Abstract
Soft tissue collapse around prepared teeth and pontic is inevitable after removal of the provisional restoration during the impression taking procedures. When inserting gingival retraction cord, soft tissue is displaced to an undesired contour. Viscosity of impression material also causes gingival displacement. Therefore, the consideration to transfer the prosthetically contoured soft tissue to master cast is required, especially in the esthetic area. In this report, the methods to maintain the soft tissue contour and transfer to the mastercast will be introduced. Harmonious contour of the soft tissue can be achieved with provisional restoration and be transferred to the master cast with two different techniques mentioned in this case report. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2013;51:323-31)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Banerjee R., Banerjee S., Usha R. Ovate pontic design: an aesthetic solution to anterior missing tooth-a case report. J Clin Diagno Res. 2010. 4:2996–9.
2.de Vasconcellos DK., Volpato CA∧., Zani IM., Bottino MA. Impression technique for ovate pontics. J Prosthet Dent. 2011. 105:59–61.

3.Seibert JS. Reconstruction of deformed, partially edentulous ridges, using full thickness onlay grafts. Part I. Technique and wound healing. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1983. 4:437–53.
4.Allen EP., Gainza CS., Farthing GG., Newbold DA. Improved technique for localized ridge augmentation. A report of 21 cases. J Periodontol. 1985. 56:195–9.

