Abstract
Purpose
The purposes of this study were to evaluate the stress distributions and the displacements of obturator for edentulous maxillectomy patients and to compare them with those of complete denture using three-dimensional finite element analysis.
Materials and methods
Based on the CT image of edentulous patient, three-dimensional finite element model of edentulous maxillae was constructed. Three-dimensional finite element model of edentulous maxillae with palatal defect was also fabricated. On each model, complete denture and obturator prosthesis were created. Vertical static force of 200 N was applied on the left maxillary premolar and molar region. The von Mises stress values and the displacements of models were analyzed using three-dimensional finite element analysis.
Results
Maximum von Mises stress values were recorded in the cortical bones of both models. The von Mises stress value in the complete denture model was 2.73 MPa and 2.69 MPa in the obturator model. High von Mises stress values were also observed on the tissue surface of prosthesis. The maximum value of the displacement in the obturator was higher than that of complete denture.
Conclusion
The obturator showed a worse result in terms of stress distribution and displacement than complete denture. In the prosthodontic rehabilitation of edentulous maxillectomy patient accurate impression procedure based on patients’ anatomy and application of prosthodontic principle should be considered. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2011;49:222-8)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.Beumer J., Curtis TA., Firtell DN. Maxillofacial Rehabilitation: Prosthetic and Surgical Considerations. St. Louis: CV Mosby;1979. p. 188–243.
3.Park KT., Kwon HB. The evaluation of the use of a delayed surgical obturator in dentate maxillectomy patients by considering days elapsed prior to commencement of postoperative oral feeding. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 96:449–53.
4.Fiebiger GE., Rahn AO., Lundquist DO., Morse PK. Movement of abutments by removable partial denture frameworks with a hemimaxillectomy obturator. J Prosthet Dent. 1975. 34:555–61.

5.Schwartzman B., Caputo A., Beumer J. Occlusal force transfer by removable partial denture designs for a radical maxillectomy. J Prosthet Dent. 1985. 54:397–403.

6.Schwartzman B., Caputo AA., Beumer J. Gravity-induced stresses by an obturator prosthesis. J Prosthet Dent. 1990. 64:466–8.

7.Lyons KM., Beumer J 3rd., Caputo AA. Abutment load transfer by removable partial denture obturator frameworks in different acquired maxillary defects. J Prosthet Dent. 2005. 94:281–8.

8.Glantz PO., Stafford GD. Clinical deformation of maxillary complete dentures. J Dent. 1983. 11:224–30.

9.Geng JP., Tan KB., Liu GR. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 2001. 85:585–98.
10.Sun J., Jiao T., Tie Y., Wang DM. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect. J Oral Rehabil. 2008. 35:695–9.

11.Parr GR., Tharp GE., Rahn AO. Prosthodontic principles in the framework design of maxillary obturator prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 62:205–12.

12.Rismanchian M., Bajoghli F., Mostajeran Z., Fazel A., Eshkevari P. Effect of implants on maximum bite force in edentulous patients. J Oral Implantol. 2009. 35:196–200.

13.Aramany MA. Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part I: classification. J Prosthet Dent. 1978. 40:554–7.

14.Sato Y., Abe Y., Okane H., Tsuga K. Finite element analysis of stress relaxation in soft denture liner. J Oral Rehabil. 2000. 27:660–3.

