Abstract
Teeth wear and extrusion of antagonist are commonly observed in deep bite patient having severe vertical and horizontal overlap. These problems cause collapse of occlusal plane and abnormal anterior guidance. Without restoring harmonious occlusion, loss of multiple teeth and decreased masticatory function could not be prevented. To resolve problems associated with deep bite, multidisciplinary treatment including oral surgical, orthodontic and prosthetic treatment should be performed. This clinical report describes the results of increasing occlusal vertical dimension with a full-mouth restoration procedure. The treatment procedures include extraoral and intraoral examination, diagnosis, treatment planning, diagnostic waxup, segmental osteotomy, orthodontic intrusion and prosthodontic rehabilitation. Full mouth rehabilitation with increasing occlusal vertical dimension can solve esthetic and functional problems.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. The glossary of prosthodontic terms. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 94:10–92.
2. Akerly WB. Prosthodontic treatment of traumatic overlap of the anterior teeth. J Prosthet Dent. 1977; 38:26–34.

3. Dawson PE. Runctional occlusion: From TMJ to smile design. Mosby;. Elsevier;Health Sciences. 2006.
4. Karlsen AT. Craniofacial characteristics in children with Angle Class II div. 2 malocclusion combined with extreme deep bite. Angle Orthod. 1994; 64:123–30.
5. Bell WH, Jacobs JD, Legan HL. Treatment of Class II deep bite by orthodontic and surgical means. Am J Orthod. 1984; 85:1–20.

6. Bergersen EO. A longitudinal study of anterior vertical overbite from eight to twenty years of age. Angle Orthod. 1988; 58:237–56.
7. Basa S, Varol A, Sener ID, Sertgoz A. Posterior maxillary segmental osteotomy for restoring the mandible with dental implants: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2008; 99:340–3.

