Abstract
The maxillary defects lead to anatomical and functional deformity of the maxillofacial region. As far as functions are concerned, such defects can produce difficulty in speech, mastication, and deglutition. Obturator prostheses play a very important role in functional recovery for post-maxillectomy patients. To achieve rigidity of the obturator, appropriate retention should be given, and the weight of the prosthesis be reduced. There are two types of hollow bulb obturator: open and closed. A closed type has many advantages. Nevertheless, some problems, including complexity of fabrication and water leakage into the bulb, have the closed hollow obturator not be widely used. The one-step polymerization technique described in this case overcomes the shortcomings by easily constructing a small hollow bulb with two thermoplastic resin sheets. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2016;54:35-40)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.Kanazawa T., Yoshida H., Furuya Y., Shimodaira K. Sectional prosthesis with hollow obturator portion made of thin silicone layer over resin frame. J Oral Rehabil. 2000. 27:760–4.

3.Roumanas ED., Nishimura RD., Davis BK., Beumer J 3rd. Clinical evaluation of implants retaining edentulous maxillary obturator prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 1997. 77:184–90.

4.Kocacikli M., Yalug S., Yazicioglu H., Yilmaz C. Fabricating a hollow obturator with visible light-cured resin system. J Prosthodont. 2008. 17:596–8.

5.Habib BH., Driscoll CF. Fabrication of a closed hollow obturator. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 91:383–5.

6.Hori K., Miyamoto T., Ono T., Yamamoto M., Shiroshita N., Maeda Y., Inoue M. One step polymerizing technique for fabricating a hollow obturator. J Prosthodont Res. 2013. 57:294–7.

