Abstract
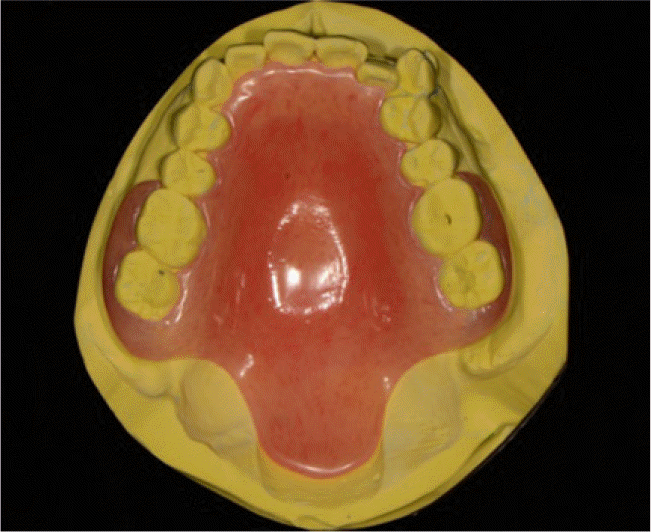
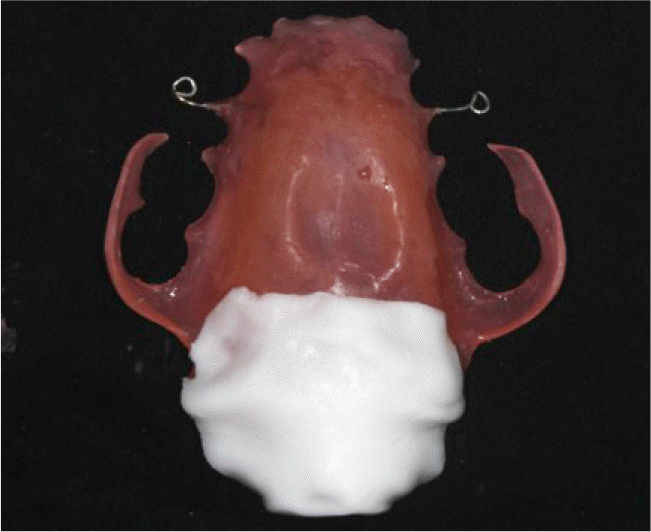
Recently, flexible removable prosthesis with thermoplastic resin clasp has increasingly become popular. In comparison with conventionally used acrylic resin, thermoplastic resin has lower flexural strength and elastic modulus. Thus, flexible removable prosthesis has low risk of fracture, so denture base can be made thin and light, increasing patient comfort. Also, it can passively sit at tooth undercut during rest, so abutment teeth need minimum or no preparation. In this case report, a 44 year old female patient with mild velopharyngeal insufficiency was treated with a palatal lift prosthesis made of polyester thermoplastic resin. Since the patient had no missing tooth and desired conservative treatment, the flexible removable prosthesis provided relatively satisfactory results. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2016;54:286-90)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Johns DF., Rohrich RJ., Awada M. Velopharyngeal incompetence: a guide for clinical evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 112:1890–7.
2.Goudy S., Ingraham C., Canady J. Noncleft velopharyngeal insufficiency: Etiology and need for surgical treatment. Int J Otolaryngol. 2012. 1–3.

3.Schneider E., Shprintzen RJ. A survey of speech pathologists: current trends in the diagnosis and management of velopharyngeal insufficiency. Cleft Palate J. 1980. 17:249–53.
4.Mazaheri M., Mazaheri EH. Prosthodontic aspects of palatal elevation and palatopharyngeal stimulation. J Prosthet Dent. 1976. 35:319–26.

5.La Velle WE., Hardy JC. Palatal lift prostheses for treatment of palatopharyngeal incompetence. J Prosthet Dent. 1979. 42:308–15.