5.Atwood DA., Coy WA. Clinical, cephalometric, and densitometric study of reduction of residual ridges. J Prosthet Dent. 1971. 26:280–95.

6.Atwood DA. Reduction of residual ridges: a major oral disease entity. J Prosthet Dent. 1971. 26:266–79.

7.Greenstein G., Jaffin RA., Hilsen KL., Berman CL. Repair of anterior gingival deformity with durapatite. A case report. J Periodontol. 1985. 56:200–3.
8.Pameijer JH. Soft tissue master cast for esthetic control in crown and bridge procedures. J Esthet Dent. 1989. 1:47–50.

Go to : 
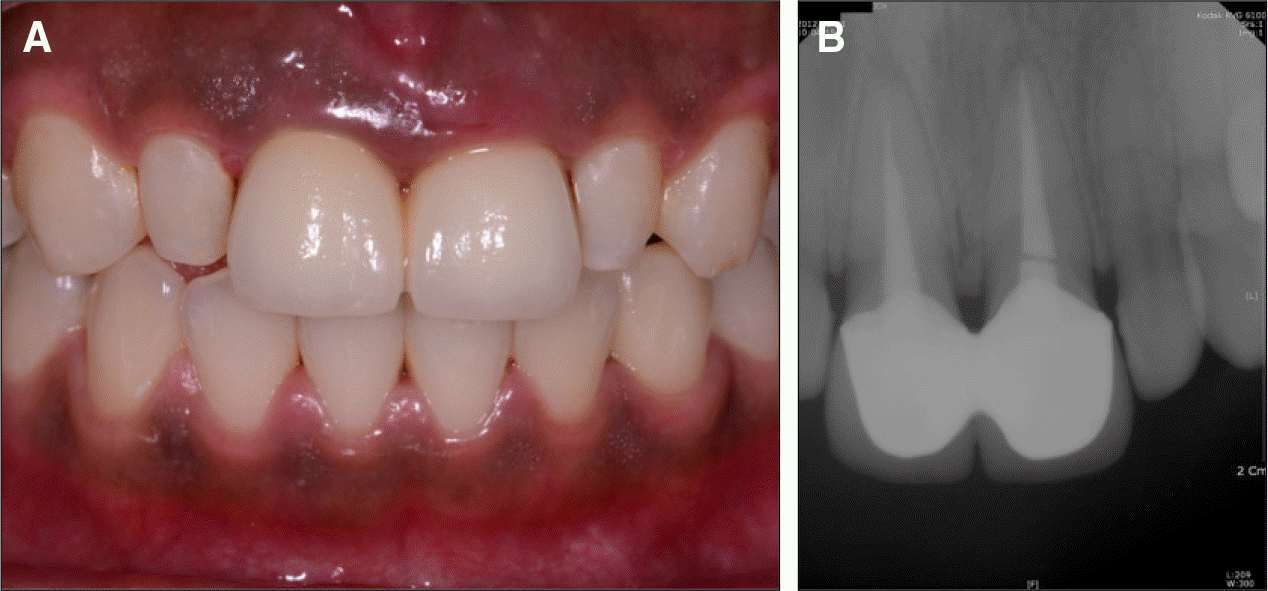
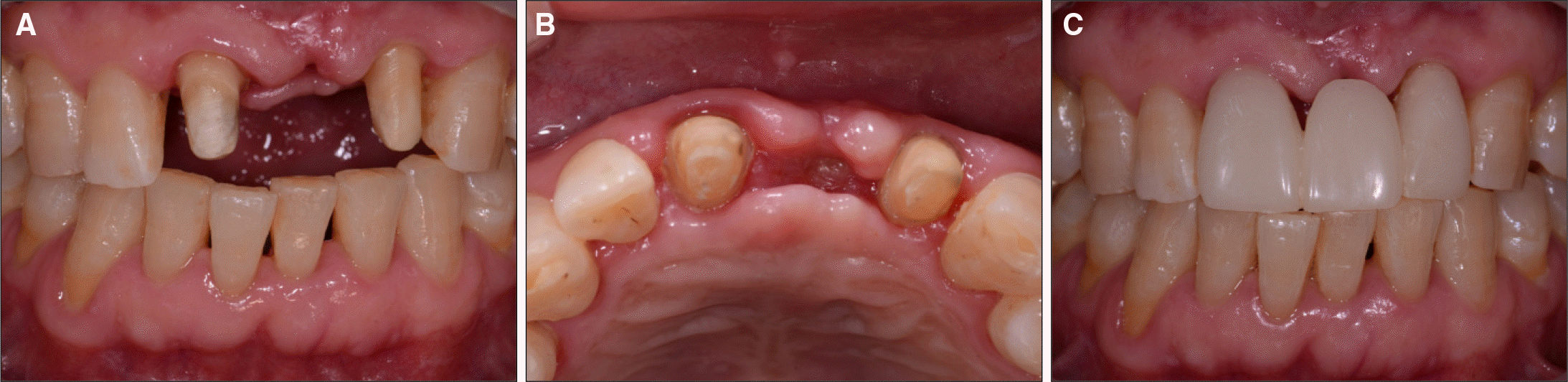 | Fig. 4.Initial view of gingival contour. A: Frontal view, B: Occlusal view, C: provisional restoration. |
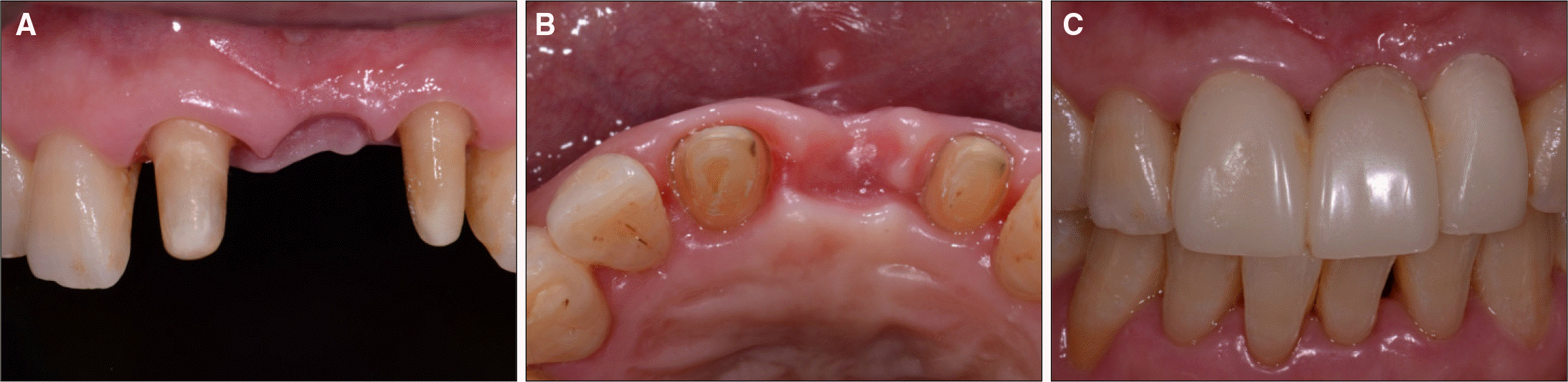 | Fig. 5.Two months after gingival sculpturing. A: Frontal view, B: Occlusal view, C: Provisional restoration. |
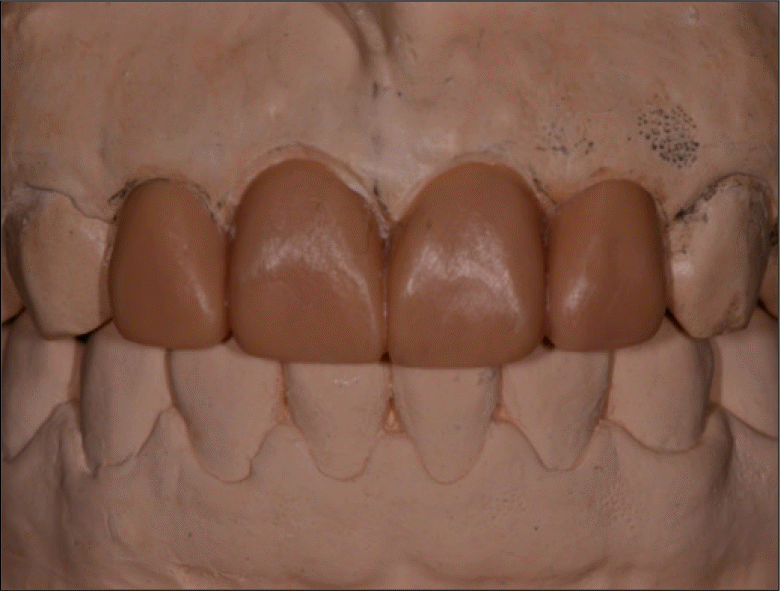
