Abstract
Purpose
This article attempted to examine how teeth for restoration is made in a clinical practice and utilize it as future educational material of teeth formation and basic data for additional research.
Materials and methods
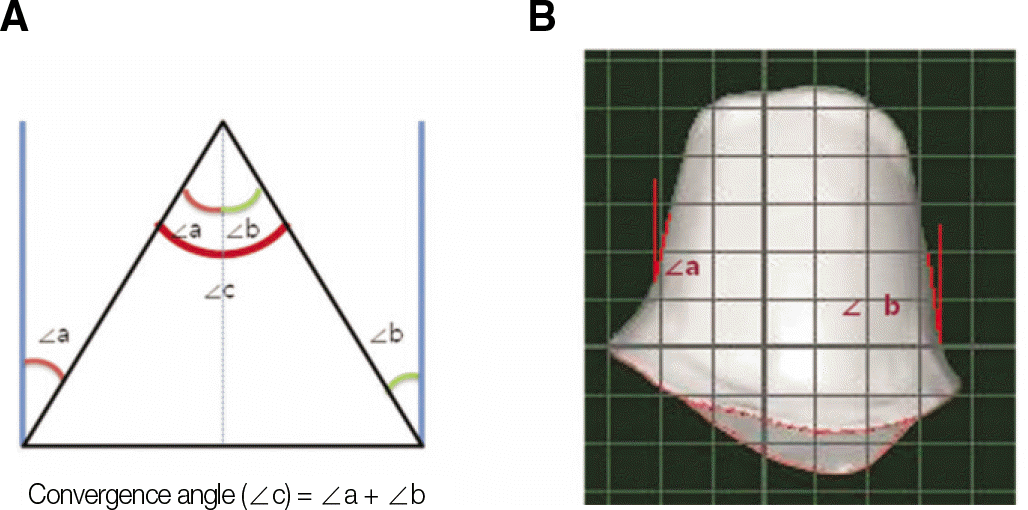
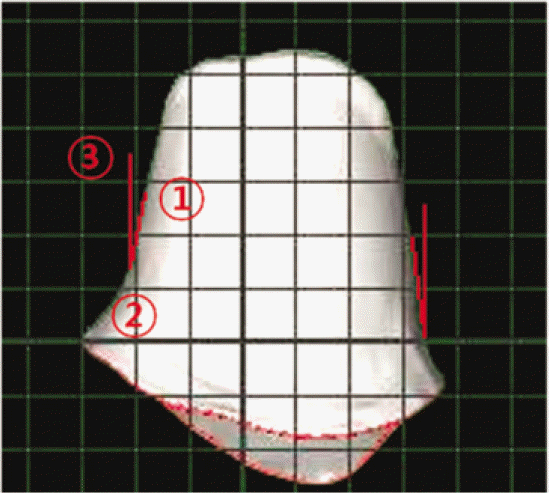
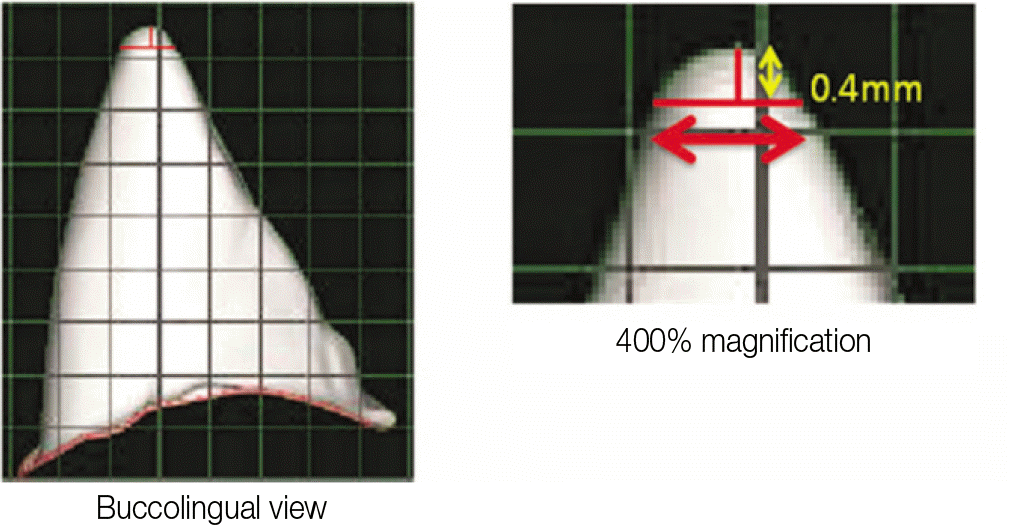
This experiment investigated the models sent to milling center for production of zirconia crowns. After scanned with Lava CAD/CAM System (3M ESPE, Seefeld, Germany), they are measured on ‘ImageJ (version 1.32j, National Institutes of Health, USA)’ program and compared and analyzed. Convergence angle from mesio-distal surfaces and bucco-lingual surfaces of each teeth are measured. Also, bucco-lingual diameter of the region lowered as much as 0.4 mm from incisal edge in anterior teeth except canines.(This measure is defined as the Peak 0.4) The analysis of data between each group was conducted by Windows SPSS statistic program, and was proved significant on 95% confidence level by independent t-test, one-way ANOVA and multiple analysis (Sheffe ′ test).
Results
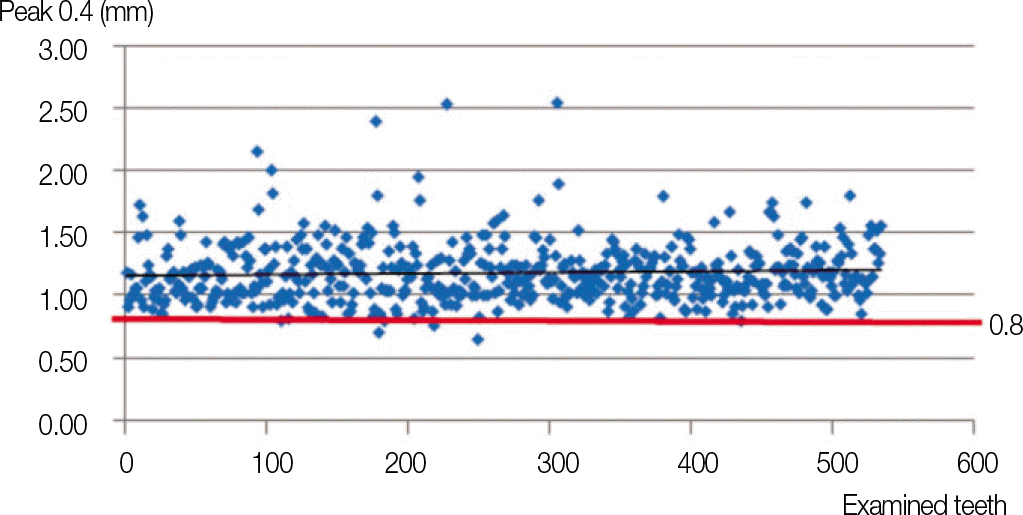
The mean value of convergence angle was 18.67° . It is ranked as molar (26.70°) > premolar (16.87°) > anterior teeth (14.81°) in the order of mesio-distal convergence angle; anterior teeth (22.32°) > molar (20.93°) > premolar (15.41°) in the order of bucco-lingual convergence angle. The mean value of Peak 0.4 was 1.18 mm.
Conclusion
Convergence angle of abutment of zirconia all ceramic crown has difference depending on the location in the arch. Due to the nature of production of zirconia all ceramic crown, convergence angle of abutment and line angle finishing degree can have an effect on internal suitability of restoration. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2011;49:22-8)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Seghi RR., Sorensen JA. Relative flexural strength of six new ceramic materials. Int J Prosthodont. 1995. 8:239–46.
2.Rekow ED. High-technology innovations-and limitations—for restorative dentistry. Dent Clin North Am. 1993. 37:513–24.
3.Oilo G., To¨rnquist A., Durling D., Andersson M. All-ceramic crowns and preparation characteristics: a mathematic approach. Int J Prosthodont. 2003. 16:301–6.
4.Prothero JH. Prosthetic dentistry. Medico-Dental Publishing Co.;1916. p. 1128.
5.Shillingburg HT Jr., Hobo S., Whitsett LD., Jacobi R., Brackett SE. Fundamentals of Fixed Prosthodontics. 3rd ed.Quintessence Publishing: IL;1997. p. 120–52.
6.Beuer F., Edelhoff D., Gernet W., Naumann M. Effect of preparation angles on the precision of zirconia crown copings fabricated by CAD/CAM system. Dent Mater J. 2008. 27:814–20.