Go to : 
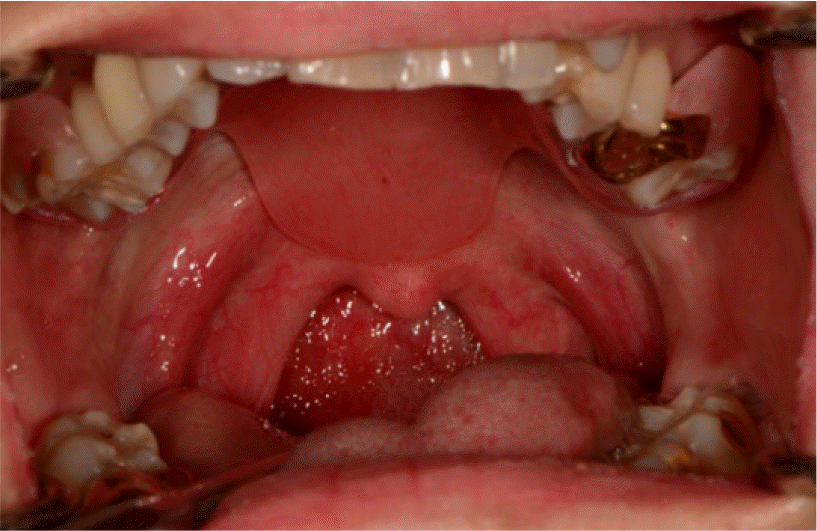
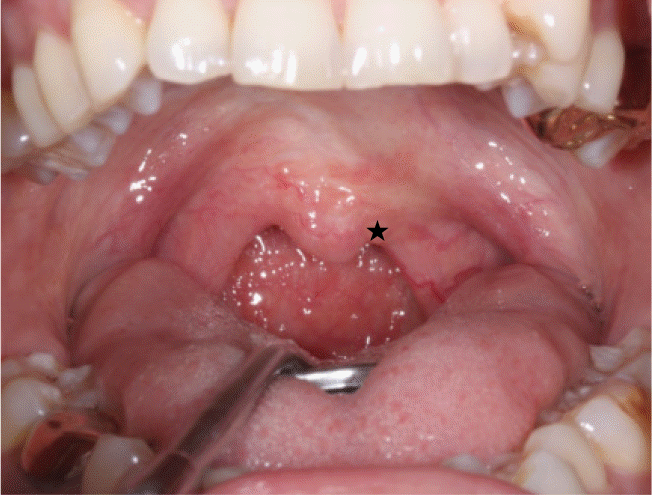 | Fig. 2.Intraoral photo during "A" phonation. Star sign shows lower elevation of left soft palate. |
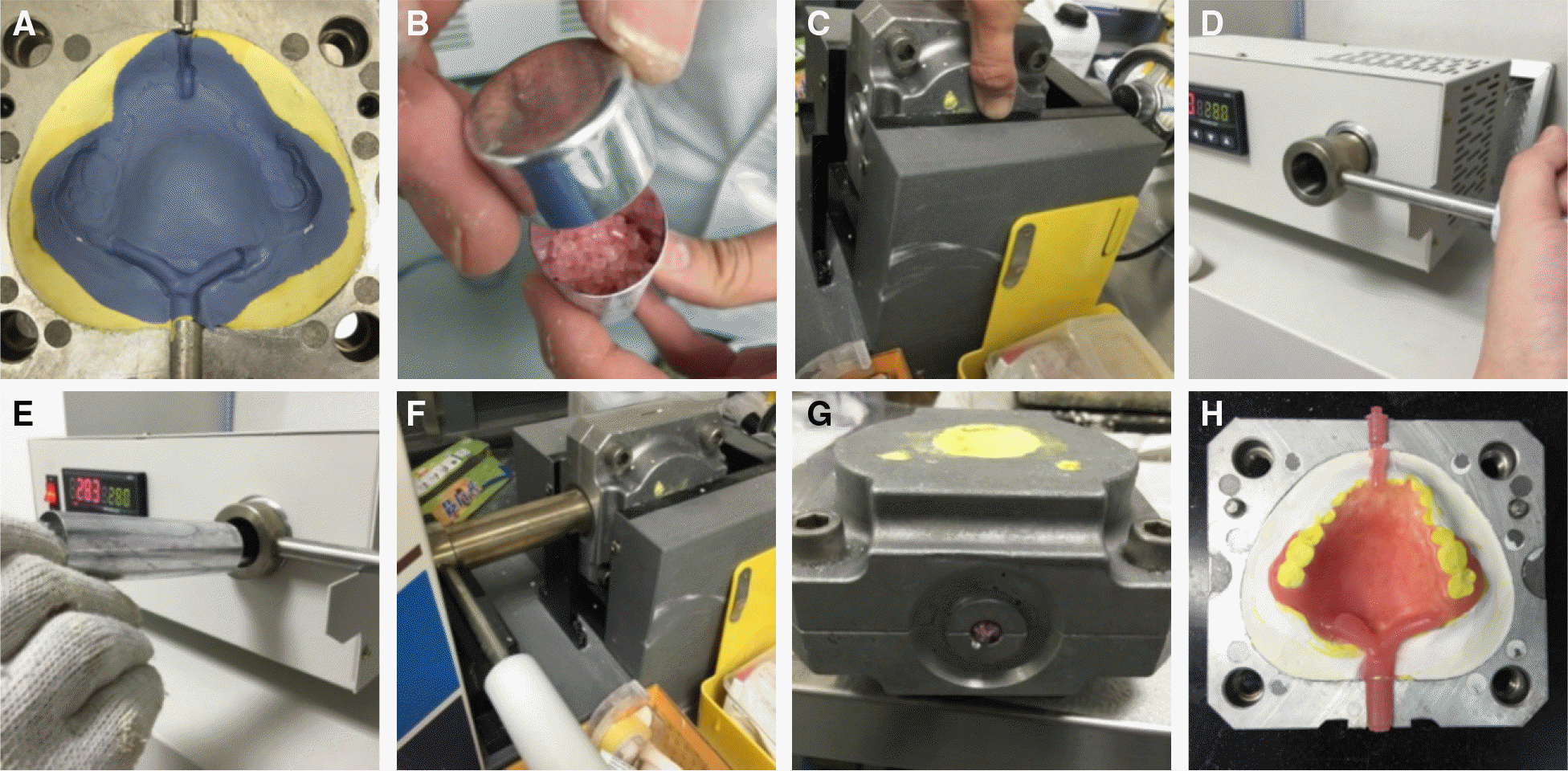 | Fig. 4.Flasking & packing process. (A) Putty investment, (B) Thermoplastic pellets, (C) Special flask for injection molding technique, (D, E) Pellets in a cartridge plasticized in an electric furnace, (F) Cartridge placed on the inlet of the flask and compressed, (G) Cooling, (H) Deflasking. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download