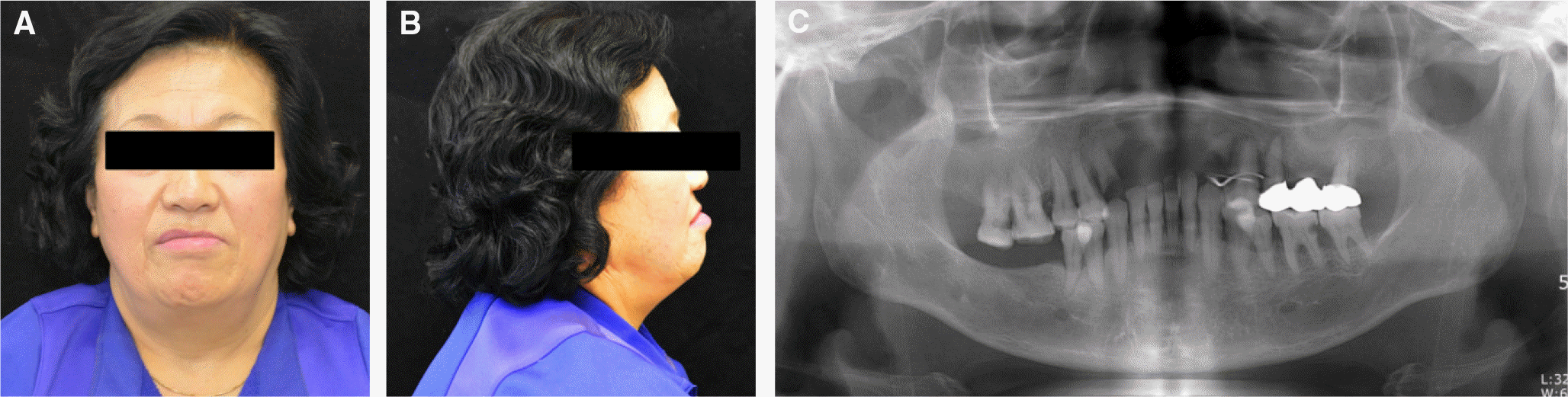 | Fig. 1.Preoperative extraoral photograph & panoramic view. (A) Frontal view, (B) Lateral view (right side). Class III appearance is observed. (C) Panoramic view. Uneven occlusal plane. |