15.Rees JS., Huggett R., Harrison A. Finite element analysis of the stress-concentrating effect of fraenal notches in complete dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 1990. 3:238–40.
Go to : 
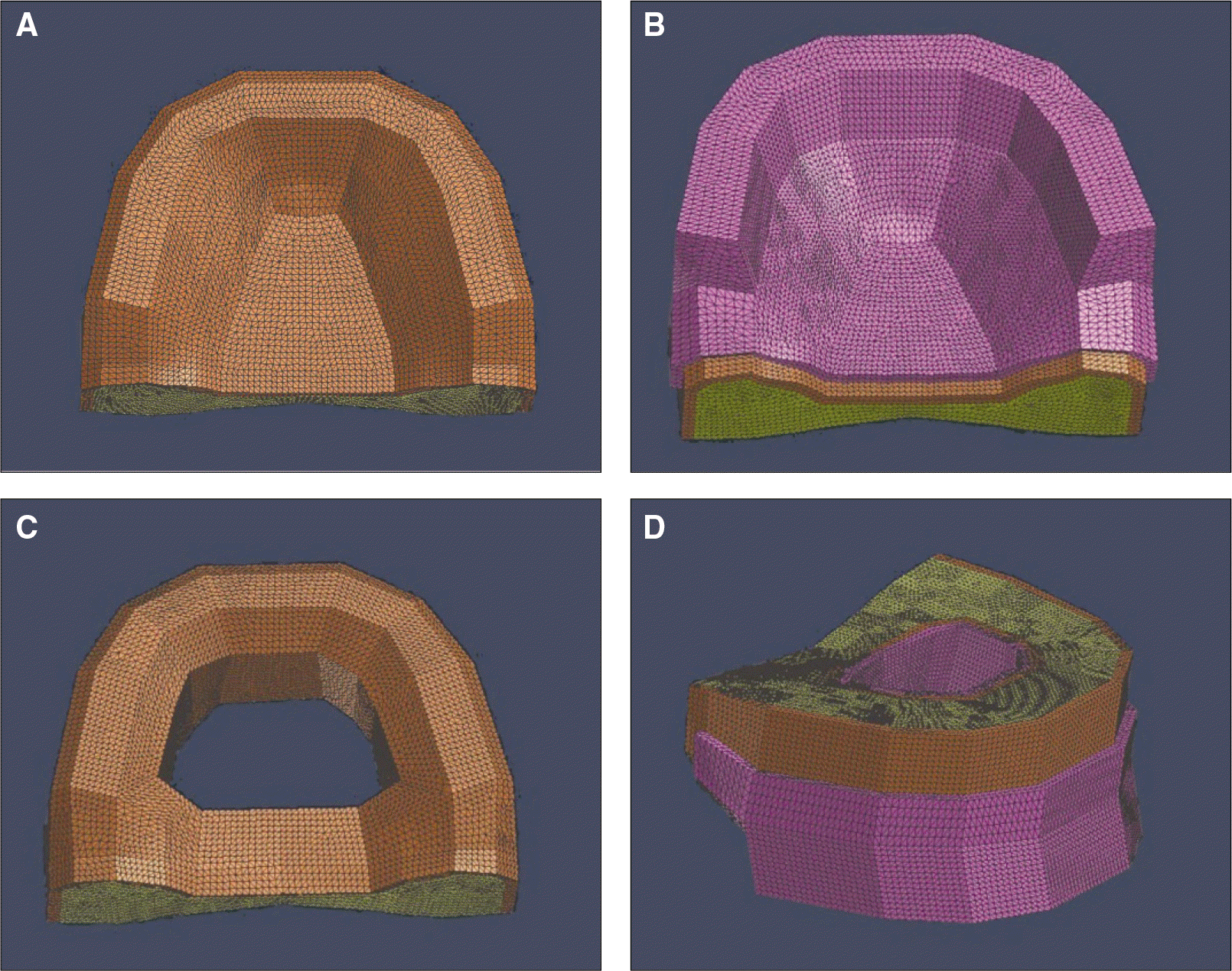 | Fig. 1.Geometries of the finite element models in this study. A: edentulous maxilla, B: maxillary complete denture, C: edentulous maxilla with palatal defect, and D: maxillary obturator. |