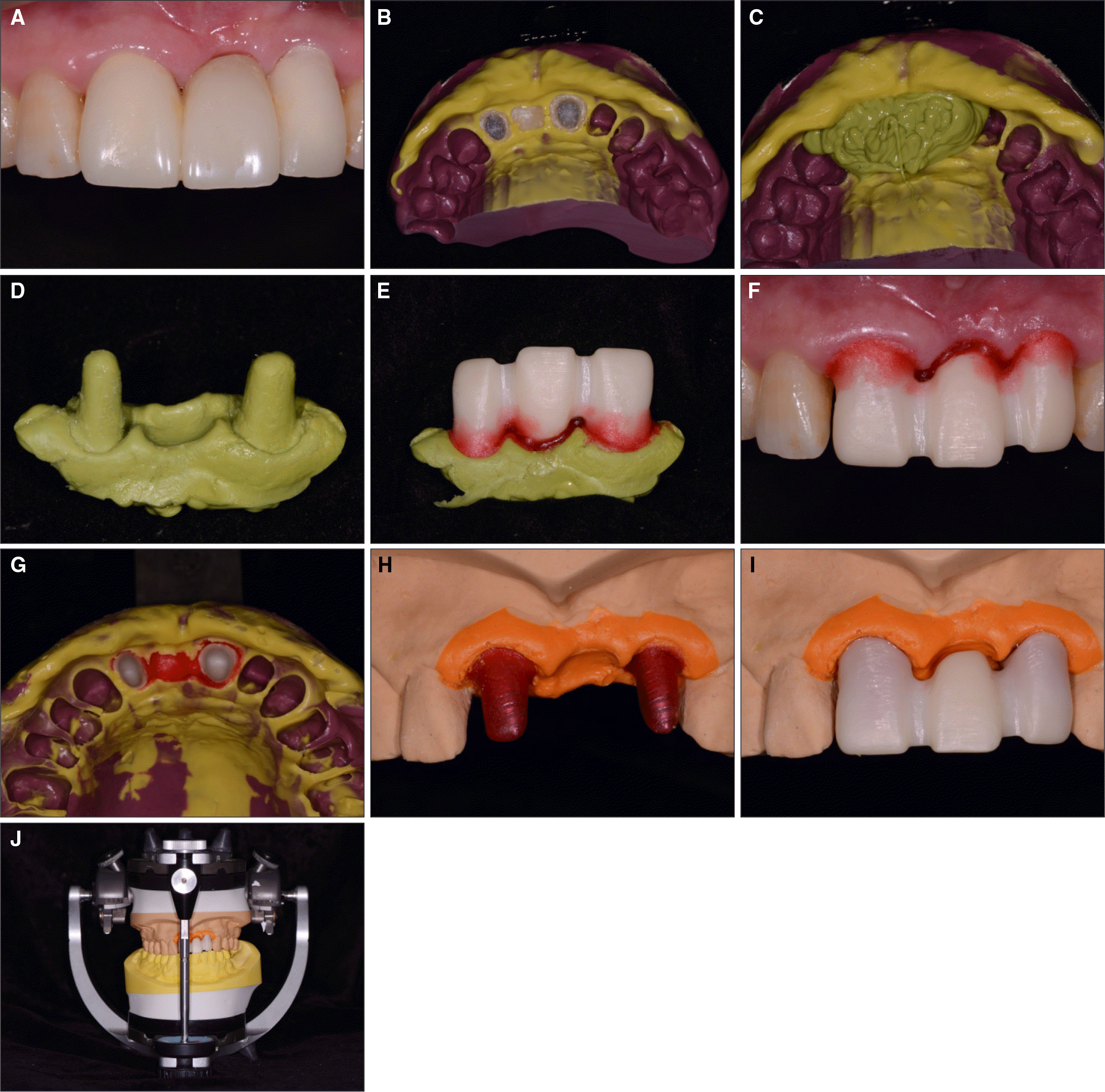 | Fig. 6.Procedure of soft tissue replication. A: Provisional restoration in position without provisional cement, B: Pick-up impression of the provisional restoration, C: Inject regular-body vinyl polysiloxane impression material, D: Silicone cast, E: Adapt the zirconia coping on the silicone cast. Place pattern resin with bead-brush technique, F: Place customized zirconia coping over the abutment teeth, G: Make definitive transfer impression using heavy- and light-body vinyl