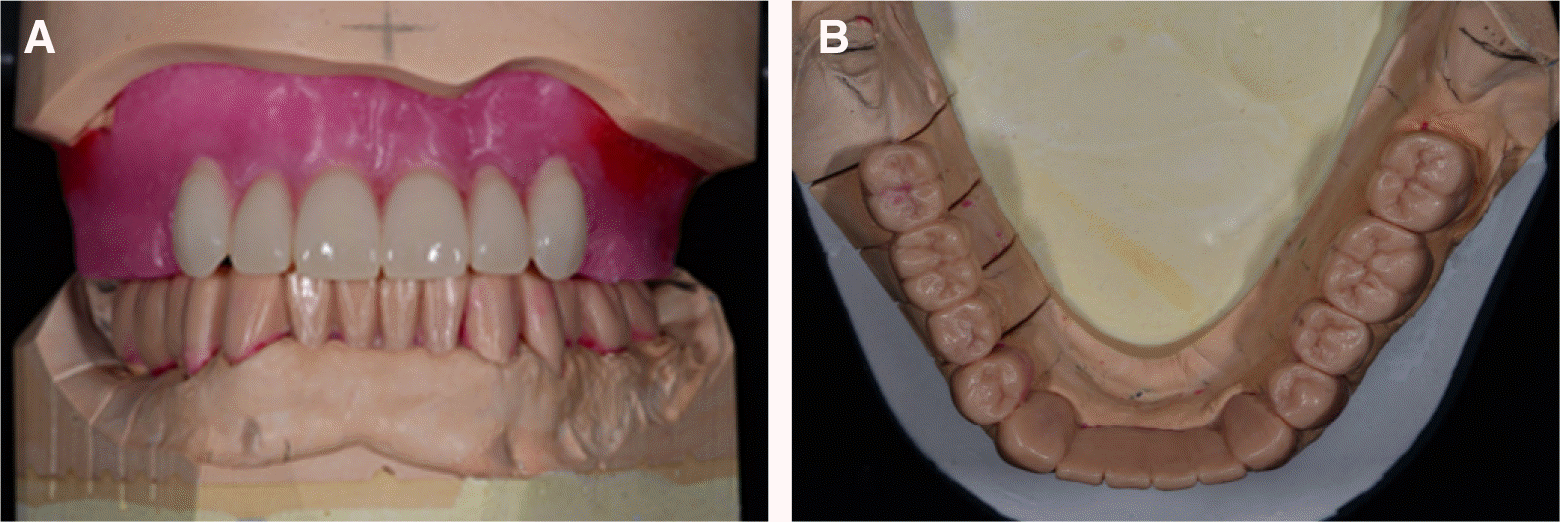
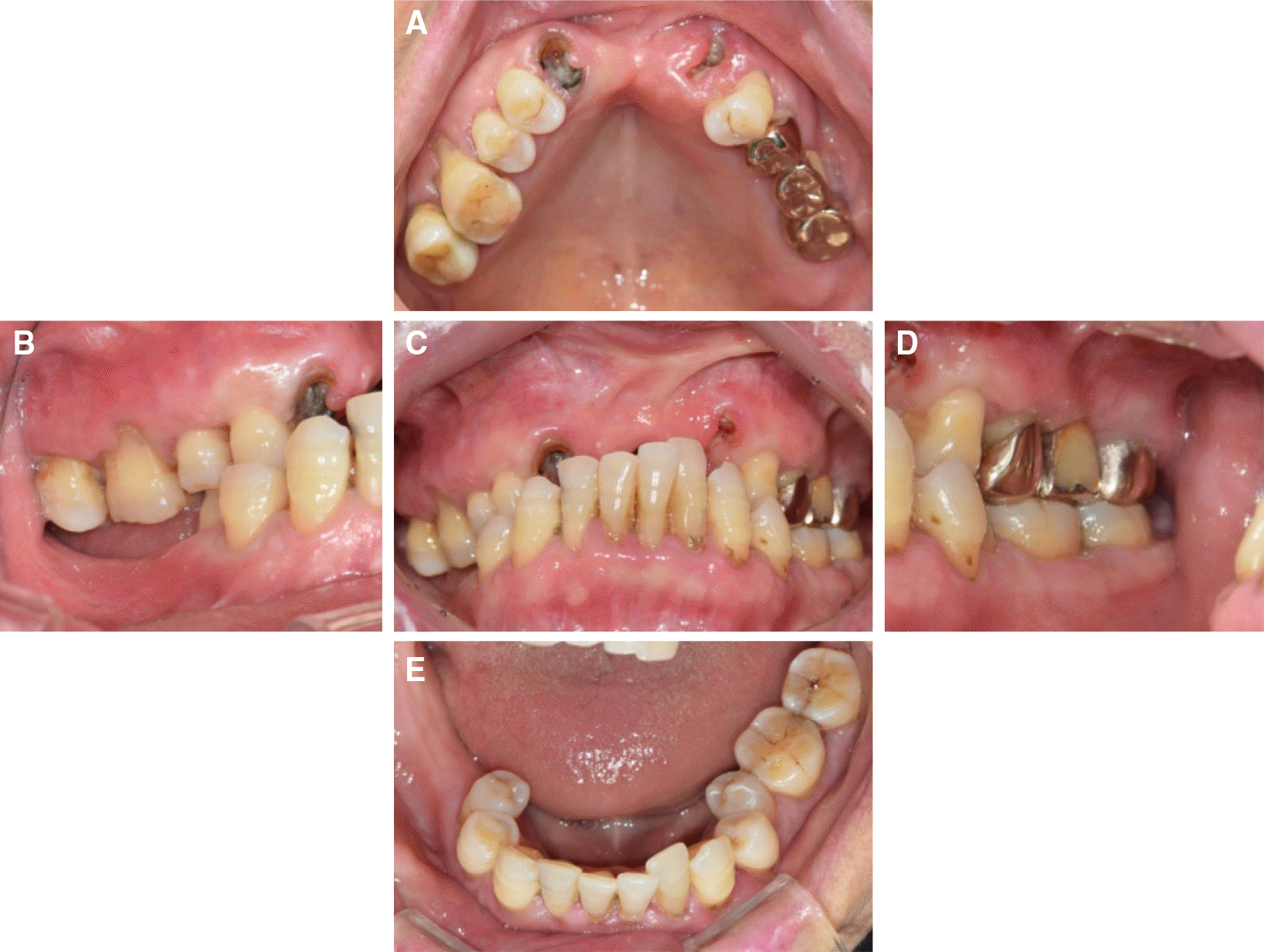 | Fig. 2.Preoperative intraoral view showing uneven occlusal plane. (A) Occlusal view of maxilla, (B) Lateral view (right