Abstract
Purpose
This study compared shear bond strengths of five self-adhesive cements with phosphate monomer to zirconium oxide ceramic with and without airborn particle abrasion.
Materials and methods
One hundred zirconia samples were air-abraded (50 ㎛ Al2O3). One hundred composite resin cylinders were fabricated. Composite cylinders were bonded to the zirconia samples with either Permacem 2.0 (P), ClearfilTM SA Luting (C), Multilink® Speed (M), RelyXTM U200 Automix (R), G-Cem LinkAceTM (G). All bonded specimens were stored in distilled water (37°C) for 24 h and half of them were additionally aged by thermocycling (5°C, 55°C, 5,000 times). The bonded specimens were loaded in shear force until fracture (1 mm/min) by using Universal Testing Machine (Model 4201, Instron Co, Canton, MA, USA). The failure sites were inspected under field-emission scanning electron microscopy. The data was analyzed with ANOVA, Tukey HSD post-hoc test and paired samples t-test (α =.05).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Anusavice KJ. Recent developments in restorative dental ceramics. J Am Dent Assoc. 1993; 124:72–4. 76-8. 80–4.

2. Kelly JR, Nishimura I, Campbell SD. Ceramics in dentistry: his-torical roots and current perspectives. J Prosthet Dent. 1996; 75:18–32.

3. Lin J, Shinya A, Gomi H, Shinya A. Effect of self-adhesive resin cement and tribochemical treatment on bond strength to zirconia. Int J Oral Sci. 2010; 2:28–34.

4. Luthardt RG, Sandkuhl O, Reitz B. Zirconia-TZP and alumina–advanced technologies for the manufacturing of single crowns. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 1999; 7:113–9.
5. Passos SP, May LG, Barca DC, Ozcan M, Bottino MA, Valandro LF. Adhesive quality of self-adhesive and conventional adhesive resin cement to Y-TZP ceramic before and after aging conditions. Oper Dent. 2010; 35:689–96.

6. Derand T, Molin M, Kvam K. Bond strength of composite luting cement to zirconia ceramic surfaces. Dent Mater. 2005; 21:1158–62.

7. Anusavice KJ. Phillips science of dental materials. 11th ed.Saunders: Missouri, USA;2003. p. 443–94.
8. Dixon DL, Breeding LC, Hughie ML, Brown JS. Comparison of shear bond strengths of two resin luting systems for a base and a high noble metal alloy bonded to enamel. J Prosthet Dent. 1994; 72:457–61.

9. In HS, Park JI, Choi JI, Cho HW, Dong JK. The study of shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin luting cement to dentin. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2008; 46:535–43.

10. Miragaya L, Maia LC, Sabrosa CE, de Goes MF, da Silva EM. Evaluation of self-adhesive resin cement bond strength to yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramic (Y-TZP) using four surface treatments. J Adhes Dent. 2011; 13:473–80.
11. Komine F, Kobayashi K, Saito A, Fushiki R, Koizumi H, Matsumura H. Shear bond strength between an indirect composite veneering material and zirconia ceramics after thermocycling. J Oral Sci. 2009; 51:629–34.

12. Ikemura K, Jogetsu Y, Shinno K, Nakatsuka T, Endo T, Kadoma Y. Effects of a newly designed HEMA-free, multi-purpose, single-bottle, self-etching adhesive on bonding to dental hard tis-sues, zirconia-based ceramics, and gold alloy. Dent Mater J. 2011; 30:616–25.

13. Kim AJ, Yu SH, Oh SH, Bae JM. Effect of self-adhesive resin cements on the shear bond strengths between bovine teeth and composite resin block. J Korean Soc Dent Mater. 2013; 40:367–72.
14. Lü thy H, Loeffel O, Hammerle CH. Effect of thermocycling on bond strength of luting cements to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:195–200.
15. Wolfart M, Lehmann F, Wolfart S, Kern M. Durability of the resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic after using different surface conditioning methods. Dent Mater. 2007; 23:45–50.

16. Ferracane JL, Stansbury JW, Burke FJ. Self-adhesive resin cements - chemistry, properties and clinical considerations. J Oral Rehabil. 2011; 38:295–314.

17. Oyagü e RC, Monticelli F, Toledano M, Osorio E, Ferrari M, Osorio R. Effect of water aging on microtensile bond strength of dual-cured resin cements to pre-treated sintered zirconium-oxide ceramics. Dent Mater. 2009; 25:392–9.
18. D'Amario M, Campidoglio M, Morresi AL, Luciani L, Marchetti E, Baldi M. Effect of thermocycling on the bond strength between dual-cured resin cements and zirconium-oxide ceramics. J Oral Sci. 2010; 52:425–30.
19. Toledano M, Osorio R, Osorio E, Aguilera FS, Yamauti M, Pashley DH, Tay F. Durability of resin-dentin bonds: effects of direct/indirect exposure and storage media. Dent Mater. 2007; 23:885–92.

20. Fischer J, Grohmann P, Stawarczyk B. Effect of zirconia surface treatments on the shear strength of zirconia/veneering ceramic composites. Dent Mater J. 2008; 27:448–54.

21. Chung KH, Greener EH. Correlation between degree of conversion, filler concentration and mechanical properties of posterior composite resins. J Oral Rehabil. 1990; 17:487–94.