7.3M ESPE. LavaTM Handling and preparation guidelines for dentists and labs. 2009.
8.Mack PJ. A theoretical and clinical investigation into the taper achieved on crown and inlay preparations. J Oral Rehabil. 1980. 7:255–65.

9.Kaufman EG., Coelho AB., Colin L. Factors influencing the retention of cemented gold castings. J Prosthet Dent. 1961. 11:486–502.

10.Annerstedt A., Engstro ¨m U., Hansson A., Jansson T., Karlsson S., Liljhagen H., Lindquist E., Rydhammar E., Tyreman-Bandhede M., Svensson P., Wandel U. Axial wall convergence of full veneer crown preparations. Documented for dental students and general practitioners. Acta Odontol Scand. 1996. 54:109–12.

11.Kim SJ., Pae AR., Woo YH., Kim HS. Clinical convergence angle of prepared tooth for full veneer crowns. J Dent Rehab Appl Sci. 2010. 26:21–32.
12.Iwai T., Komine F., Kobayashi K., Saito A., Matsumura H. Influence of convergence angle and cement space on adaptation of zirconium dioxide ceramic copings. Acta Odontol Scand. 2008. 66:214–8.

13.Ohm E., Silness J. The convergence angle in teeth prepared for artificial crowns. J Oral Rehabil. 1978. 5:371–5.

14.Leempoel PJ., Lemmens PL., Snoek PA., van't Hof MA. The convergence angle of tooth preparations for complete crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1987. 58:414–6.