Go to : 
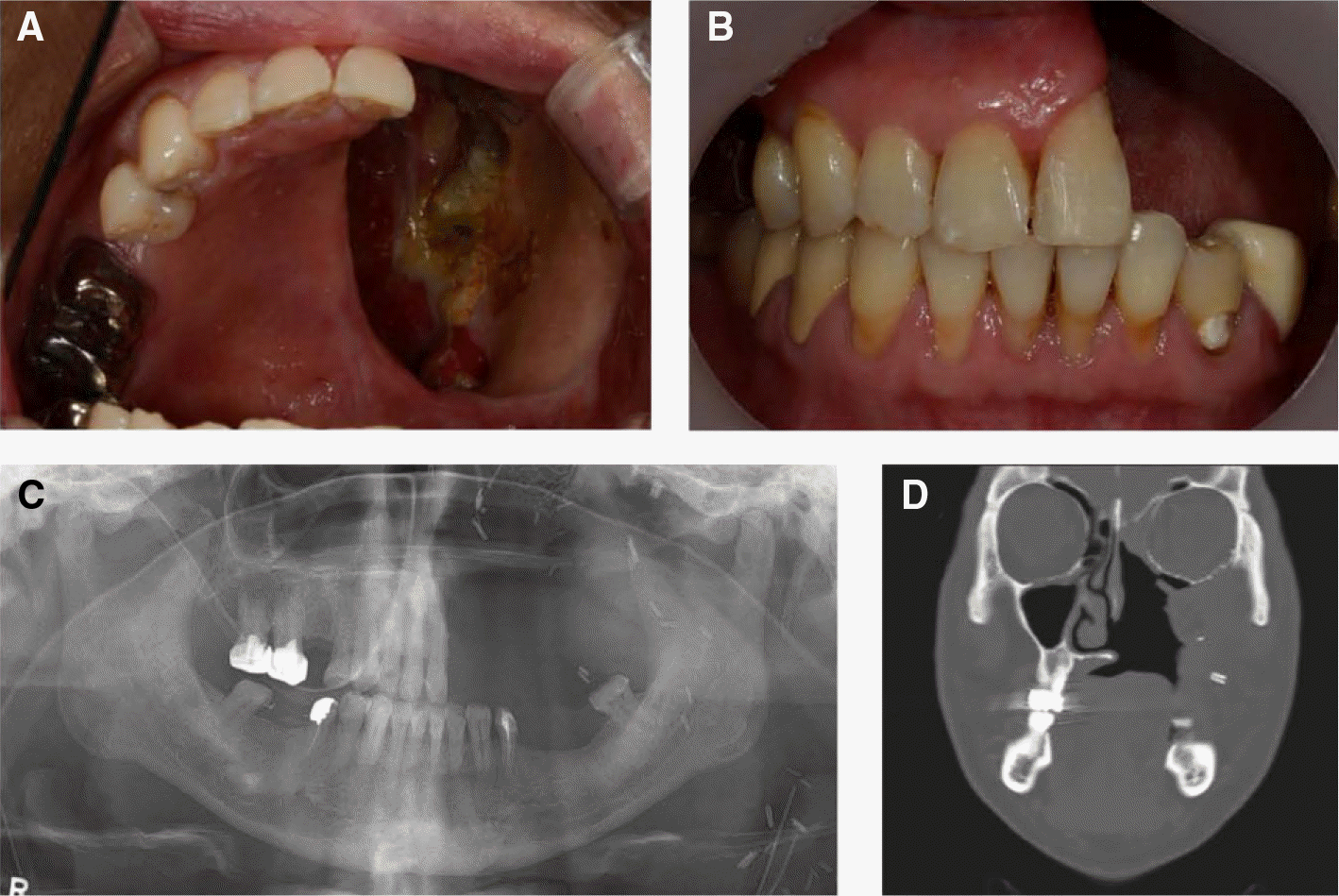 | Fig. 1.Initial photographs. (A) Intraoral maxillary occlusal view, (B) Frontal view, (C) Post-operative panoramic radiograph, (D) Post-operative CT image. |
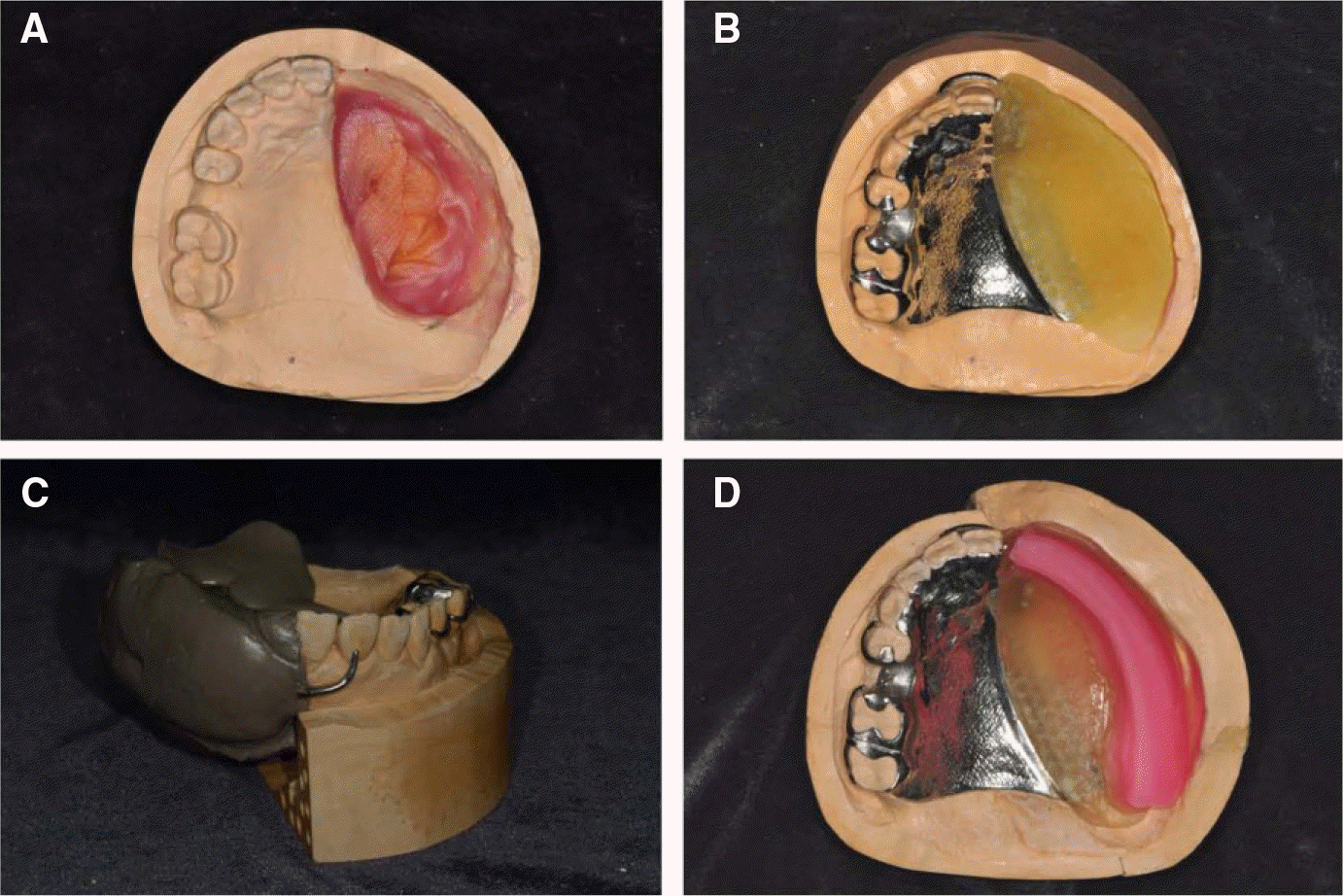 | Fig. 2.(A) Master cast, (B) Individual tray for secondary impression, (C) Altered cast fabrication, (D) Recording base and wax-rim. |