8. Hwang JH, Jung BY, Lim CS, Cha IH, Park W. Posterior maxillary segmental osteotomy concomitant with sinus lift using a piezoelectric device. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69:2339–44.

9. Lownie JF, Cleaton-Jones PE, Coleman H, Forbes M. Long-term histologic changes in the dental pulp after posterior segmental os-teotomies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999; 87:299–304.

Go to : 
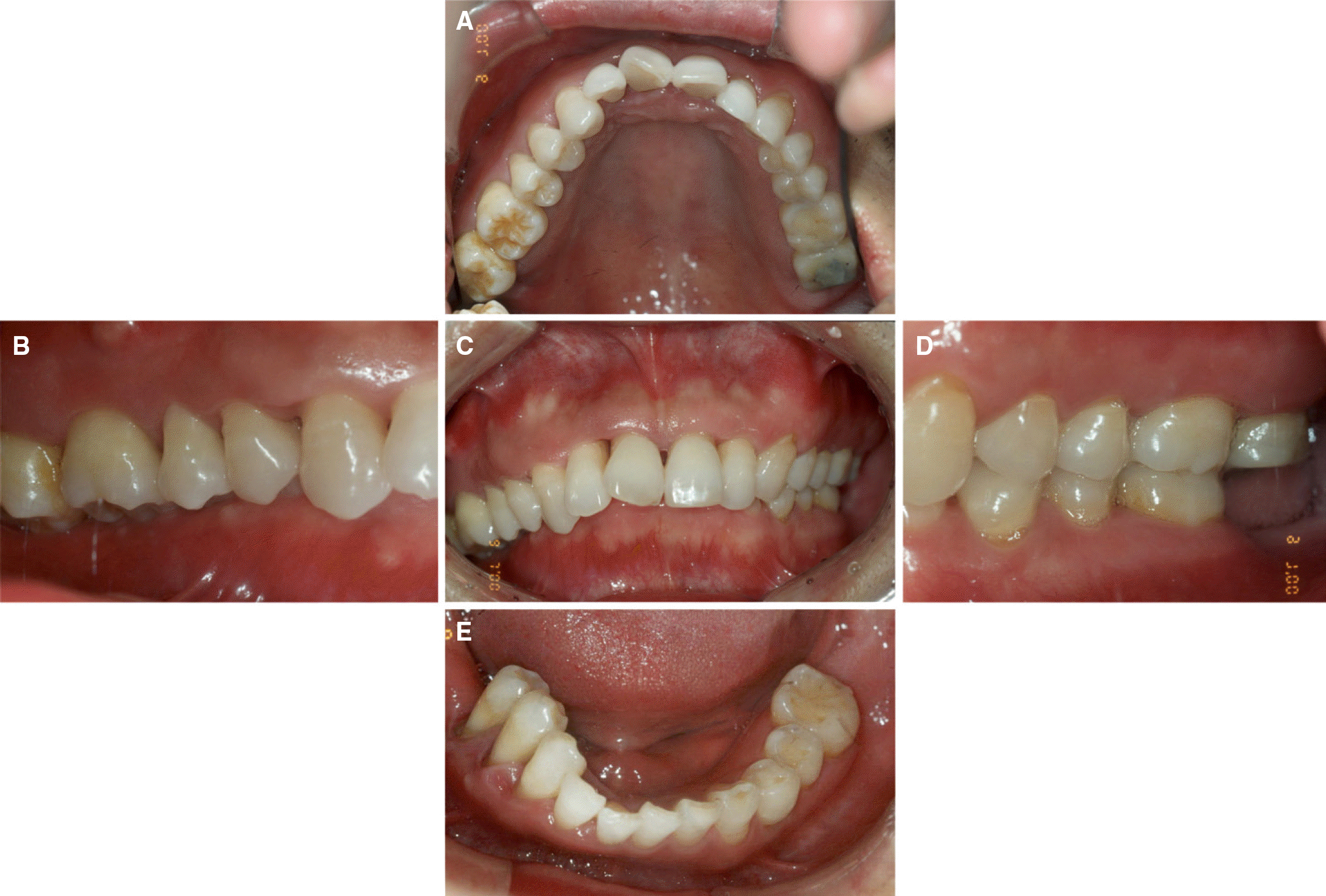 | Fig. 1.Intraoral view at first visit. (A) Maxillary occlusal view, (B) Right lateral view, (C) Frontal view, (D) Left lateral view, (E) Mandibular occlusal view. |
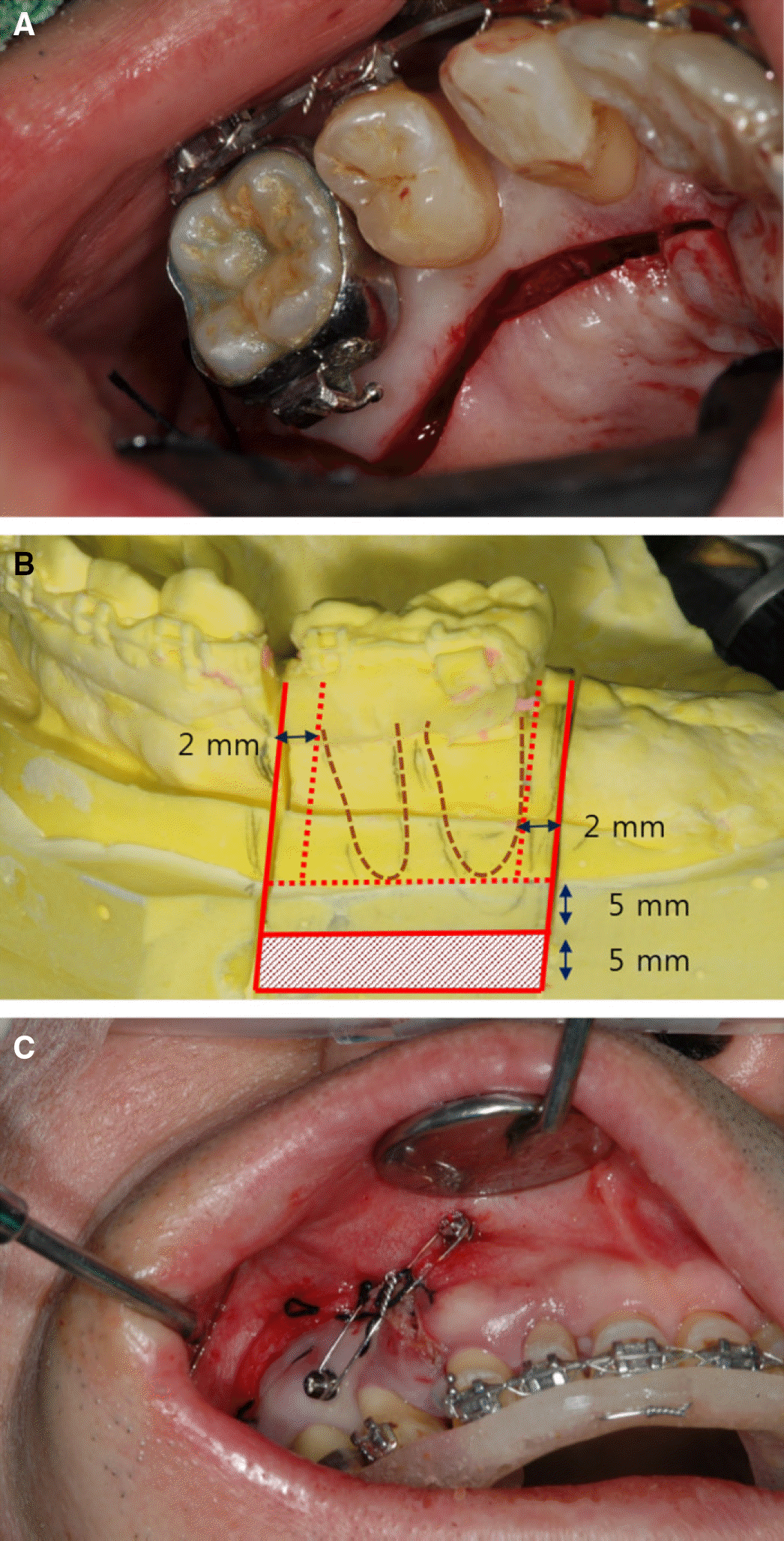 | Fig. 5.Segmental osteotomy. (A) Palatal incision, (B) Horizontal, vertical osteotomy, (C) Surgical stent. |