polysiloxane, H: Pour the impression with soft tissue cast material, I: Place customized zirconia coping on soft tissue cast, J: Mounting on articulator with customized anterior guide table. |
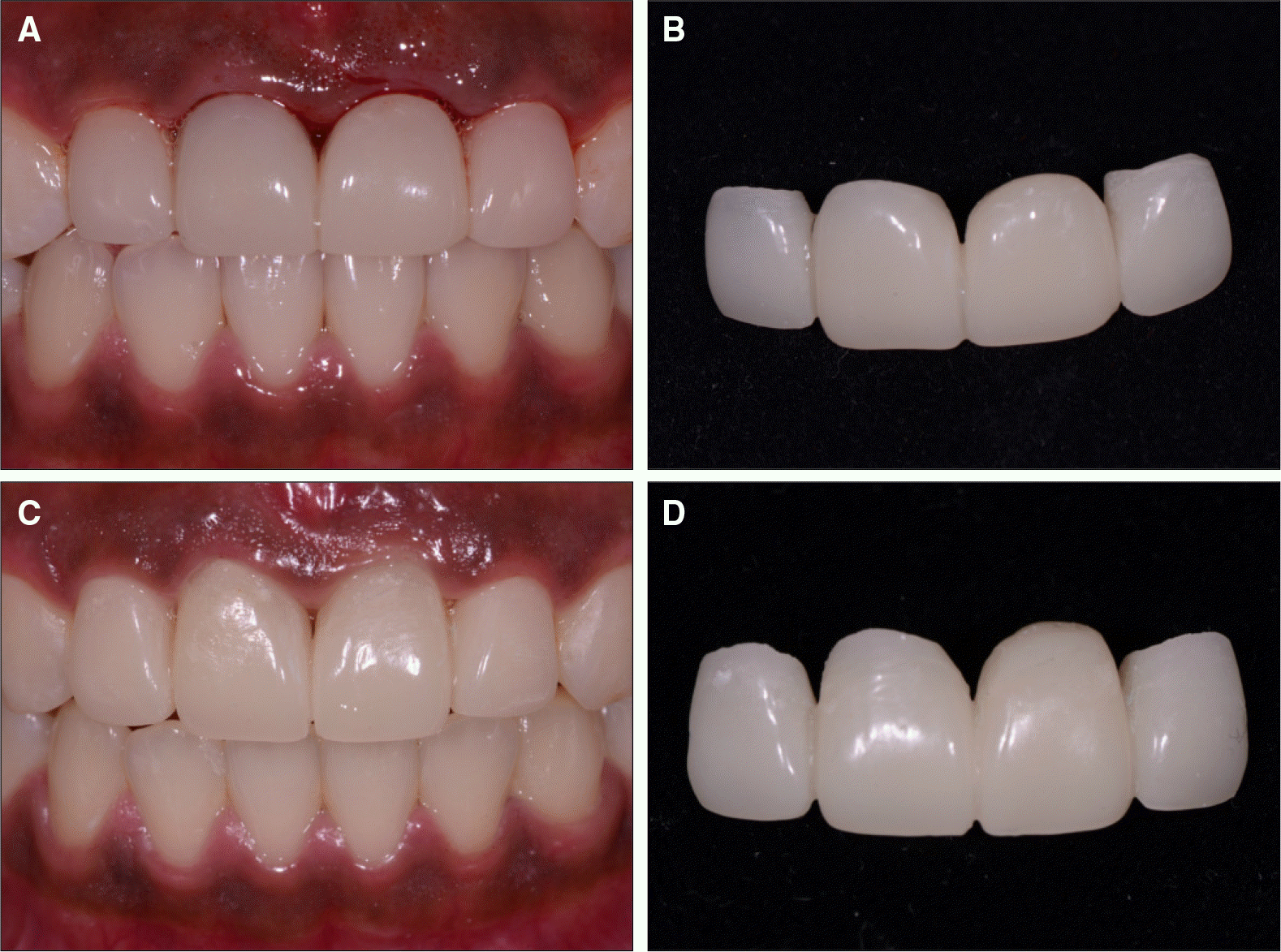
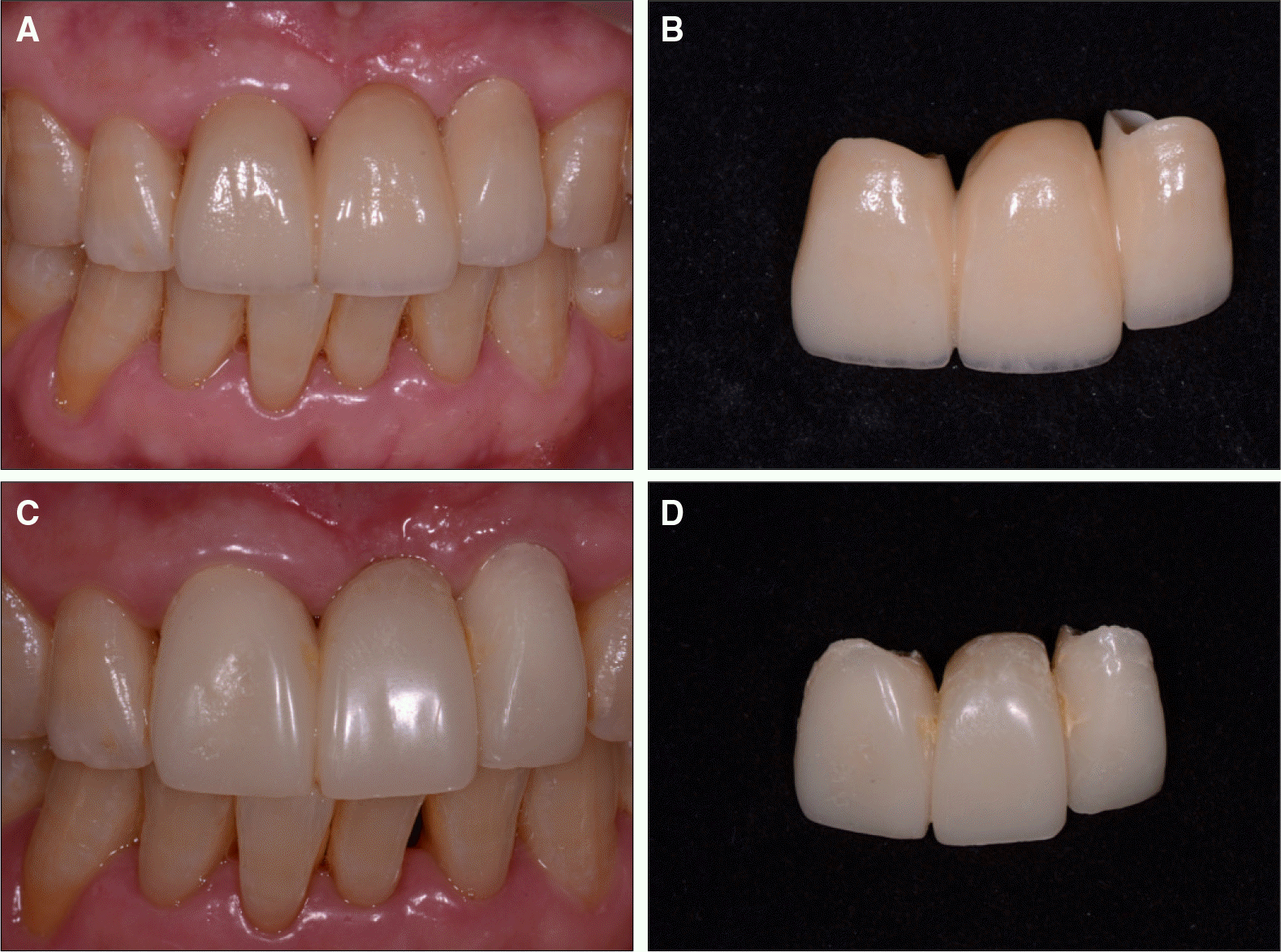 | Fig. 7.A: Intraoral view of the final prosthesis, B: Final prosthesis, C: Two months after gingival sculpturing, D: Provisional restoration. |
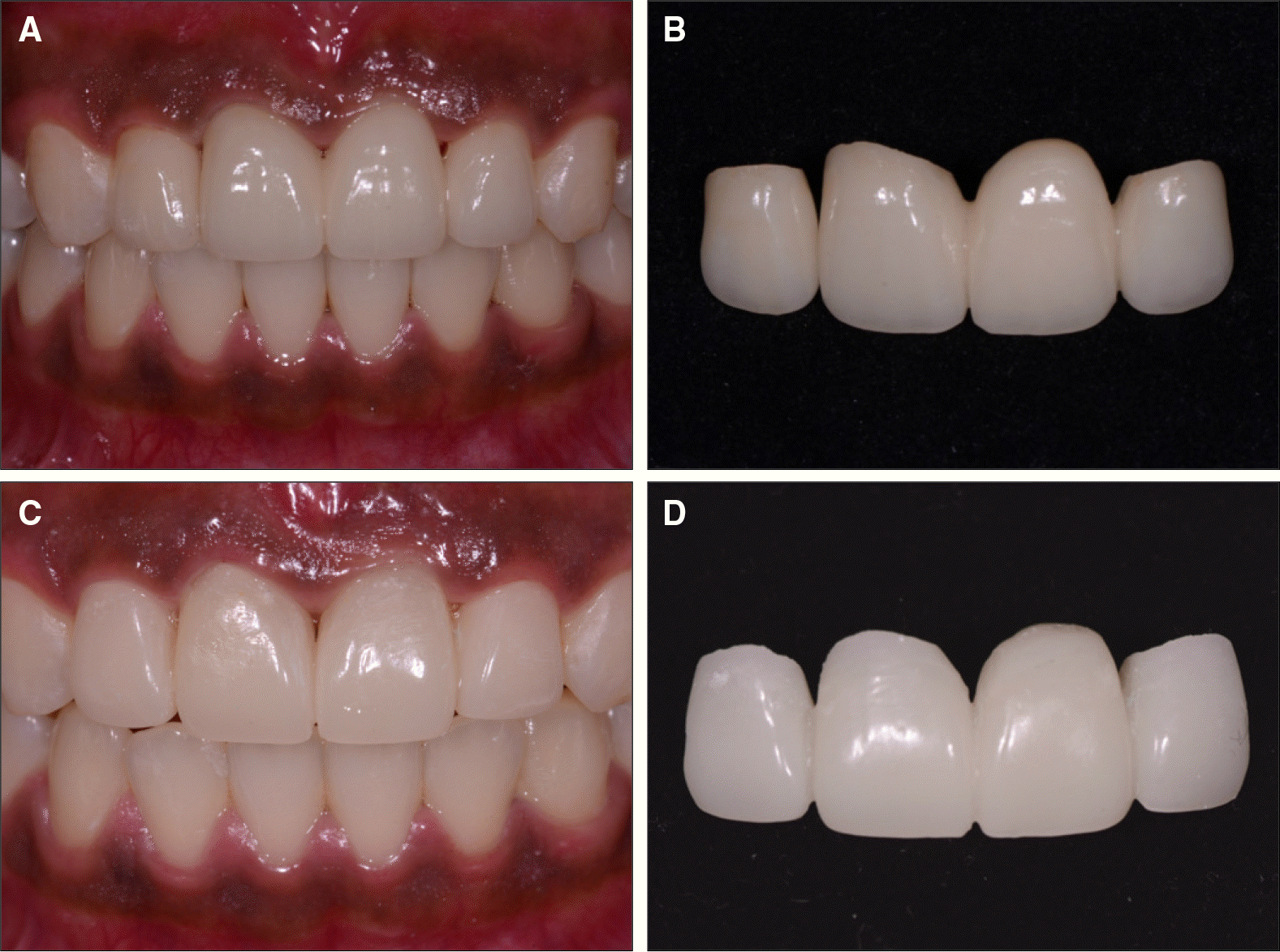