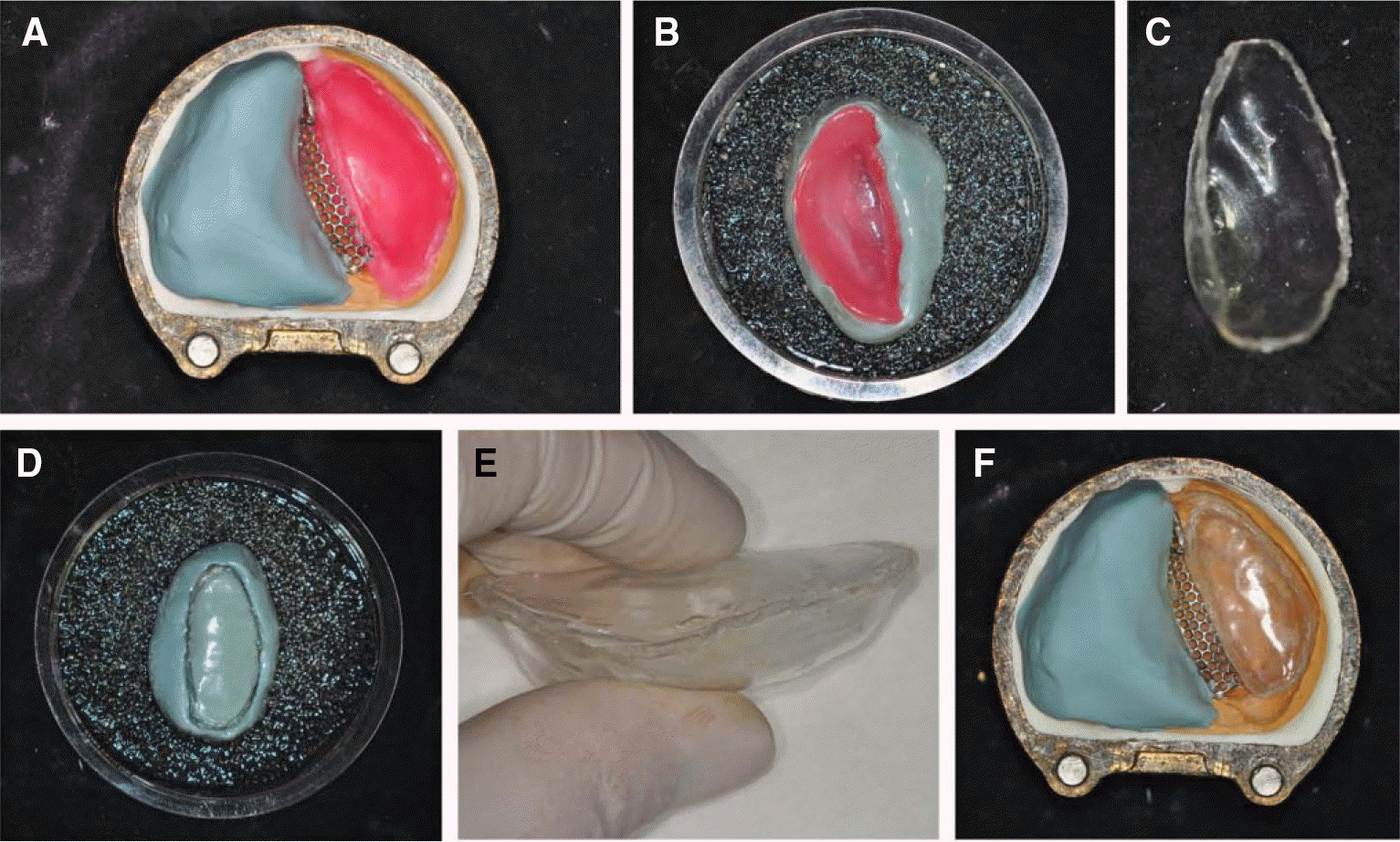 | Fig. 3.The hollow body fabrication. (A) Attaching paraffin wax for relief (lower investment), (B) Placed thermoplastic resin sheet(lower part), (C) Trimming of lower thermoplastic resin sheet, (D) Placed thermoplastic resin sheet(upper part), (E) The hollow body made by bonding two thermoformed resin sheets, (F) The hollow body placed into the lower investment. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download