Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the shear bond strength between Ni-Cr alloy and composite resin using universal adhesive systems coMPared to conventional method using metal primers.
Materials and methods
For this study, a total of 120 cast commercial Ni-Cr alloy (Vera Bond 2V) disks were embedded in acrylic resin, and their surfaces were smoothed with silicon carbide papers and airborne-particle abrasion. Specimens of each metal were divided into 6 groups based on the combination of metal primers (Metal primer II, Alloy primer, Metal & Zirconia primer, MKZ primer) and universal adhesive systems (Single Bond Universal, All Bond Universal). All specimens were stored in distilled water at 37°C for 24 hours. Shear bond strength testing was performed with a universal testing machine at a cross head speed of 1 m/min. Data (MPa) were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and the post hoc Tukey’ s multiple comparison test (α =.05).
Results
There were significant differences between Single Bond Universal, All Bond Universal, Metal Primer II and Alloy Primer, MKZ Primer, Metal & Zirconia Primer (P<.001).
Conclusion
Universal Adhesive system groups indicated high shear bond strength value bonded to Ni-Cr alloy than that of conventional system groups using primers except Metal Primer II. Within the limitations of this study, improvement of universal adhesive systems which can be applied to all types of restorations is recommended especially non-precious metal alloy. More research is needed to evaluate the effect of silane inclusion or exclusion in universal adhesive systems.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Tanaka T, Fujiyama E, Shimizu H, Takaki A, Atsuta M. Surface treatment of nonprecious alloys for adhesion-fixed partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent. 1986; 55:456–62.

2. Kohli S, Levine WA, Grisius RJ, Fenster RK. The effect of three different surface treatments on the tensile strength of the resin bond to nickel-chromium-beryllium alloy. J Prosthet Dent. 1990; 63:4–8.

3. Kolodney H, Puckett AD, Brown K. Shear strength of laboratory-processed composite resins bonded to a silane-coated nickel-chromi-um-beryllium alloy. J Prosthet Dent. 1992; 67:419–22.

4. Kern M, Thompson VP. Sandblasting and silica-coating of dental alloys: volume loss, morphology and changes in the surface composition. Dent Mater. 1993; 9:151–61.

5. Wood DP, Jordan RE, Way DC, Galil KA. Bonding to porcelain and gold. Am J Orthod. 1986; 89:194–205.

6. Yamashita A, Yamami T. Procedures for applying adhesive resin (MMA-TBB) to crown and bridge restorations. Part 1. The influence of dental non-precious alloys and the treatment of in-ner surface of metal to adhesion. J Jpn Prosthodont Soc. 1982; 26:584–91.
7. Andreasen GF, Stieg MA. Bonding and debonding brackets to porcelain and gold. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988; 93:341–5.

8. Tanaka T, Fujiyama E, Shimizu H, Takaki A, Atsuta M. Surface treatment of nonprecious alloys for adhesion-fixed partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent. 1986; 55:456–62.

9. Yoshida Y, Nagakane K, Fukuda R, Nakayama Y, Okazaki M, Shintani H, Inoue S, Tagawa Y, Suzuki K, De Munck J, Van Meerbeek B. Comparative study on adhesive performance of functional monomers. J Dent Res. 2004; 83:454–8.

10. Kondo Y, Uramoto T, Yamashita A. Adhesive strength of adhesive resin Panvia EX to dental alloy. Part 1. Adhesive strength of Ni-Cr alloys. J Jpn Prosthodont Soc. 1984; 28:587–98.
11. Barzilay I, Myers ML, Cooper LB, Graser GN. Mechanical and chemical retention of laboratory cured composite to metal surfaces. J Prosthet Dent. 1988; 59:131–7.

12. Randle R, Gordiev K. Metal-on-metal articulation in total hip arthroplasty: preliminary results in 57 cases. Aust N Z J Surg. 1997; 67:634–6.

13. Tsuchimoto Y, Yoshida Y, Mine A, Nakamura M, Nishiyama N, Van Meerbeek B, Suzuki K, Kuboki T. Effect of 4-MET- and 10-MDP-based primers on resin bonding to titanium. Dent Mater J. 2006; 25:120–4.

14. Ikemura K, Endo T, Kadoma Y. A review of the developments of multi-purpose primers and adhesives comprising novel dithiooctanoate monomers and phosphonic acid monomers. Dent Mater J. 2012; 31:1–25.

15. Fonseca RG, de Almeida JG, Haneda IG, Adabo GL. Effect of metal primers on bond strength of resin cements to base metals. J Prosthet Dent. 2009; 101:262–8.

16. Lung CY, Matinlinna JP. Aspects of silane coupling agents and surface conditioning in dentistry: an overview. Dent Mater. 2012; 28:467–77.

Go to : 
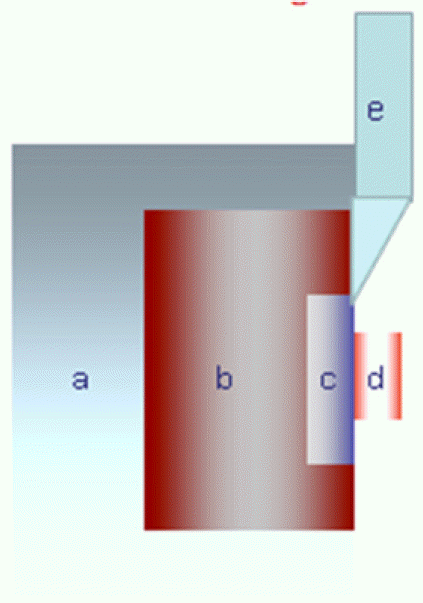 | Fig. 1.Cross-sectional illustration of shear bond strength test set up. (a) Mounting jig, (b) Pink acrylic resin, (c) Ni-Cr disk, (d) Composite resin, (e) Instron rod. |
Table 1.
The resin bonding systems used in this study
Table 2.
Classification of experimental group




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download