Abstract
Purpose
Increasing use of computer aided design-computer aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) system and number of design software made design of restoration easy and quick. Outcome of restoration has been dependent on dental technician's wax up proficiency, dentists can design restoration for themselves now. This study aims to investigate the outcome of restoration designs, according to handling skill of CAD-CAM design tool.
Materials and methods
A patient's mandibular right 1st molar was prepared. After taking impression, stone model was made, scanned the stone model with 3 shape intra-oral scanner, stereolithography (STL) file was extracted. With 3shape dental designer, one dental technician with more than 5 years work experience (designer 0) and three dental technicians with less than 2years work experience (designer 1, 2, 3-group DT) and 4 1st year residents (designer 4, 5, 6, 7-group RT) designed gold crown on the same STL file. Designed crown's MD (mesiodistal) and BL (bucco-lingual) diameter, height of crown, inter-cuspal distance, number of occlusal contact points were compared. Statistical analysis was carried out, test of normality within each group, using independent t-test. Number of contact points were compared, using Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
There was no significant difference between group DT and group RT. Number of contact points also resulted in no significant difference.
Conclusion
The outcome of each designed crowns showed no statistical differences, in values which can be expressed as numbers. Subjective factors were different. With increasing proficiency in handling designing software, fabrication of restorations according to each designer's occlusal concept can be made easy. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2016;54:234-8)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Mörmann WH. The evolution of the CEREC system. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006. 137:7S–13S.