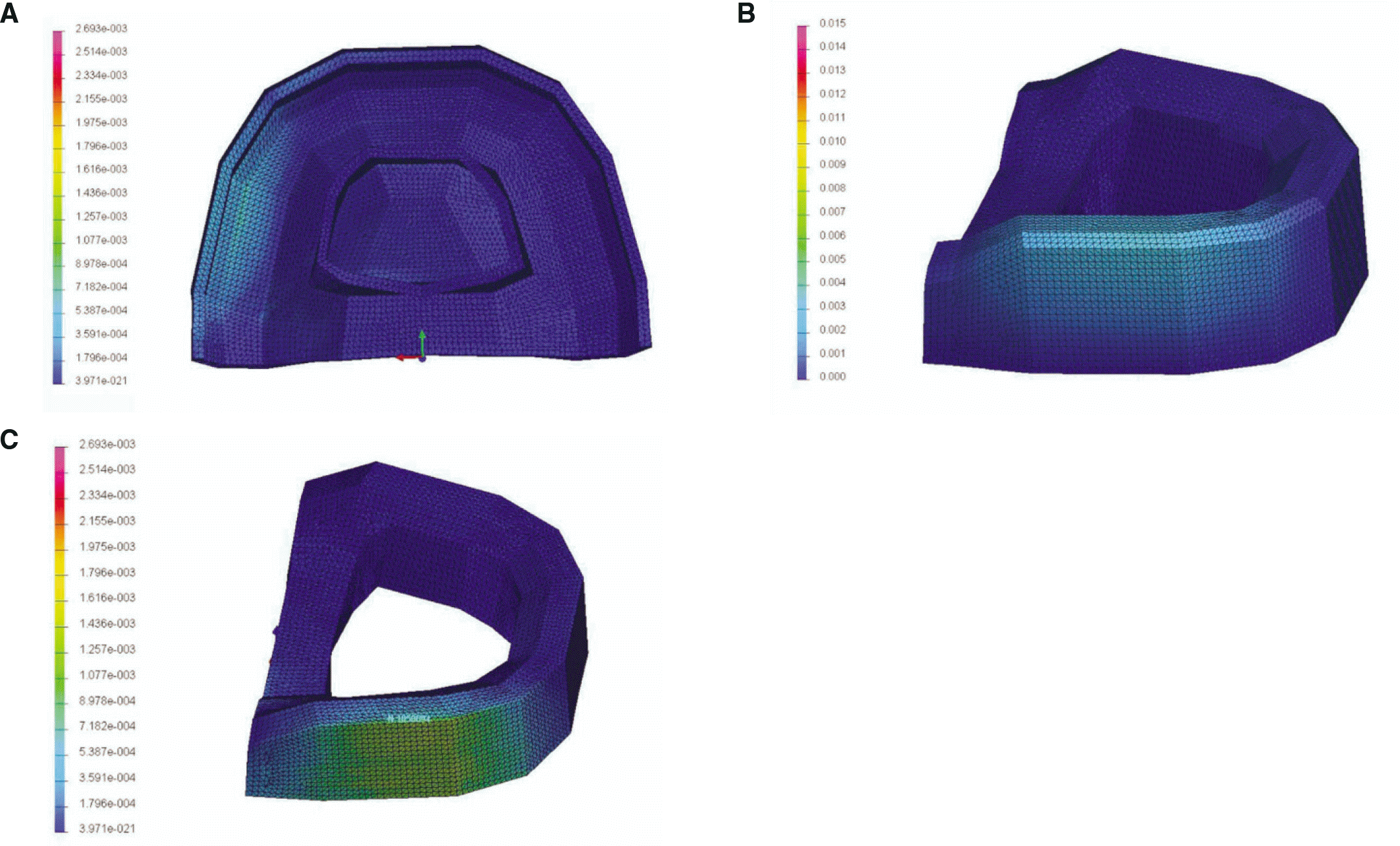 | Fig. 2.Contour plots of von Mises stress distribution in obturator model model (GPa). A: tissue surface of obturator, B: cortical bone, and C: cancellous bone. |
 | Fig. 3.Contour plots of displacement in the obturator prosthesis (mm). A: tissue surface of obturator, and B: cortical bone. |
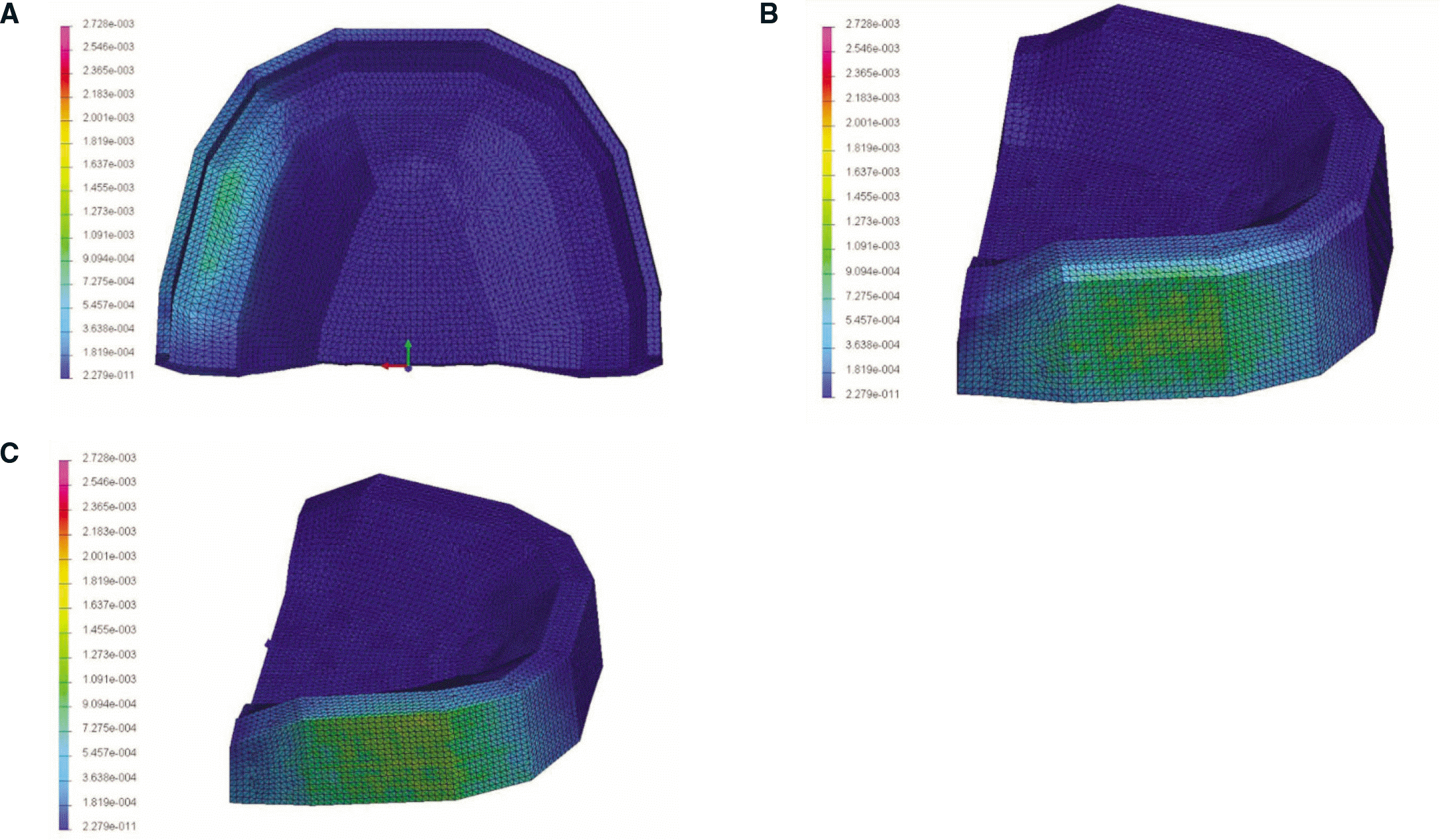 | Fig. 4.Contour plots of von Mises stress distribution in the complete denture model(GPa). A: tissue surface of complete denture, B: cortical bone, and C: cancellous bone. |
