Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to measure patient satisfaction and oral health-related quality of life and to assess an association between patients’ satisfaction and oral health-related quality of life after implant surgery by using structural equation modeling.
Materials and methods
A total of 257 participants who visited 6 dental clinics located in Daegu city for the purpose of implant treatment participated in this study. Six months after completion of implant surgery, the patients’ satisfaction and oral health-related quality of life were surveyed. The effect of factors associated with patients’ satisfaction such as functions and aesthetics, maintenance and cost on oral health-related quality of life after implant surgery was analyzed using AMOS 4.0.
Results
Oral health-related quality of life was improved in all dimensions of OHIP-14 after implant surgery. Functions and aesthetics as well as maintenance had a significant effect on oral health-related quality of life (P<.05), while cost was not a critical factor influencing oral health-related quality of life.
Conclusion
High satisfaction with functional aspects and maintenance aspects significantly affected good quality of life. The result of this study supported the fact that education and management for patients after implant therapy were positively related to good quality of life based on a theoretical model. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2011;49:291-9)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Stellingsma K., Bouma J., Stegenga B., Meijer HJ., Raghoebar GM. Satisfaction and psychosocial aspects of patients with an extremely resorbed mandible treated with implant-retained overdentures. A prospective, comparative study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003. 14:166–72.
2.Sheiham A., Steele JG., Marcenes W., Tsakos G., Finch S., Walls AW. Prevalence of impacts of dental and oral disorders and their effects on eating among older people; a national survey in Great Britain. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2001. 29:195–203.

3.Pjetursson BE., Karoussis I., Bu¨rgin W., Bra¨gger U., Lang NP. Patients' satisfaction following implant therapy. A 10-year prospective cohort study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:185–93.

4.Simonis P., Dufour T., Tenenbaum H. Long-term implant survival and success: a 10-16-year follow-up of non-submerged dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 21:772–7.

5.Korea Food and Drug Administration. Dental implant, Clear evidence of relacement from foreign to domestic manufacture. http://www.kfda.go.kr. 2010.
6.Osstem Implant. Quarterly Financial Report Q3 2008. http://www.osstem.co.kr. 2008.
7.Shin HS., Hong SY. The supply and demand for dentists in Korea. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2007. 27:81–102.
8.Osstem Implant. Investor Relations in Korean. http://www.osstem.co.kr. 2010.
9.Jung RE., Pjetursson BE., Glauser R., Zembic A., Zwahlen M., Lang NP. A systematic review of the 5-year survival and complication rates of implant-supported single crowns. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:119–30.

10.Eckert SE., Choi YG., Sa′nchez AR., Koka S. Comparison of dental implant systems: quality of clinical evidence and prediction of 5-year survival. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005. 20:406–15.

11.Lee SY., Piao CM., Koak JY., Kim SK., Kim YS., Ku Y., Rhyu IC., Han CH., Heo SJ. A 3-year prospective radiographic evaluation of marginal bone level around different implant systems. J Oral Rehabil. 2010. 37:538–44.

12.Albrektsson T., Bra�nemark PI., Hansson HA., Lindstro¨m J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop Scand. 1981. 52:155–70.
13.Anderson JD. The need for criteria on reporting treatment outcomes. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 79:49–55.

14.Eitner S., Wichmann M., Schlegel KA., Kollmannsberger JE., Nickenig HJ. Oral health-related quality of life and implant therapy: An evaluation of preoperative, intermediate, and posttreatment assessments of patients and physicians. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011 Apr 7. [Epub ahead of print].

15.Abu Hantash RO., Al-Omiri MK., Al-Wahadni AM. Psychological impact on implant patients' oral health-related quality of life. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:116–23.

16.Cibirka RM., Razzoog M., Lang BR. Critical evaluation of patient responses to dental implant therapy. J Prosthet Dent. 1997. 78:574–81.

17.Jeong SH., Park JH., Ahn SH., Lee JH., Choi YH., Song KB. Assessing changes of the oral health related quality of Life following implant therapy. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2009. 33:585–96.
18.Chung SY., Cho JH., Cho CH., Choi YH., Song KB. Factors associated with patient satisfaction and decision to get implant surgery. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2011. 35:179–86.
19.Slade GD., Spencer AJ. Development and evaluation of the Oral Health Impact Profile. Community Dent Health. 1994. 11:3–11.
20.Locker D. Measuring oral health: a conceptual framework. Community Dent Health. 1988. 5:3–18.
21.Slade GD. Derivation and validation of a short-form oral health impact profile. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1997. 25:284–90.

22.Bae KH., Kim HD., Jung SH., Park DY., Kim JB., Paik DI., Chung SC. Validation of the Korean version of the oral health impact profile among the Korean elderly. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2007. 35:73–9.

23.Heydecke G., Boudrias P., Awad MA., De Albuquerque RF., Lund JP., Feine JS. Within-subject comparisons of maxillary fixed and removable implant prostheses: Patient satisfaction and choice of prosthesis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003. 14:125–30.
24.Vermylen K., Collaert B., Linde′n U., Bjo¨rn AL., De Bruyn H. Patient satisfaction and quality of single-tooth restorations. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003. 14:119–24.

25.Leles CR., Ferreira NP., Vieira AH., Campos AC., Silva ET. Factors influencing edentulous patients' preferences for prostho-dontic treatment. J Oral Rehabil. 2011. 38:333–9.

26.Carlsson GE., Omar R. The future of complete dentures in oral rehabilitation. A critical review. J Oral Rehabil. 2010. 37:143–56.