15.Goodacre CJ., Campagni WV., Aquilino SA. Tooth preparations for complete crowns: an art form based on scientific principles. J Prosthet Dent. 2001. 85:363–76.

16.Kent WA., Shillingburg HT Jr., Duncanson MG Jr. Taper of clinical preparations for cast restorations. Quintessence Int. 1988. 19:339–45.
17.Nordlander J., Weir D., Stoffer W., Ochi S. The taper of clinical preparations for fixed prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent. 1988. 60:148–51.

18.Smith CT., Gary JJ., Conkin JE., Franks HL. Effective taper criterion for the full veneer crown preparation in preclinical prosthodontics. J Prosthodont. 1999. 8:196–200.

19.Kong SH., Woo YH. Accidental damage to teeth adjacent to prepared tooth. Masters thesis, Dept. of Dentistry, Graduate School, Kyung-Hee University, Seoul, Korea,. 2004.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Numbers of examined teeth with regard to tooth and dental arch
| Incisors/Canines | Premolars | Molars | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla | 373 | |||
| Right | 143 | 40 | 14 | 197 |
| Left | 132 | 37 | 7 | 176 |
| Mandible | 123 | |||
| Right | 18 | 29 | 27 | 74 |
| Left | 13 | 17 | 19 | 49 |
| Total | 306 | 123 | 67 | 496 |
Table 2.
Assessment of measurement reliability
| Incisors/Canines | Premolars | Molars | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 25.41 | 19.95 | 22.24 |
| Second | 26.02 | 19.77 | 21.99 |
Table 3.
Mean mesio-distal and bucco-lingual convergence angles of dies
| M-D | B-L | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 16.93 | 20.42 | 18.67 |
| SD | 8.04 | 9.35 | 8.89 |
| P | .000∗ |
Table 4.
Mean convergence angle of anteroposterior position of the teeth in arch
| M-D | B-L | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incisors/Canines | |||
| Mean | 14.81 | 22.32 | 18.57 |
| SD | 6.00 | 9.48 | 8.77 |
| Premolars | |||
| Mean | 16.87 | 15.41 | 16.14 |
| SD | 7.16 | 7.43 | 7.32 |
| Molars | |||
| Mean | 26.70 | 20.93 | 23.82 |
| SD | 10.27 | 8.66 | 9.89 |
Table 5.
Multiple comparison (Sheffe′test) of anteroposterior position of the teeth in arch
| M-D | B-L | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incisors/Canines - Premolars | |||
| P | .005∗ | .000∗ | .000∗ |
| Incisors/Canines Molars | |||
| P | .000∗ | .269 | .000∗ |
| Premolars Molars | |||
| P | .000∗ | .000∗ | .000∗ |
Table 6.
Mean convergence angle on maxilla and mandible
| M-D | B-L | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla (n = 373) | |||
| Mean | 16.01 | 21.24 | 18.62 |
| SD | 6.76 | 9.64 | 8.72 |
| Mandible (n = 123) | |||
| Mean | 19.72 | 17.95 | 18.84 |
| SD | 10.60 | 7.95 | 9.39 |
| P | .000∗ | .000∗ | .000∗ |
Table 7.
Mean convergence angle depending on right and left of arch
| M-D B-L | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Right (n = 271) | ||
| Mean | 17.14 21.05 | 19.09 |
| SD | 8.07 9.55 | 9.05 |
| Left (n = 225) | ||
| Mean | 16.67 19.66 | 18.17 |
| SD | 8.00 9.08 | 8.68 |
| P | 0.525 .100 | .103 |
Table 8.
Overall mean convergence angle depending on types of definitive prosthesis
| M-D | B-L | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zirconia | Metal-ceramic | Zirconia | Metal-ceramic | Zirconia | Metal-ceramic | |
| Mean | 16.93 | 16.91 | 20.42 | 16.19 | 18.67 | 16.55 |
| SD | 8.04 | 10.73 | 9.35 | 11.19 | 8.89 | 10.96 |
| P | .985 | .000∗ | .000∗ | |||
Table 9.
Mean convergence angle of incisors, premolars, and molars depending on types of definitive prosthesis
| M-D | B-L | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zirconia | Metal-ceramic | Zirconia | Metal-ceramic | Zirconia | Metal-ceramic | |
| Incisors/Canines | ||||||
| Mean | 14.81 | 12.14 | 22.32 | 17.71 | 18.57 | 14.51 |
| SD | 6.00 | 8.01 | 9.48 | 13.55 | 8.77 | 11.05 |
| P | .001∗ | .002∗ | .000∗ | |||
| Premolars | ||||||
| Mean | 16.87 | 14.01 | 15.41 | 12.15 | 16.14 | 12.75 |
| SD | 7.16 | 9.92 | 7.43 | 9.56 | 7.32 | 9.67 |
| P | 0.129 | .009∗ | .002∗ | |||
| Molars | ||||||
| Mean | 26.70 | 23.35 | 20.93 | 17.23 | 23.82 | 20.29 |
| SD | 10.27 | 10.52 | 8.66 | 9.11 | 9.89 | 10.29 |
| P | .037∗ | .008∗ | .001∗ | |||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download