Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the difference in shear bonding strength between resin cements to dental materials when a universal primer (Monobond plus) was applied in place of a conventional primer.
Materials and methods
Four groups of testing materials: gold alloy (Argedent Euro, n = 16), non precious metal (T-4, n = 20), zirconia (Cercon, n = 20) and glass ceramic (IPS e.max press, n = 20), were fabricated into discs, which were embedded in an acrylic resin matrix. The gold alloy specimens were airborne-particle abraded, 8 of the specimens were coated with Metal primer II, while the remaining 8 specimens were coated with Monobond plus. The non precious and zirconia specimen were airborne-particle abraded then, the control group received Alloy primer coating, while the other was coated with Monobond plus. Glass ceramic specimens were etched. 10 specimens were coated with Monobond-S and the remaining specimens were coated using Monobond plus. On top of the surface, Multilink N was polymerized in a disc shape. All of the specimens were thermal cycled before the shear bonding strength was measured. Statistical analysis was done with Two sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test (α=.05).
Results
There were no significant differences in bonding strength depending on the type of primer used in the gold alloy and glass ceramic groups (P>.05), however, the bonding strengths of resin cements to non precious metal and zirconia groups, were significantly higher when the alloy primer was used (P<.05).
Conclusion
Within the limitations of this study, improvement of universal primers which can be applied to all types of restorations is recommended to precious metals and zirconia ceramics. But, the bond strengths of non precious metals and zirconia ceramics were significantly lower when compared to a 10-MDP primer. More research is needed to apply universal primers to all types of restorations.
Figures and Tables
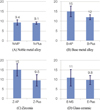 | Fig. 4Shear bond strength (MPa) between resin cement and restorative materials.
*B: base metal alloy, E: glass ceramic, N: noble metal alloy, Z: zirconia, AP: Alloy primer, MP: Metal primer II, MS: Monobond-S, Plus: Monobond plus.
|
References
1. Zidan O, Ferguson GC. The retention of complete crowns prepared with three different tapers and luted with four different cements. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 89:565–571.

2. Rosenstiel SF, Land MF, Crispin BJ. Dental luting agents: A review of the current literature. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 80:280–301.

3. Kern M, Wegner SM. Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:64–71.

4. Watanabe I, Matsumura H, Atsuta M. Effect of two metal primers on adhesive bonding with type IV gold alloys. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 73:299–303.

5. Scherrer SS, De Rijk WG, Belser UC. Fracture resistance of human enamel and three all-ceramic crown systems on extracted teeth. Int J Prosthodont. 1996. 9:580–585.
6. Bindl A, Lüthy H, Mörmann WH. Strength and fracture pattern of monolithic CAD/CAM-generated posterior crowns. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:29–36.

7. Borges GA, Sophr AM, de Goes MF, Sobrinho LC, Chan DC. Effect of etching and airborne particle abrasion on the microstructure of different dental ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 89:479–488.

8. Roulet JF, Söderholm KJ, Longmate J. Effects of treatment and storage conditions on ceramic/composite bond strength. J Dent Res. 1995. 74:381–387.

9. Della Bona A, Anusavice KJ, Shen C. Microtensile strength of composite bonded to hot-pressed ceramics. J Adhes Dent. 2000. 2:305–313.
10. Lu R, Harcourt JK, Tyas MJ, Alexander B. An investigation of the composite resin/porcelain interface. Aust Dent J. 1992. 37:12–19.

11. Jung JH, Jung SH, Cho HW, Kim YL. The influence of surface conditioning on the shear bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to zirconia ceramics. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2010. 48:251–258.

12. Kim SJ, Lee KW, Han CH. Bonding between resin and ceramics. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2007. 45:159–168.
13. Olsson KG, Fürst B, Andersson B, Carlsson GE. A long-term retrospective and clinical follow-up study of In-Ceram Alumina FPDs. Int J Prosthodont. 2003. 16:150–156.

14. Pröbster L. Four year clinical study of glass-infiltrated, sintered alumina crowns. J Oral Rehabil. 1996. 23:147–151.

15. Okuya N, Minami H, Kurashige H, Murahara S, Suzuki S, Tanaka T. Effects of metal primers on bonding of adhesive resin cement to noble alloys for porcelain fusing. Dent Mater J. 2010. 29:177–187.

16. Antoniadou M, Kern M, Strub JR. Effect of a new metal primer on the bond strength between a resin cement and two high-noble alloys. J Prosthet Dent. 2000. 84:554–560.

17. Bindl A, Richter B, Mörmann WH. Survival of ceramic computer-aided design/manufacturing crowns bonded to preparations with reduced macroretention geometry. Int J Prosthodont. 2005. 18:219–224.

18. Pisani-Proenca J, Erhardt MC, Valandro LF, Gutierrez-Aceves G, Bolanos-Carmona MV, Del Castillo-Salmeron R, Bottino MA. Influence of ceramic surface conditioning and resin cements on microtensile bond strength to a glass ceramic. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 96:412–417.

19. Della Bona A, Shen C, Anusavice KJ. Work of adhesion of resin on treated lithia disilicate-based ceramic. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:338–344.

20. Kern M, Barloi A, Yang B. Surface conditioning influences zirconia ceramic bonding. J Dent Res. 2009. 88:817–822.

21. Heikkinen TT, Lassila LVJ, Matinlinna JP, Vallittu PK. Effect of Primers and Resins on The Shear Bond Strength of Resin Composite to Zirconia. SRX Dent. 2010. Article ID 295137, 8 Pages. doi:10.3814/2010/295137.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download