27.Ikebe K., Hazeyama T., Ogawa T., Kagawa R., Matsuda K., Wada M., Gonda T., Maeda Y. Subjective values of different age groups in Japan regarding treatment for missing molars. Gerodontology. 2011. 28:192–6.

28.Pommer B., Zechner W., Watzak G., Ulm C., Watzek G., Tepper G. Progress and trends in patients' mindset on dental implants. II: implant acceptance, patient-perceived costs and patient satisfaction. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 22:223–9.

29.Bae BR. LISREL Structural equation modelling -comprehension, application and programming-. 2nd ed.Seoul: Cheong Ram;2005. p. 21–40.
30.Chang MT. A literature review on the survival rate of single implant-supported restorations. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2002. 32:69–87.

31.McGrath C., Bedi R. Can dentures improve the quality of life of those who have experienced considerable tooth loss? J Dent. 2001. 29:243–6.

32.Heydecke G., Tedesco LA., Kowalski C., Inglehart MR. Complete dentures and oral health-related quality of life - do coping styles matter? Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2004. 32:297–306.

33.Allen PF., McMillan AS. A longitudinal study of quality of life outcomes in older adults requesting implant prostheses and complete removable dentures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003. 14:173–9.

34.Berretin-Felix G., Nary Filho H., Padovani CR., Machado WM. A longitudinal study of quality of life of elderly with mandibular implant-supported fixed prostheses. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:704–8.

35.Awad MA., Locker D., Korner-Bitensky N., Feine JS. Measuring the effect of intra-oral implant rehabilitation on health-related quality of life in a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Dent Res. 2000. 79:1659–63.

36.Heydecke G., Locker D., Awad MA., Lund JP., Feine JS. Oral and general health-related quality of life with conventional and implant dentures. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2003. 31:161–8.

37.Thomason JM., Heydecke G., Feine JS., Ellis JS. How do patients perceive the benefit of reconstructive dentistry with regard to oral health-related quality of life and patient satisfaction? A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. 18:168–88.

38.Ikebe K., Hazeyama T., Kagawa R., Matsuda K., Maeda Y. Subjective values of different treatments for missing molars in older Japanese. J Oral Rehabil. 2010. 37:892–9.

Go to : 
 | Fig. 2.Patients Satisfaction on five categories related to function, aesthetic, maintenance, cost, and general satisfaction after implant surgery (each item was recorded by 5-point Likert scale and of the 12 items, 5 ones were excluded). |
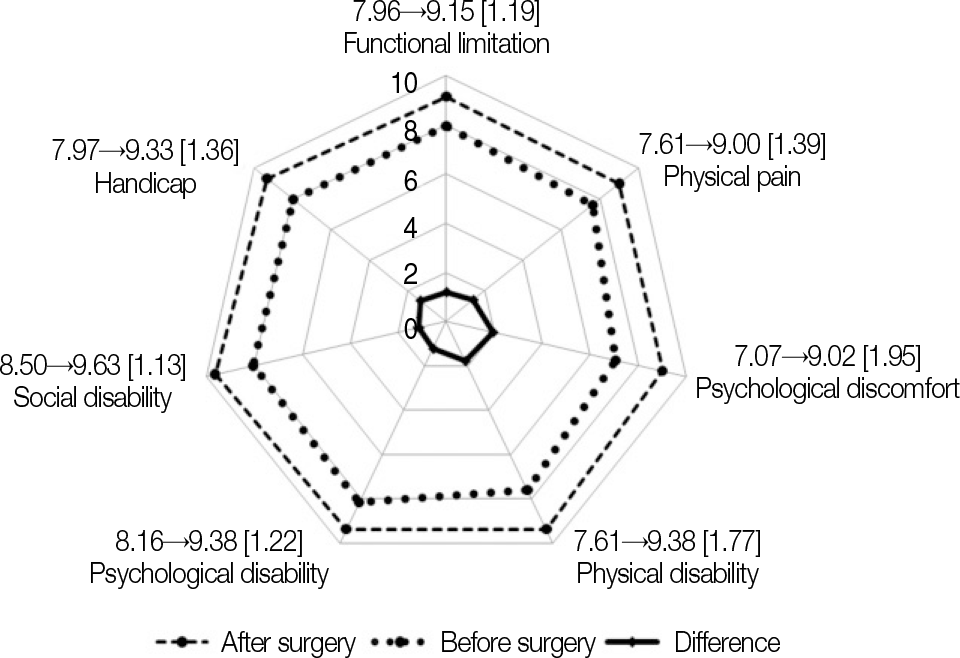 | Fig. 3.Oral health-related quality of life on seven categories related to functional limitation, physical pain, psychological discomfort, physical disability, psychological disability, social disability and handicap before and after implant surgery (The numerical values in brackets were differences of OHIP-14 score between before and after implant surgery). |
Table 1.
Questionnaires for measurement of treatment satisfaction given to patients 6 months after implant surgery
Table 2.
Questionnaires for measurement of oral health-related quality of life given to patients at the baseline and 6 months after implant surgery
Table 3.
Confirmatory factor analysis for patients’ satisfaction
Table 4.
Confirmatory factor analysis for oral health-related quality of life
Table 5.
Correlation matrix of components
| Function and aesthetics (FA) | Maintenance (MA) | Cost (CO) | OHRQoL (OQ) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Function and aesthetics (FA) | 1 | |||
| Maintenance (MA) | 0.461∗ | 1 | ||
| Cost (CO) | 0.053 | 0.115 | 1 | |
| OHRQoL (OQ) | 0.320∗ | 0.271∗ | 0.005 | 1 |
Table 6.
Estimation of structural equation models and hypothesis testing between patient satisfaction and OHRQoL after implant surgery




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download