2.Ellerbrock C., Kordass B. Comparison of computer generated occlusal surfaces with functionally waxed-on surfaces. Int J Comput Dent. 2011. 14:23–31.
3.Atta MO., Smith BG., Brown D. A comparison of chairside and laboratory etching techniques for cast metal bridge retainers. Restorative Dent. 1987. 3:11–2.
4.Ting-Shu S., Jian S. Intraoral Digital Impression Technique: A Review. J Prosthodont. 2015. 24:313–21.

6.Stein JM. Case report: the single-visit chairside CAD/CAM restoration. J Mass Dent Soc. 2014. 63:52–3.
7.Kollmuss M., Jakob FM., Kirchner HG., Ilie N., Hickel R., Huth KC. Comparison of biogenerically reconstructed and waxed-up complete occlusal surfaces with respect to the original tooth morphology. Clin Oral Investig. 2013. 17:851–7.

Go to : 
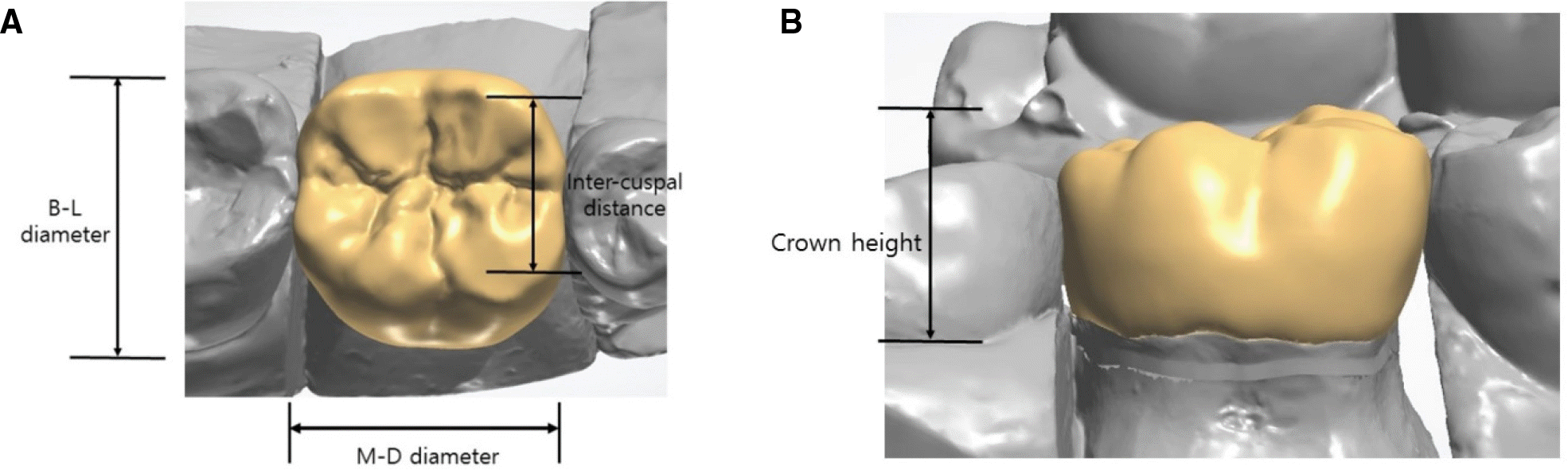 | Fig. 1.M-D (mesiodistal) diameter, B-L (bucco-lingual) diameter, inter-cuspal distance was measured in occlusal view (A) and crown height was measured in buccal view (B) on 3shape dental designer. |
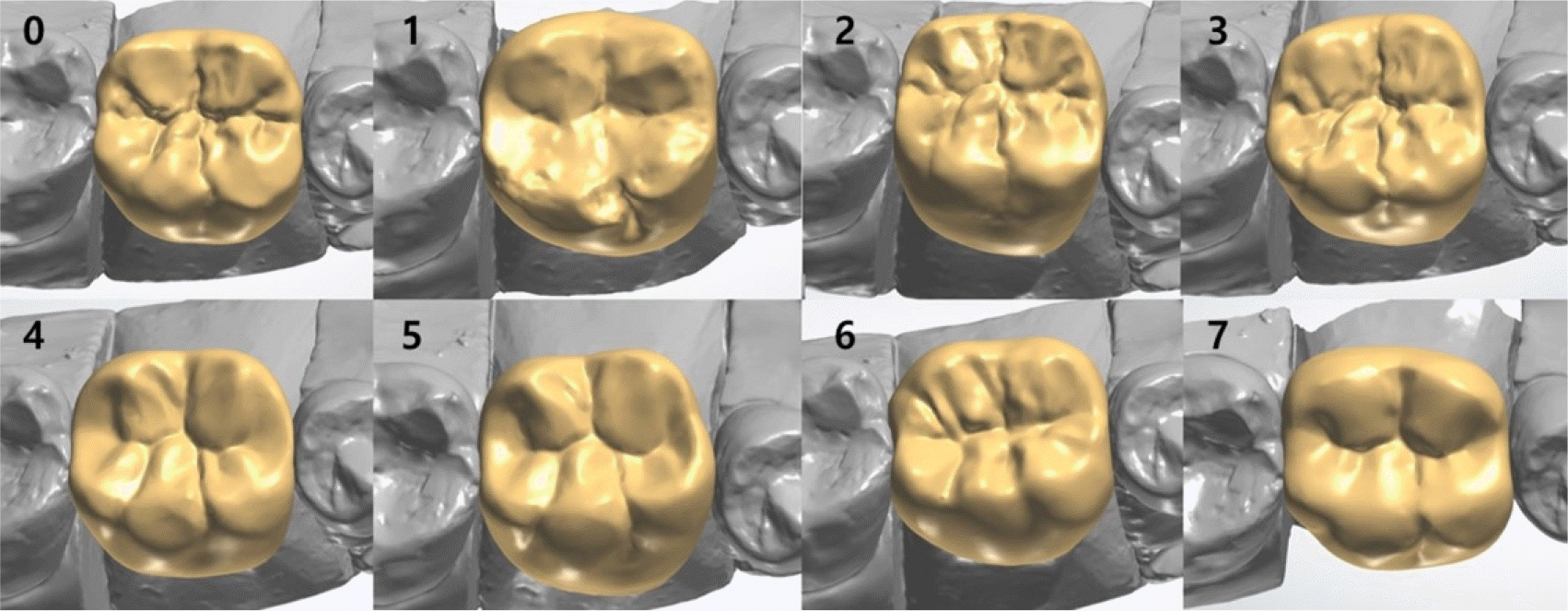 | Fig. 2.Occlusal view of designed crown. 0, 1, 2, 3: Crown design of group DT. 4, 5, 6, 7: Crown design of group RT. |
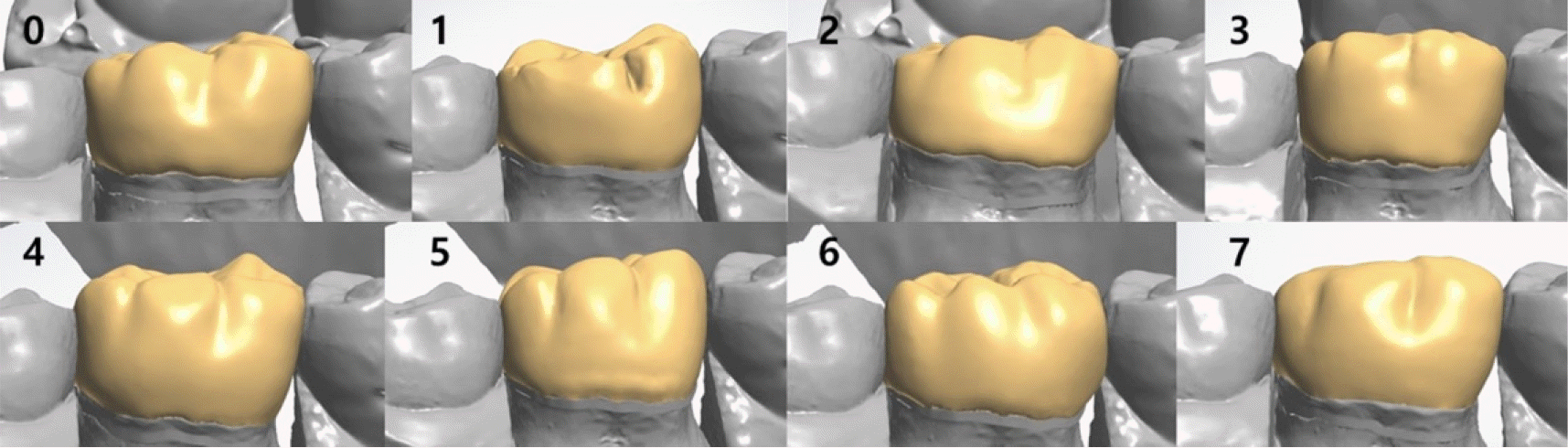 | Fig. 3.Buccal view of designed crown. 0, 1, 2, 3: Crown design of group DT. 4, 5, 6, 7: Crown design of group RT. |
Table 1.
Difference in MD, BL, CH, CD among designer1-7 relative to designer 0 (mm)
Table 2.
Mean of difference between value from MD, BL, CH, CD of group DT and group RT and that of designer 0 (mm)
| Group DT | Group RT | |
|---|---|---|
| D0MD-MD | 0.147 | 0.145 |
| D0BL-BL | 0.483 | 0.388 |
| D0CD-CH | 0.465 | 0.591 |
| D0CD-CD | 0.917 | 0.976 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download