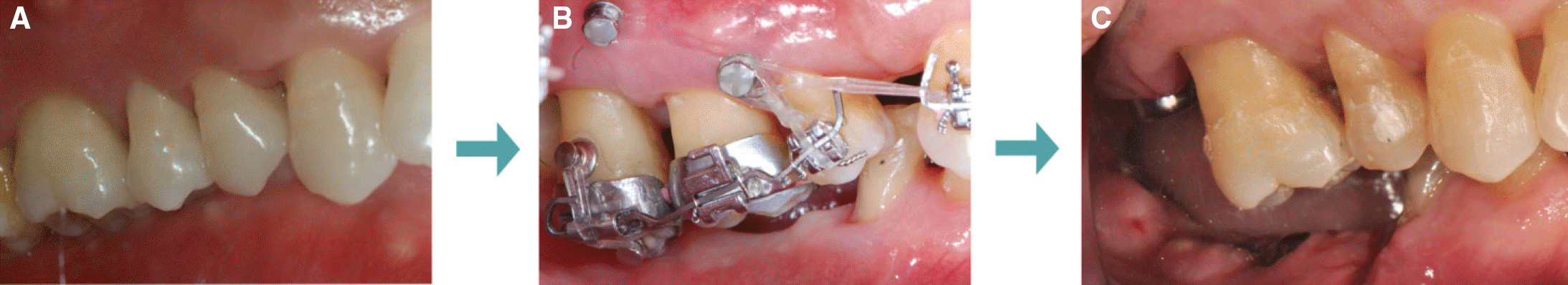 | Fig. 6.Molar intrusion procedures. (A) First visit, (B) During treatment, (C) After treatment. |
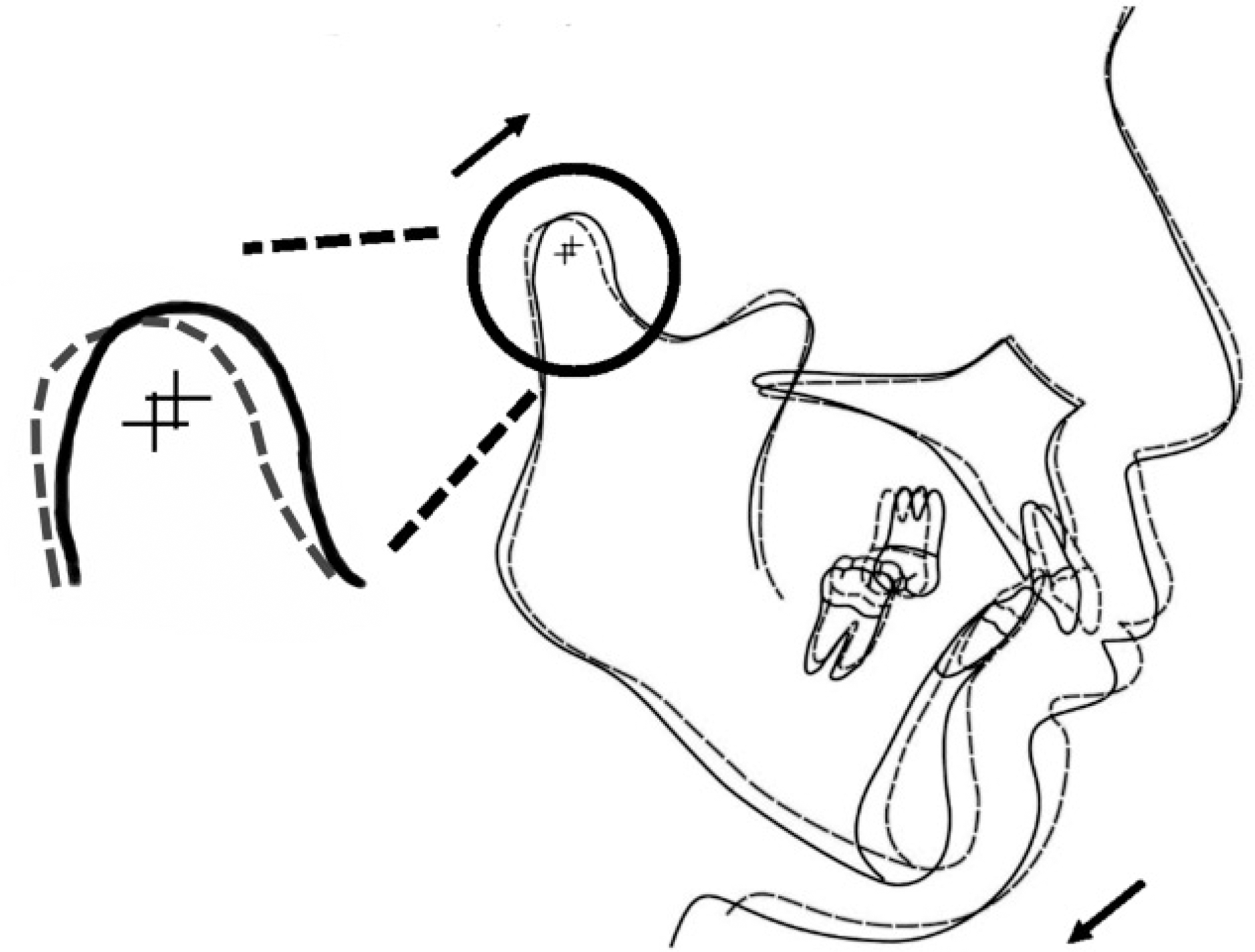
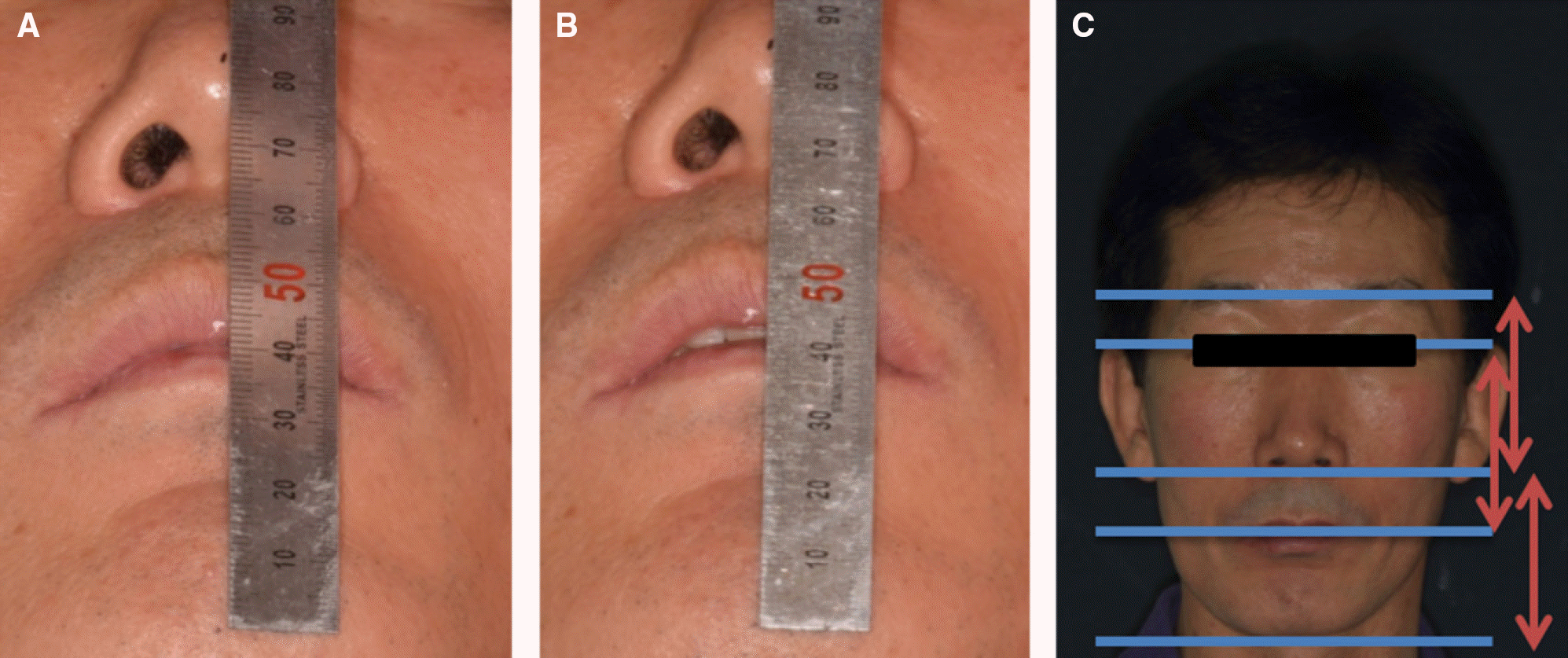 | Fig. 7.Vertical dimension evaluation. (A) Free-way space evaluation (maximum intercuspation), (B) Free-way space evaluation (centric occlusion), (C) Facial appear-ance evaluation. |
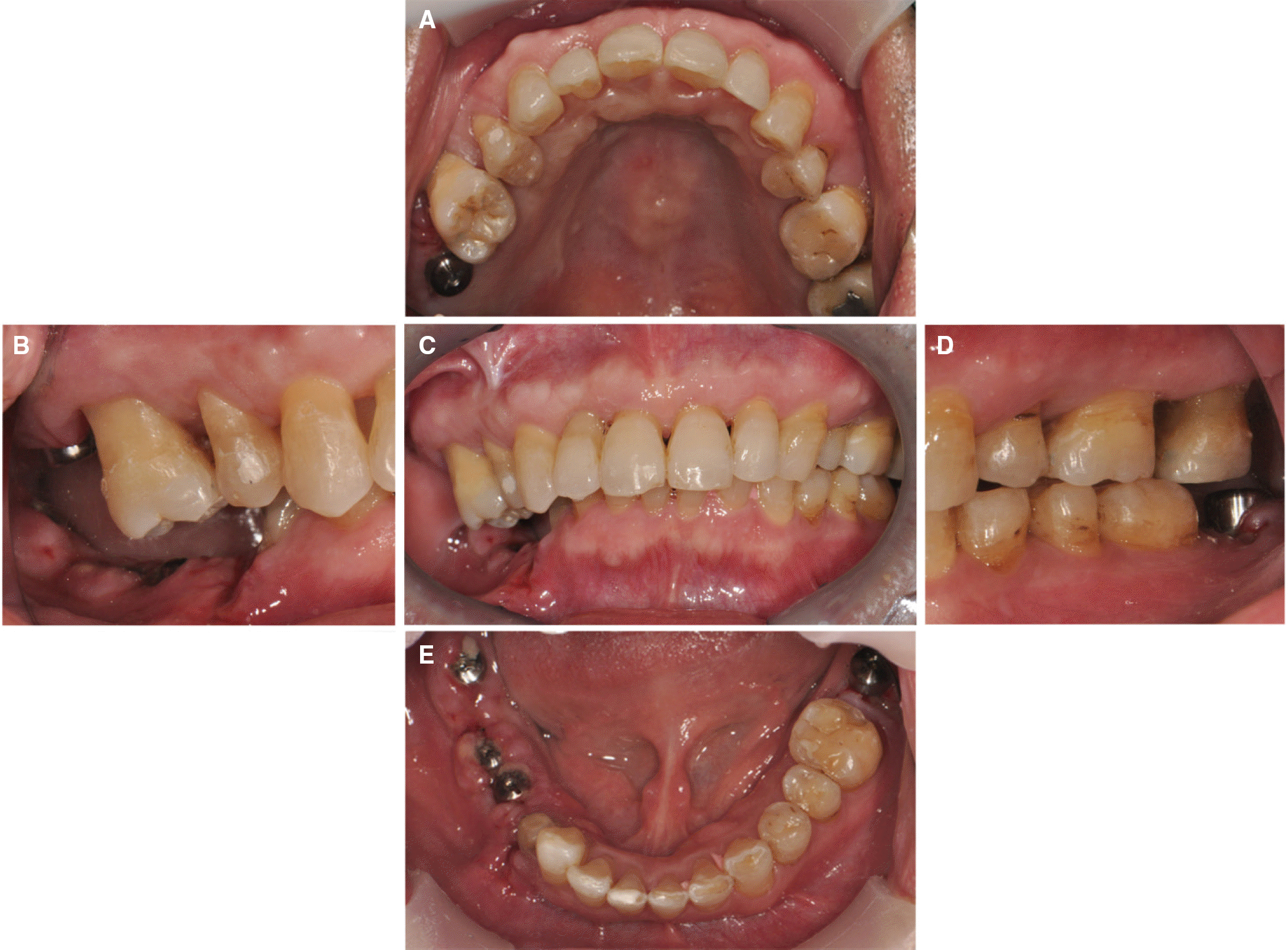 | Fig. 8.Post-orthodontic intraoral views. (A) Maxillary occlusal view, (B) Right lateral view, (C) Frontal view, (D) Left lateral view, (E) Mandibular occlusal view. |
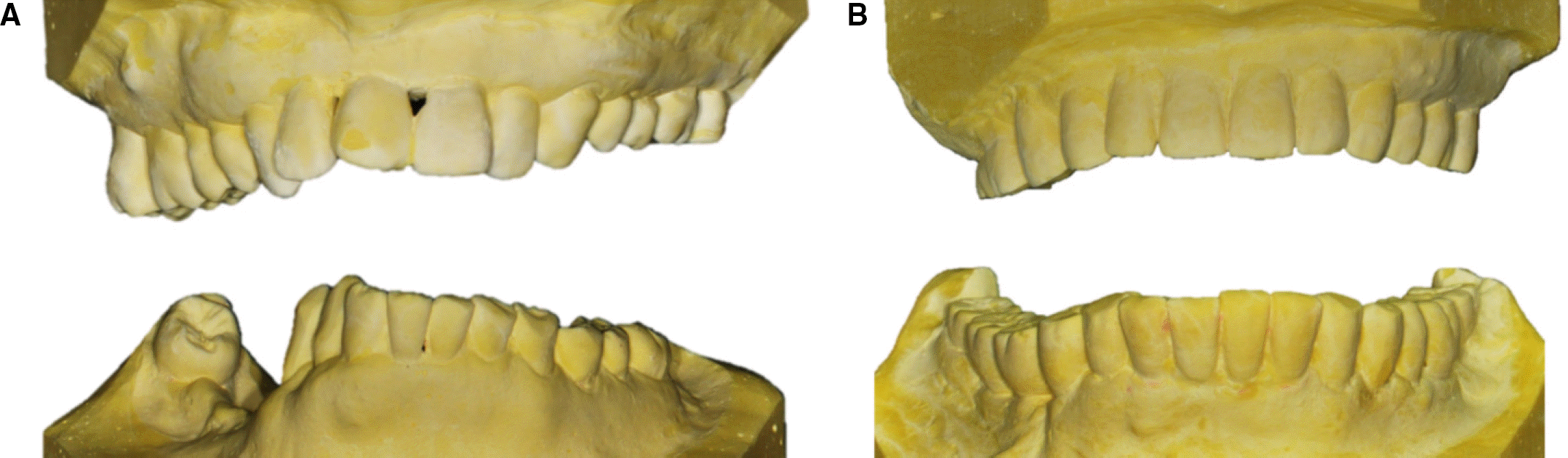