Go to : 
 | Fig. 4.Failure mode before and after thermocycling (-1 : before thermocycling,-2 : after thermocycling). |
 | Fig. 5.Scanning electron microscope image of zirconia surface (×5,000 magnification).(A) polished with 1 ㎛ diamond paste, (B) sandblasting with 50 ㎛ Al2 O3. |
 | Fig. 6.Scanning electron microscope image of zirconia surface after shear-bond strength test (×2,000 magnification, -1: before thermocycling, -2: after thermocycling). (A) P: Permacem 2.0, (B) C: Clearfil TM SA Luting, (C) M: Multilink® Speed,(D) R: RelyX TM U200, (E) G: G-Cem LinkAce TM. |
Table 1.
Self-adhesive resin cements used in this study
Table 2.
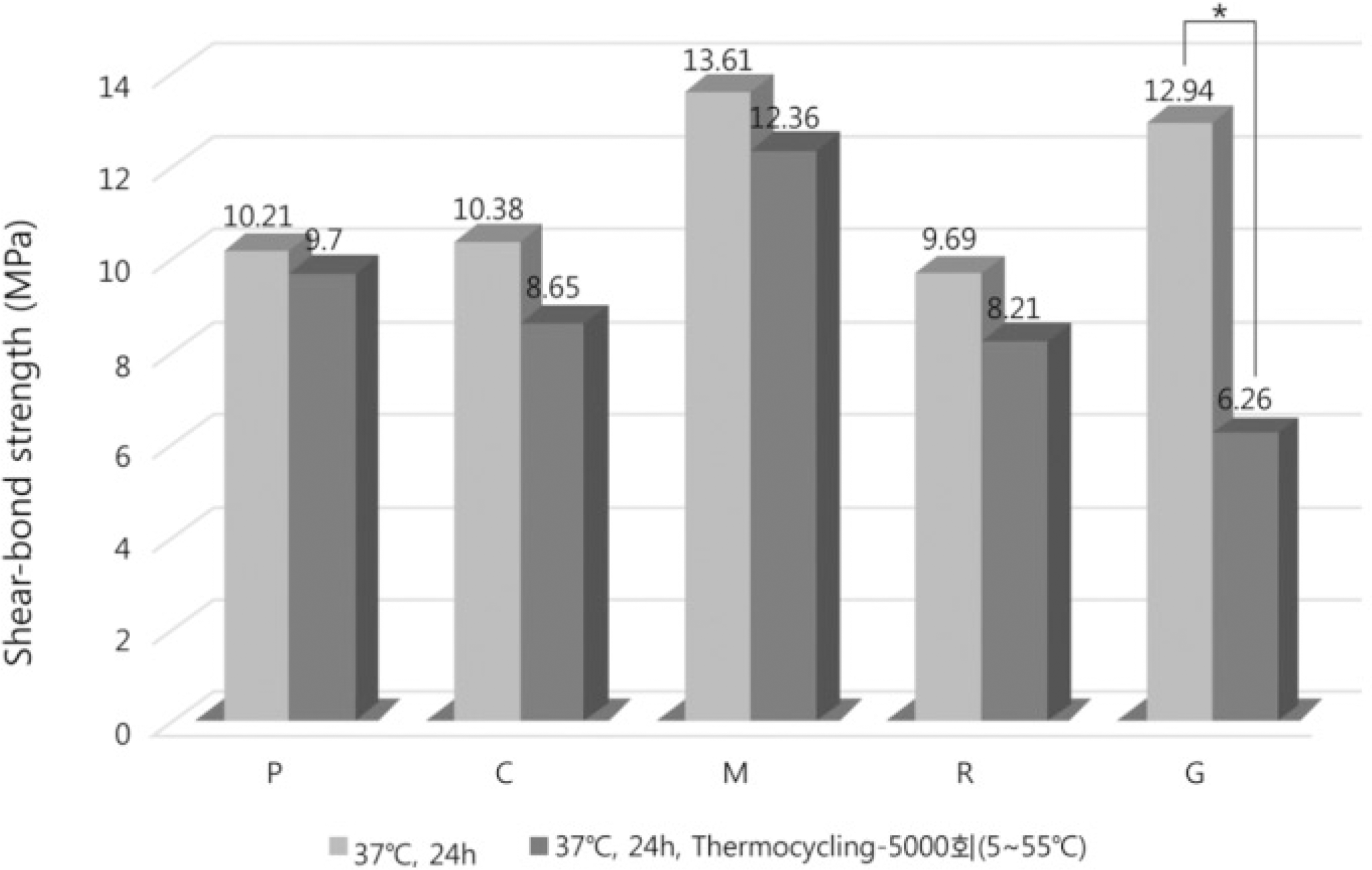
Mean shear bond strength (MPa) with SD
| Group | N | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-11) | 10 | 10.21 | 1.36 |
| P-22) | 10 | 9.70 | 1.57 |
| C-1 | 10 | 10.38 | 1.29 |
| C-2 | 10 | 8.65 | 2.39 |
| M-1 | 10 | 13.61 | 1.45 |
| M-2 | 10 | 12.36 | 2.40 |
| R-1 | 10 | 9.69 | 1.55 |
| R-2 | 10 | 8.21 | 2.45 |
| G-1 | 10 | 12.94 | 1.64 |
| G-2 | 10 | 6.26 | 2.41 |
Table 3.
The results of Tukey HSD post hoc test (before thermocycling)
Table 4.
The results of Tukey HSD post hoc test (after thermocycling)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download