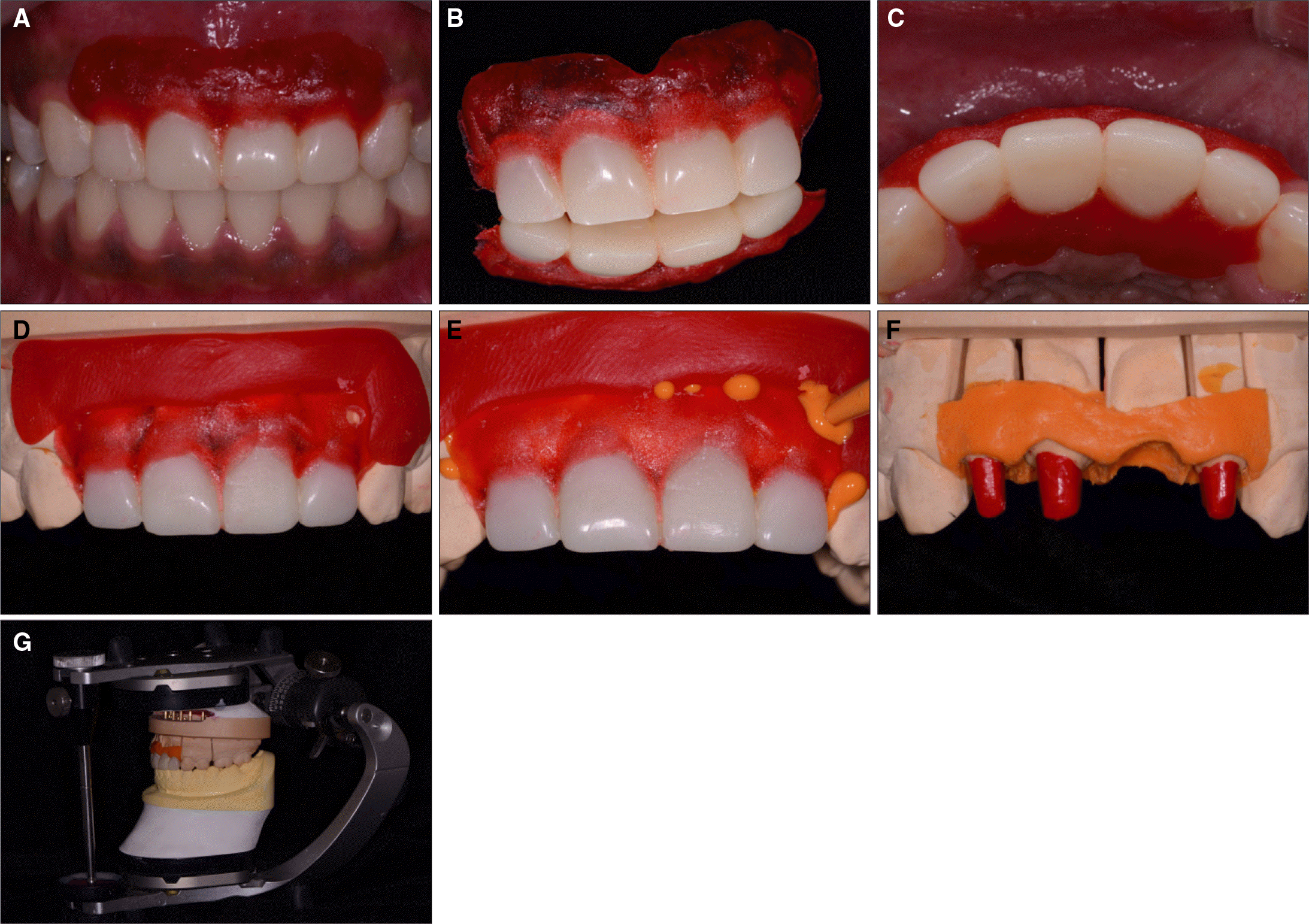 | Fig. 11.Procedure of soft tissue replication. A, B, C: Provisional restoration in position without provisional cement with bead-brush technique, place pattern resin on soft tissue around provisional restoration, D: Place provisional restoration with pattern resin dam on definitive cast, E: Inject light-body polyvinylsiloxane impression material, F: soft tissue cast, G: Mounting on articulator with customized anterior guide table. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download