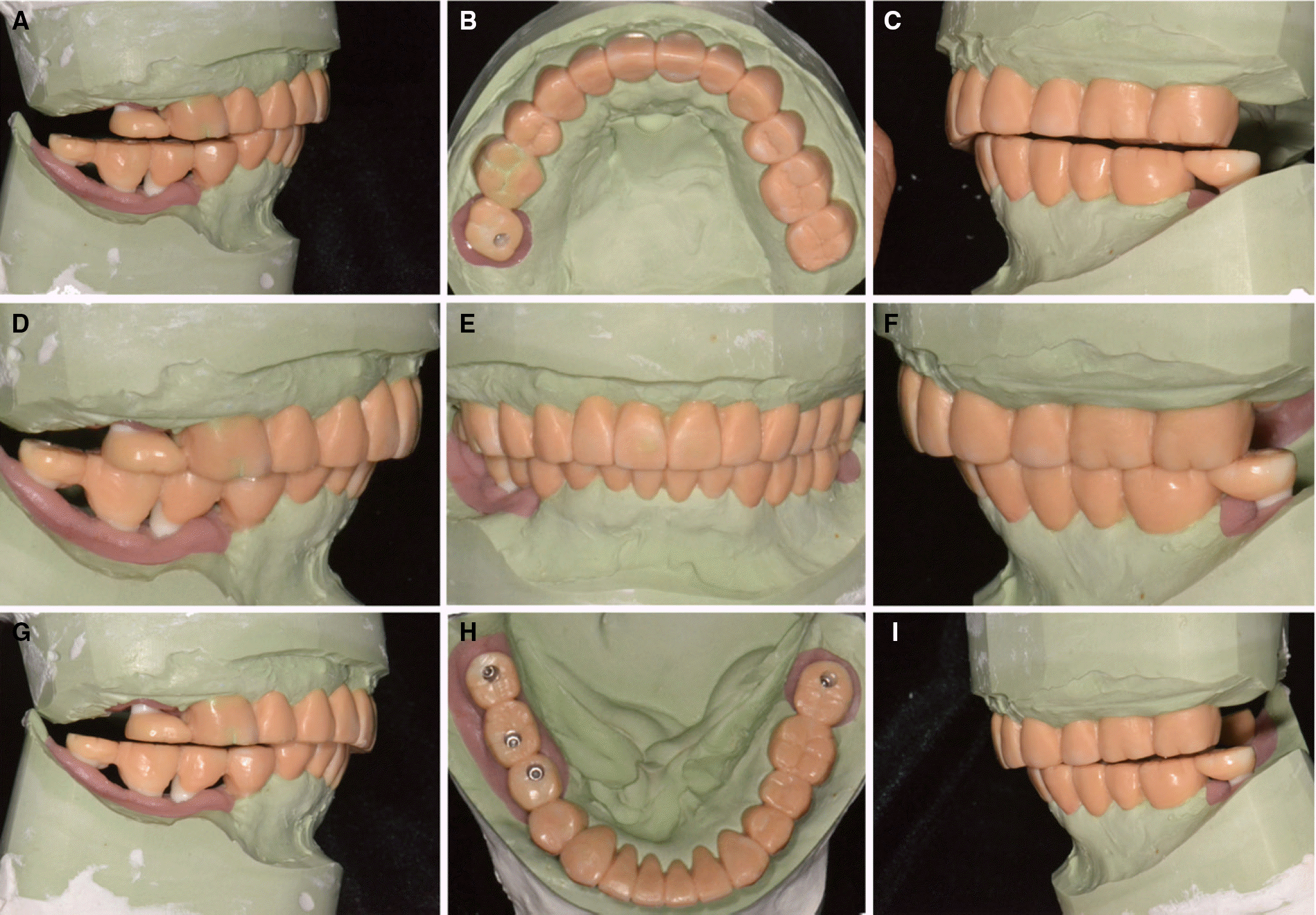 | Fig. 9.Diagnostic waxup. (A) Working side during right lateral excursion, (B) Maxillary occlusal view, (C) Non-working side during right lateral excursion, (D) Left lateral view at centric occlusion, (E) Frontal view at centric occlusion, (F) Right lateral view at centric occlusion, (G) Non-working side during left lateral excursion, (H) Mandibular occlusal view, (I) Working side during left lateral excursion. |
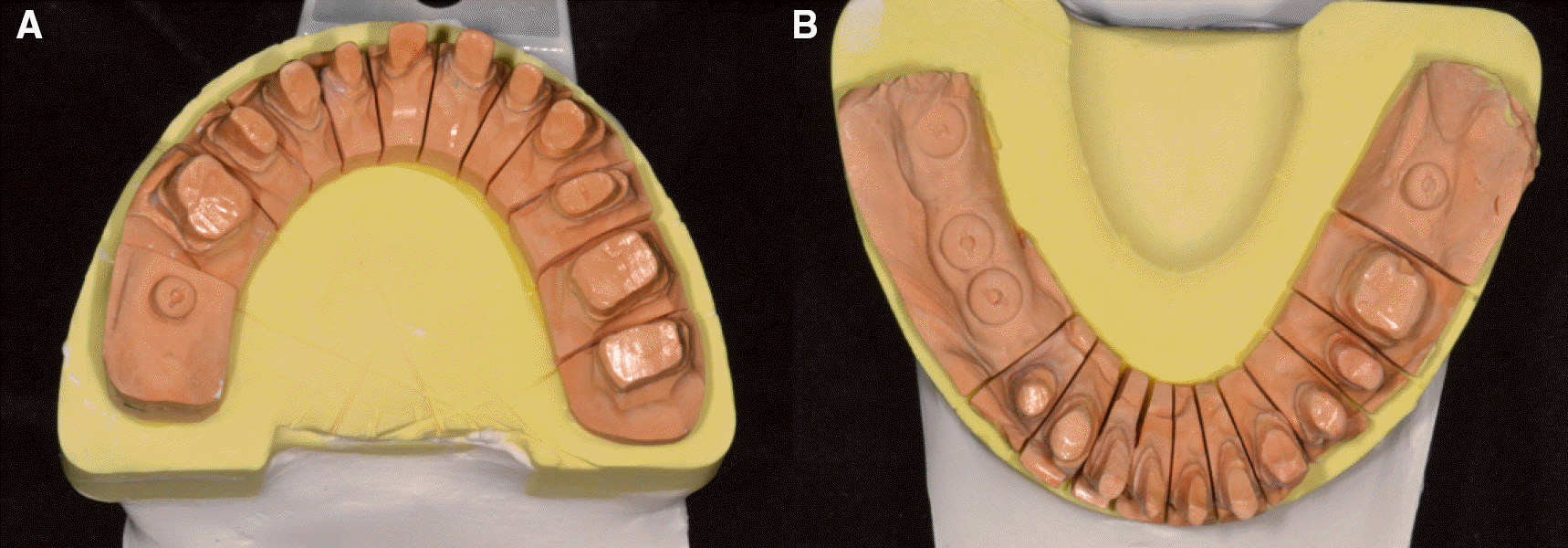
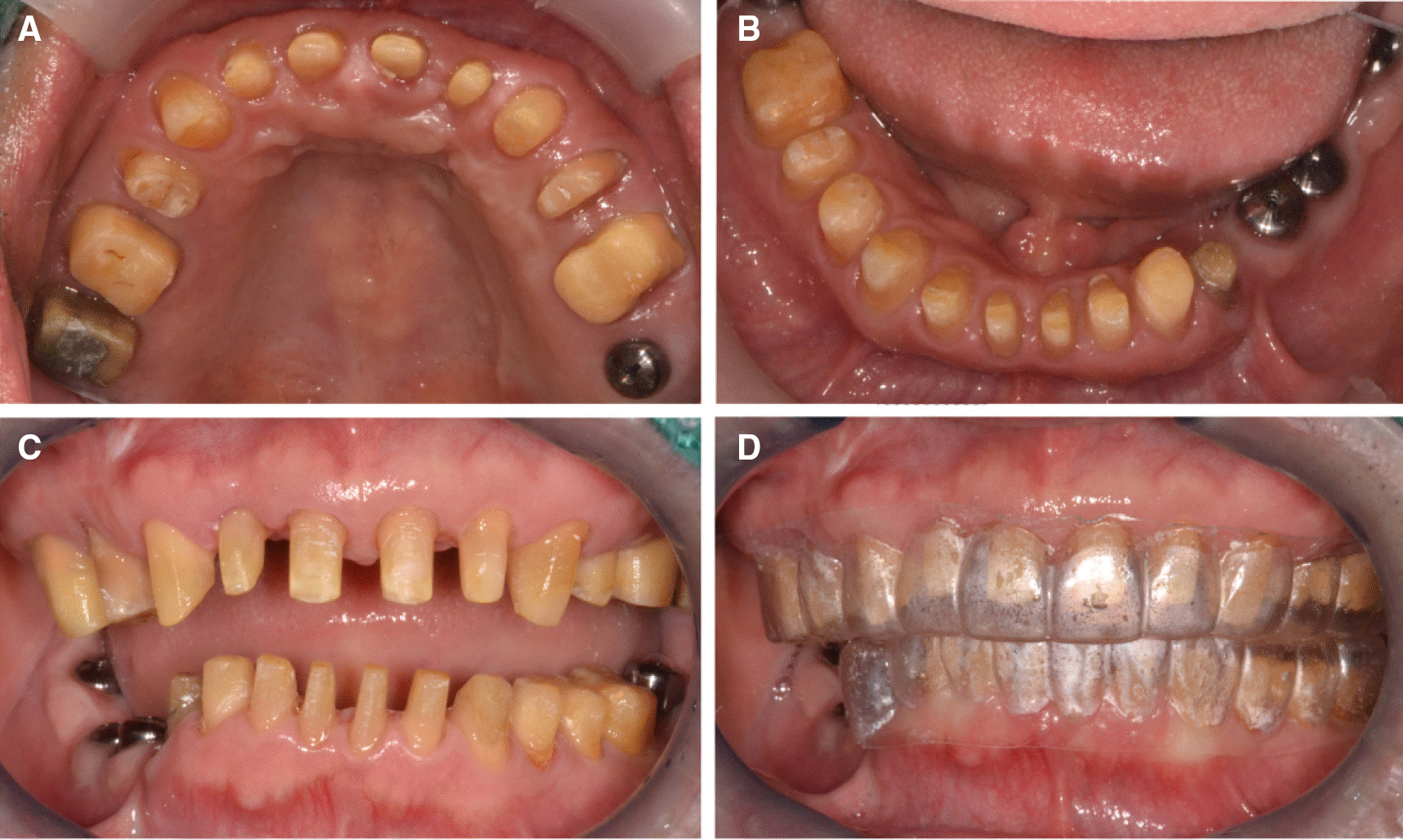 | Fig. 10.Teeth preparation procedures. (A) Occlusal view (maxilla), (B) Occlusal view (mandible), (C) Frontal view of centric occlusion, (D) Frontal view with matrix. |