side). Extrusion of right upper molars. (C) Frontal view. Extrusion anterior teeth of mandible, (D) Lateral view (left side), (E) Occlusal view of mandible. |
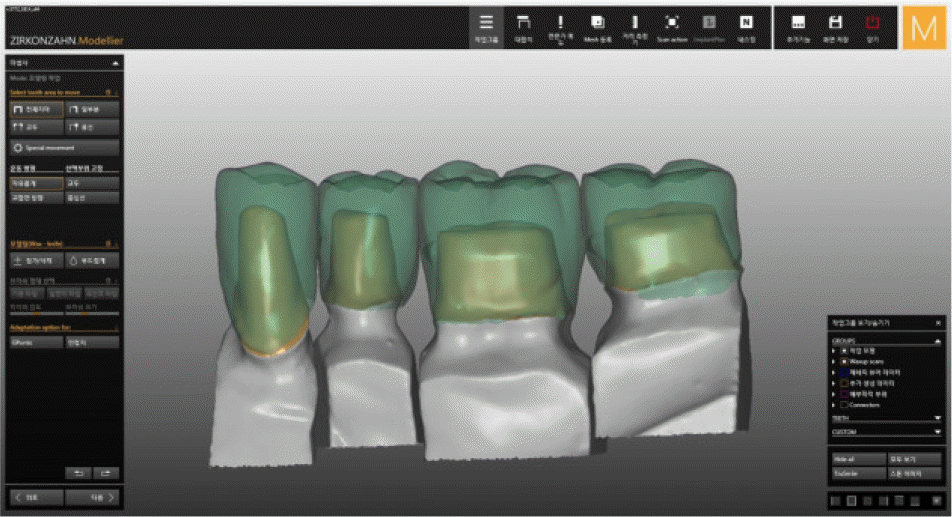
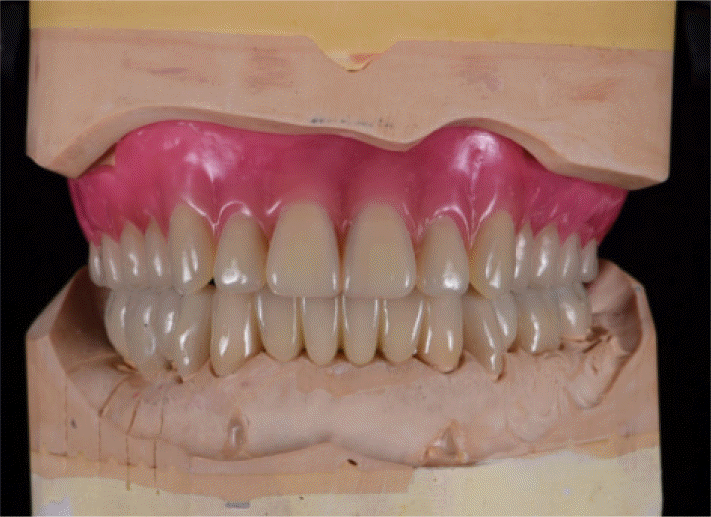