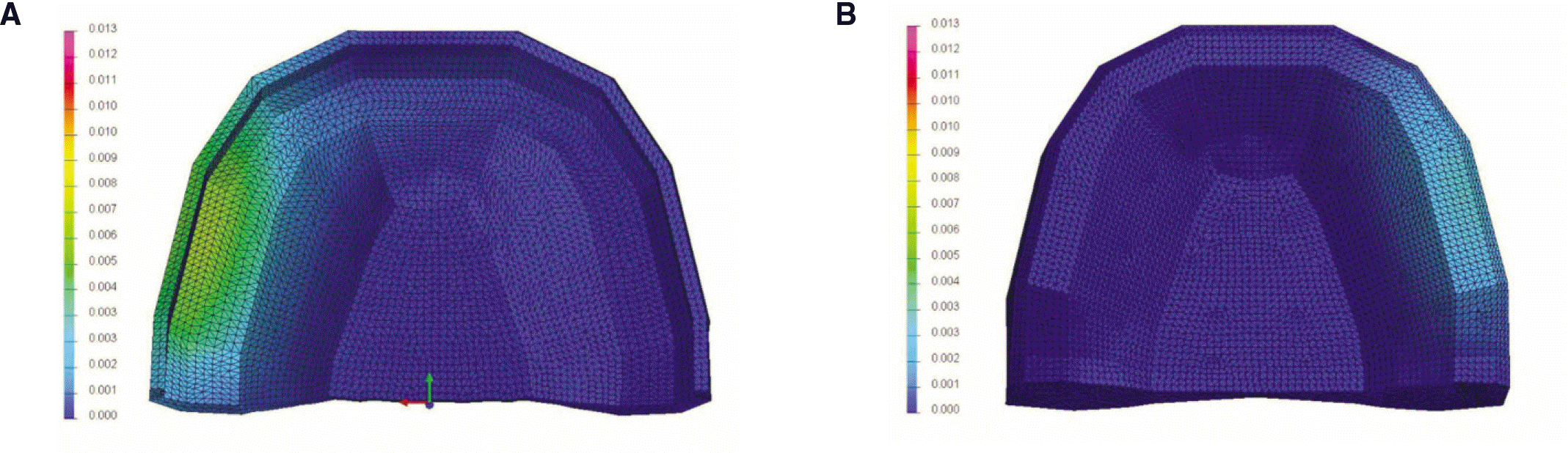 | Fig. 5.Contour plots of displacement in complete denture (mm). A: tissue surface of obturator, and B: cortical bone. |
Table 1.
Elements and nodes
Table 2.
Material's properties
| Material | Young's modulus (Gpa) | Poisson's ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Denture resin (PMMA) | 2.0 | 0.35 |
| Cortical bone | 14.0 | 0.30 |
| Cancellous bone | 1.5 | 0.45 |
| Mucosa | 0.003 | 0.45 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download