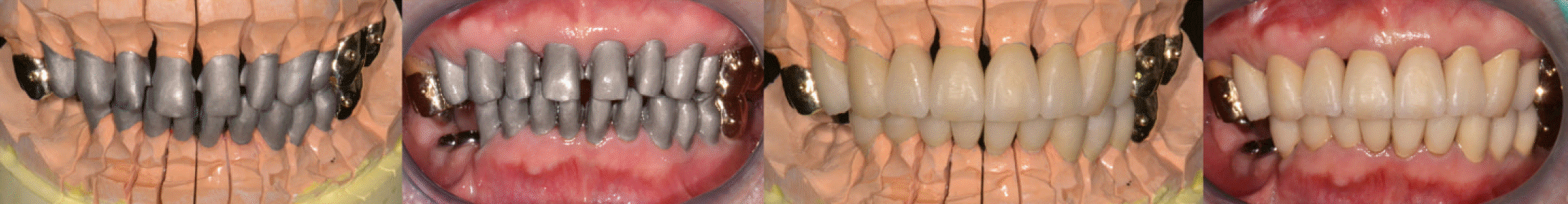
 | Fig. 11.(A) Provisional restorations in diagnostic cast, (B) Cementation of provisional restorations. |
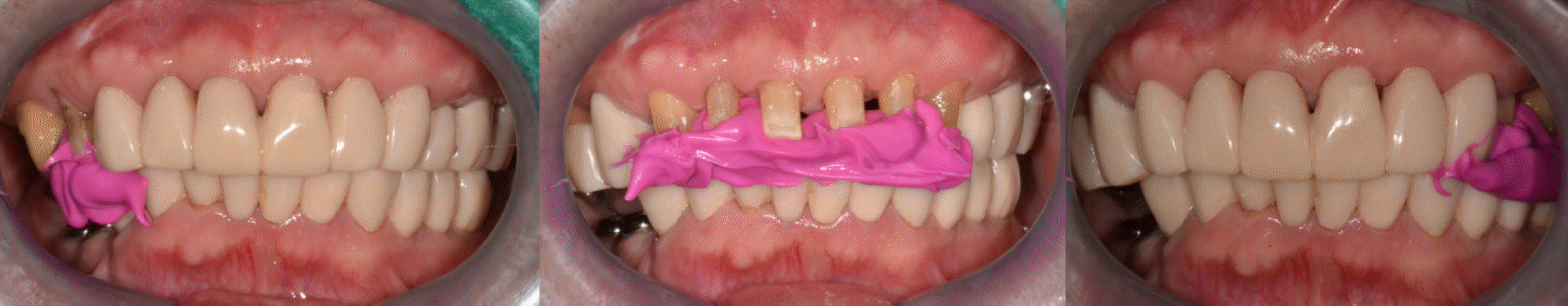
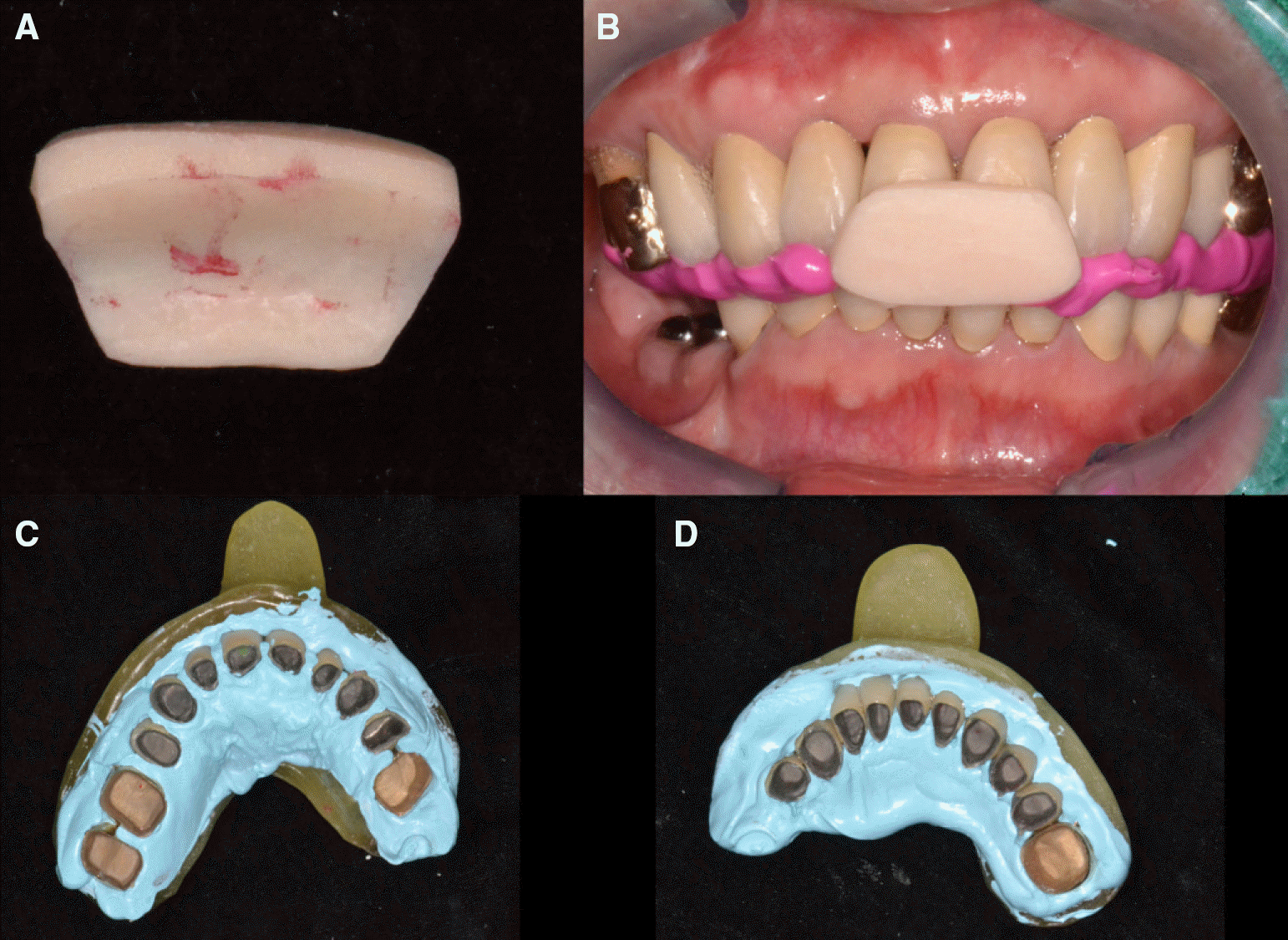 | Fig. 16.Clinical remounting using anterior programming device and pick-up impression. (A) Anterior programming device, (B) Interocclusal relation recording, (C) Pick-up impression for maxillary prosthesis, (D) Pick-up impression for mancibular prosthesis. |
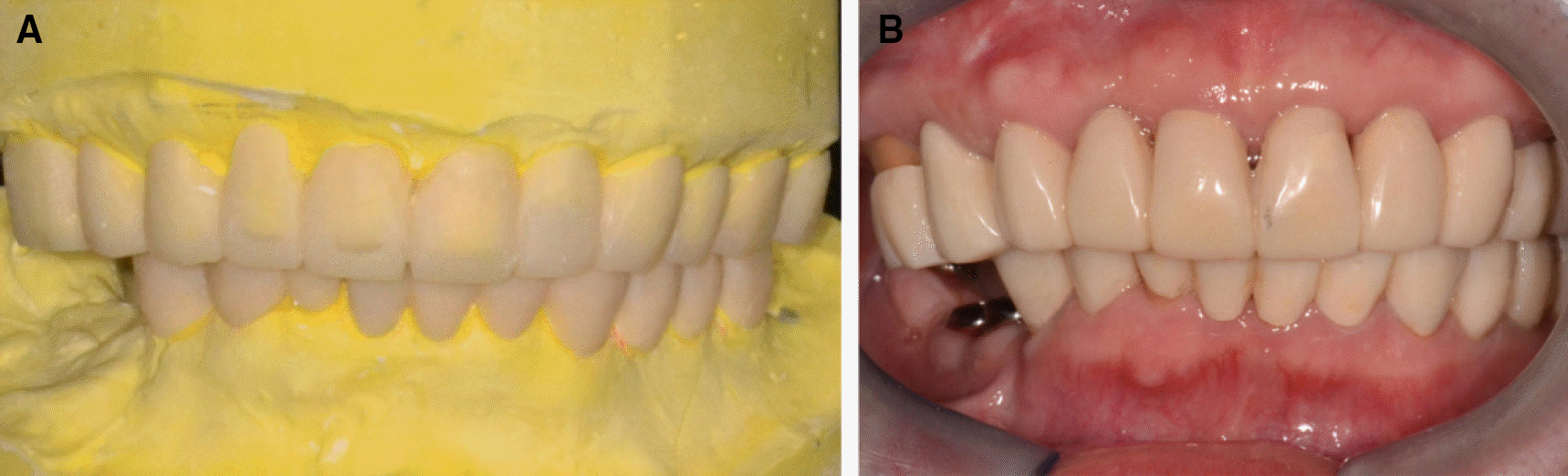
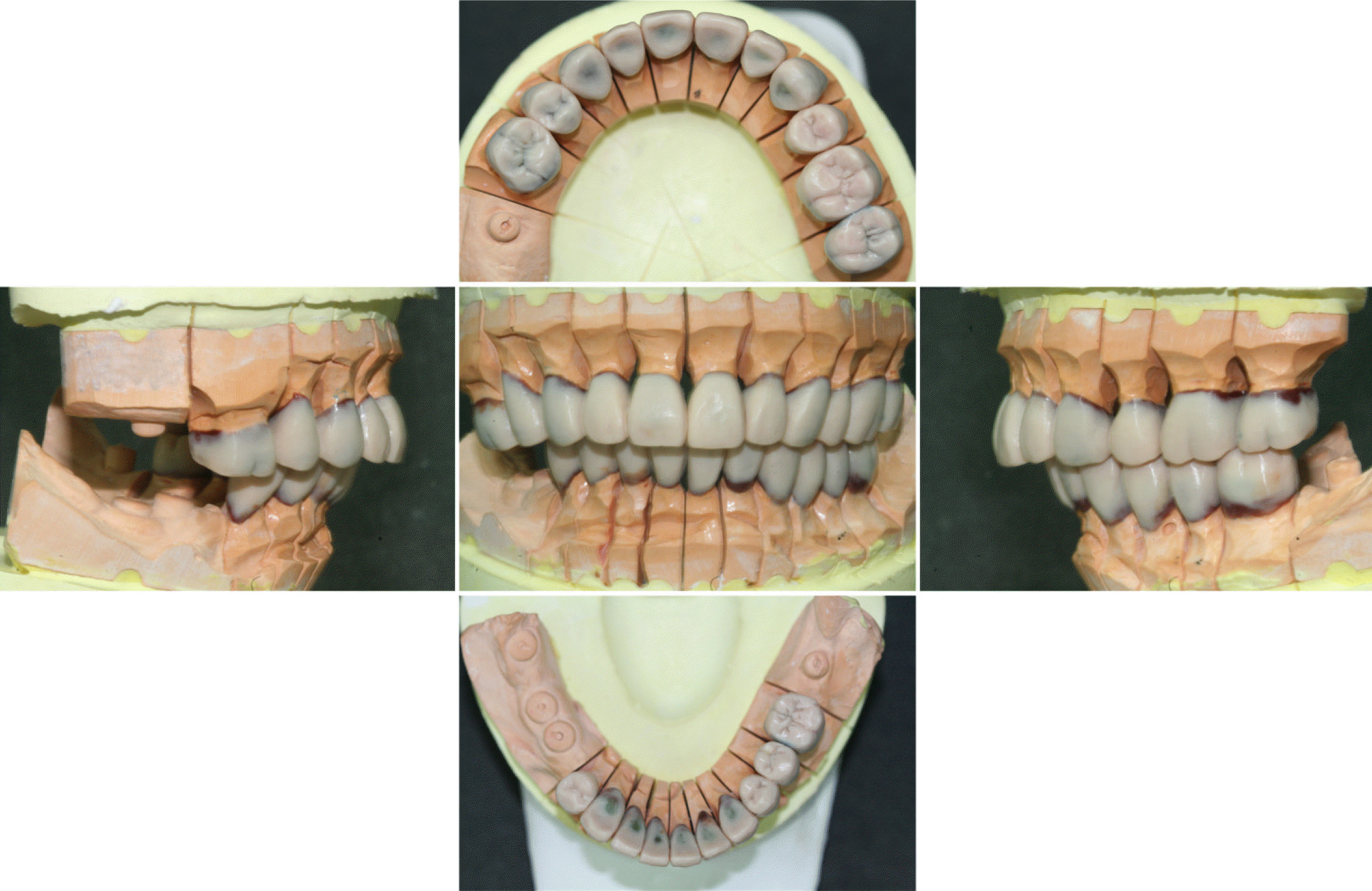