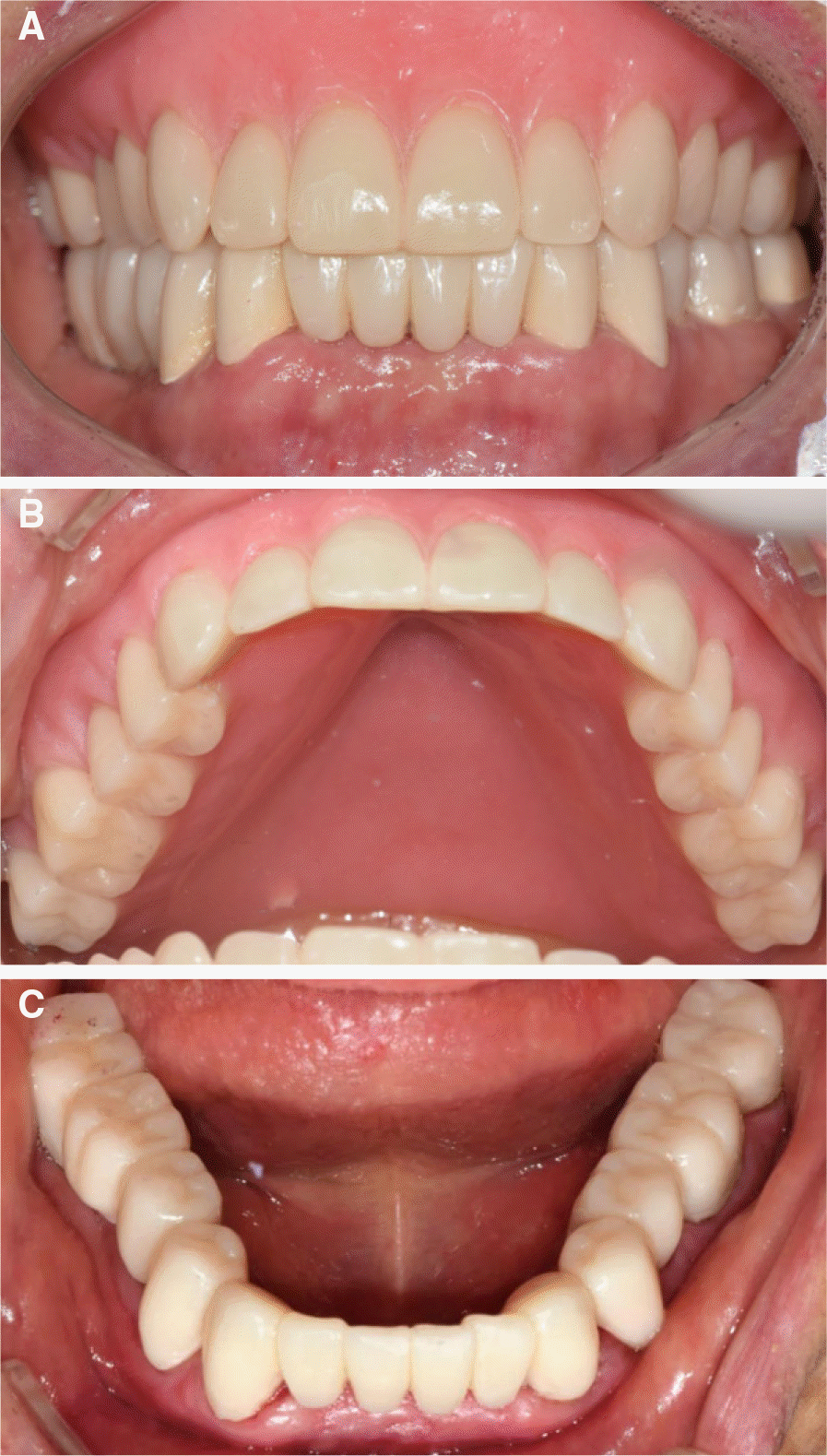 | Fig. 3.Interim prostheses. (A) Frontal view, (B) Occlusal view of maxilla, (C) Occlusal view of mandible. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download