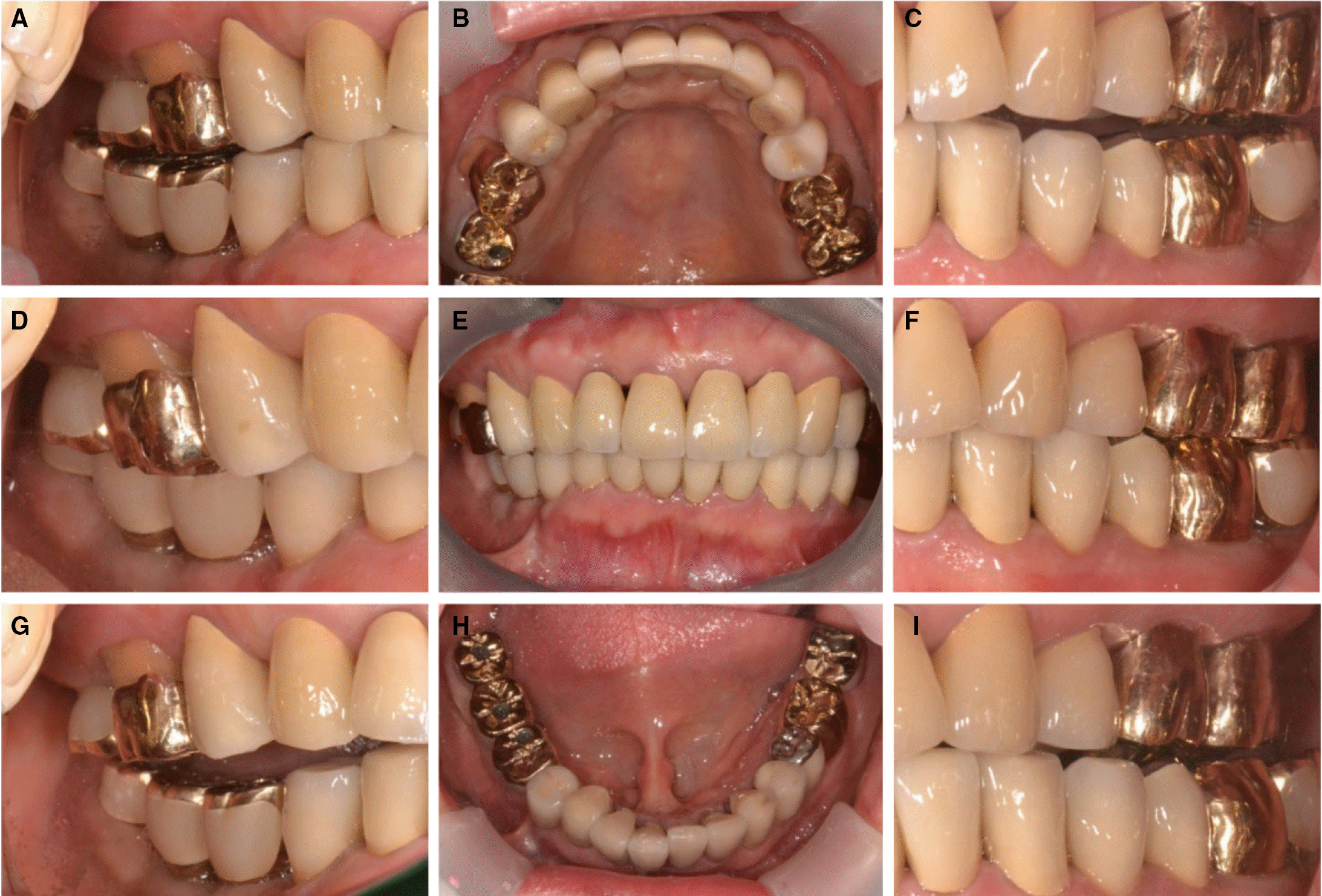 | Fig. 17.Definitive prosthesis. (A) Working side during right lateral excursion, (B) Maxillary occlusal view, (C) Non-working side during right lateral excursion, (D) Left lateral view at centric occlusion, (E) Frontal view at centric occlusion, (F) Right lateral view at centric occlusion, (G) Non-working side during left lateral excursion, (H) Mandibular occlusal view, (I) Working side during left lateral excursion. |
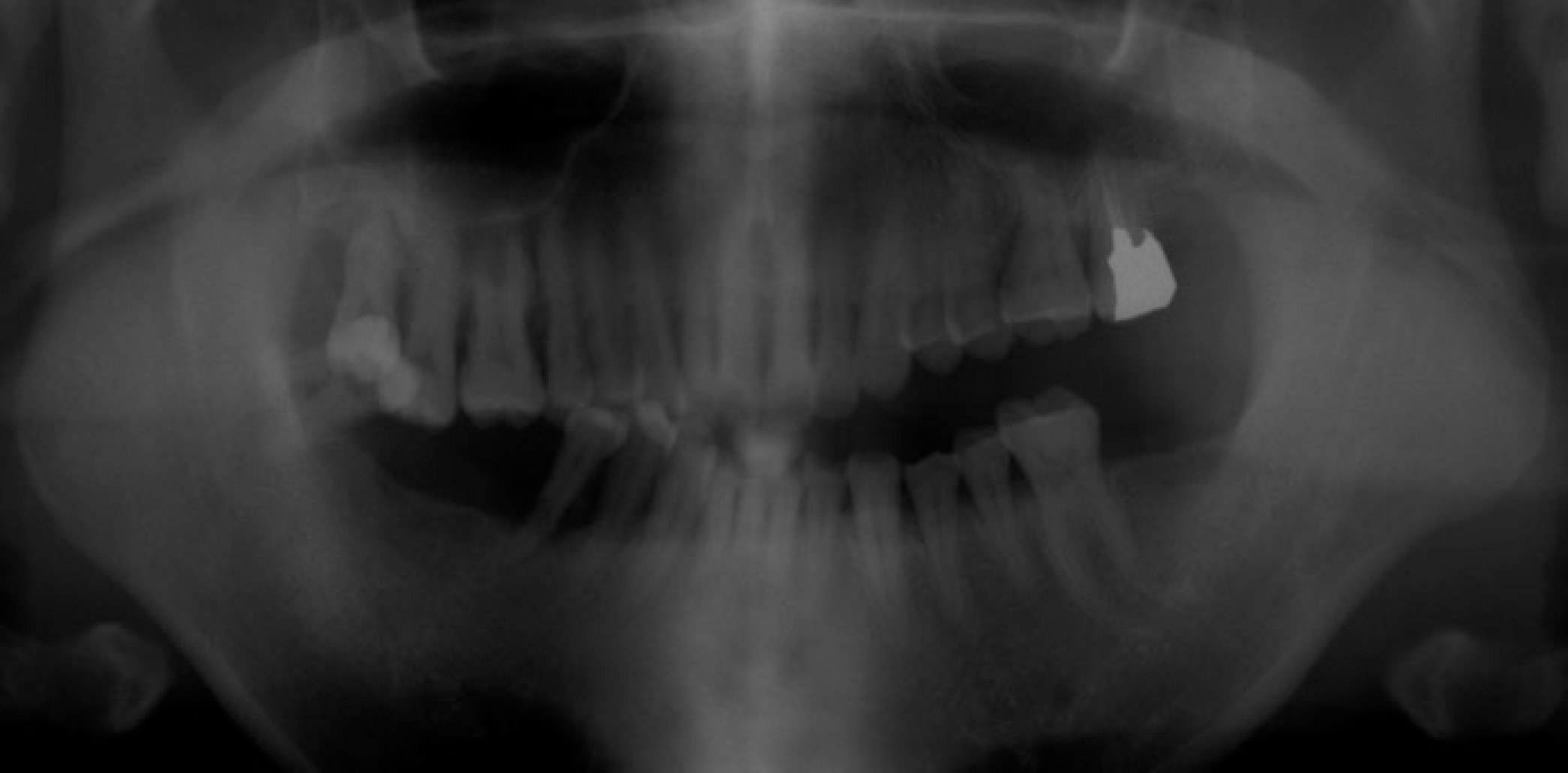
 | Fig. 18.Transcranial view at (A) placement of definitive prosthesis, (B) 1 year recall check. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


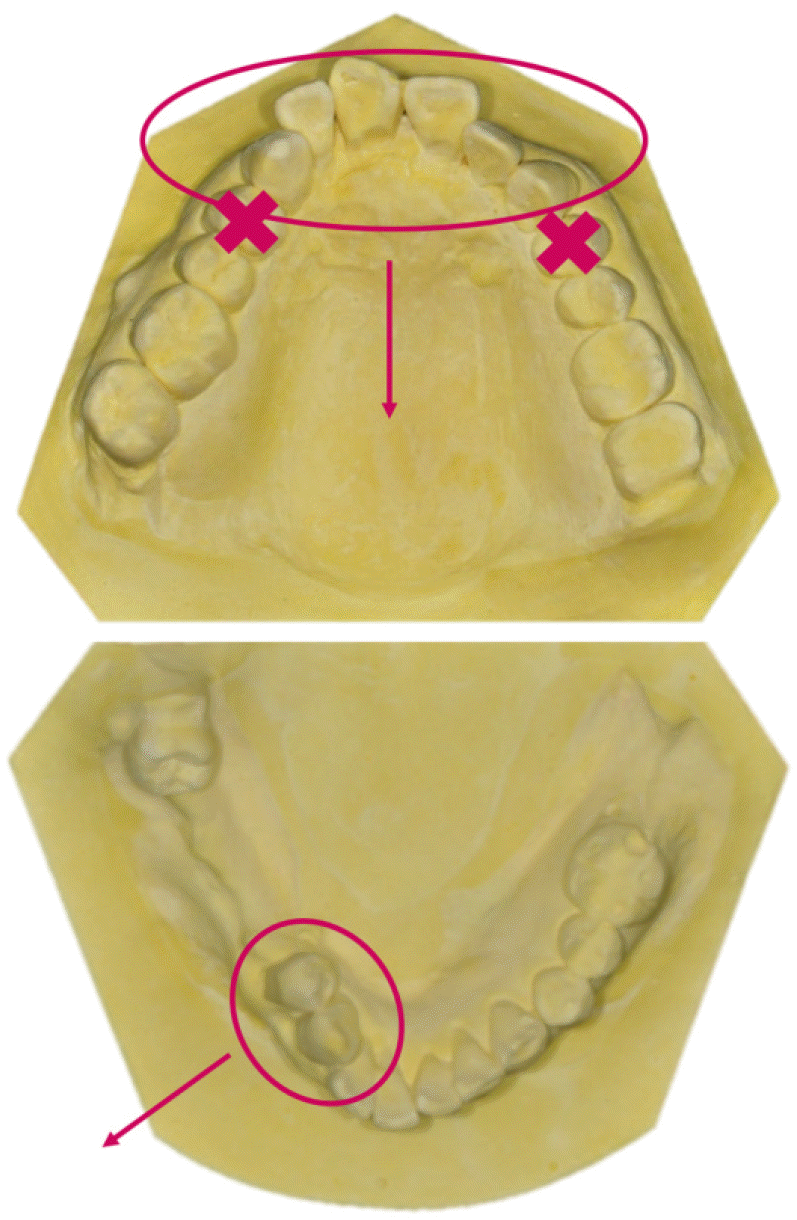
 XML Download
XML Download