Abstract
Purpose
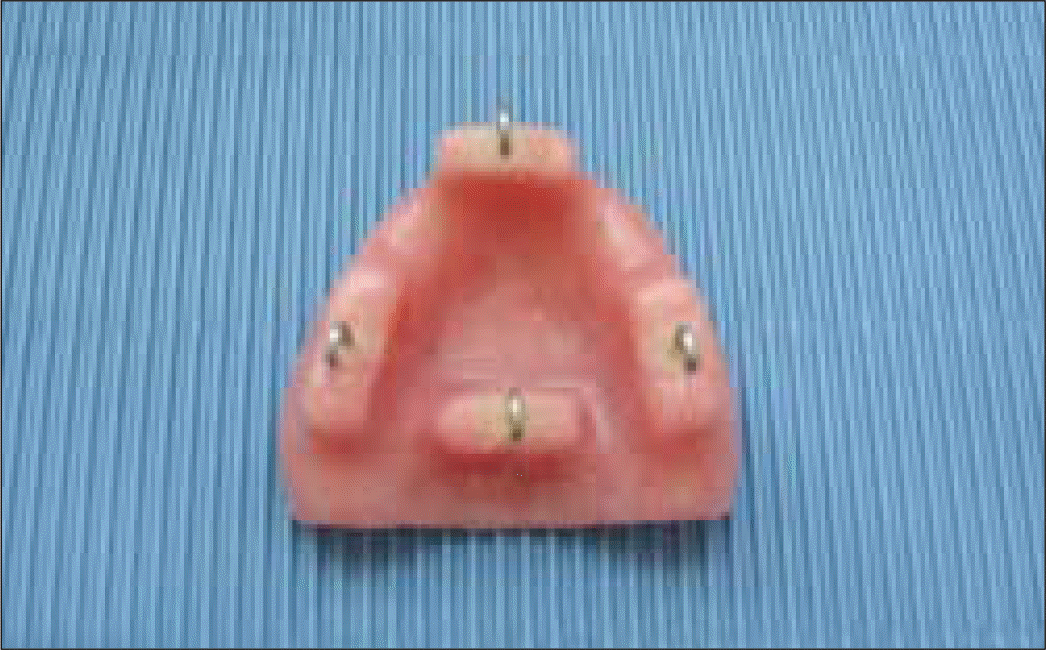
The purpose of this study was to compare the retention of the two denture adhesives with a silicone edentulous model and a resin denture base in vitro study.
Material and methods
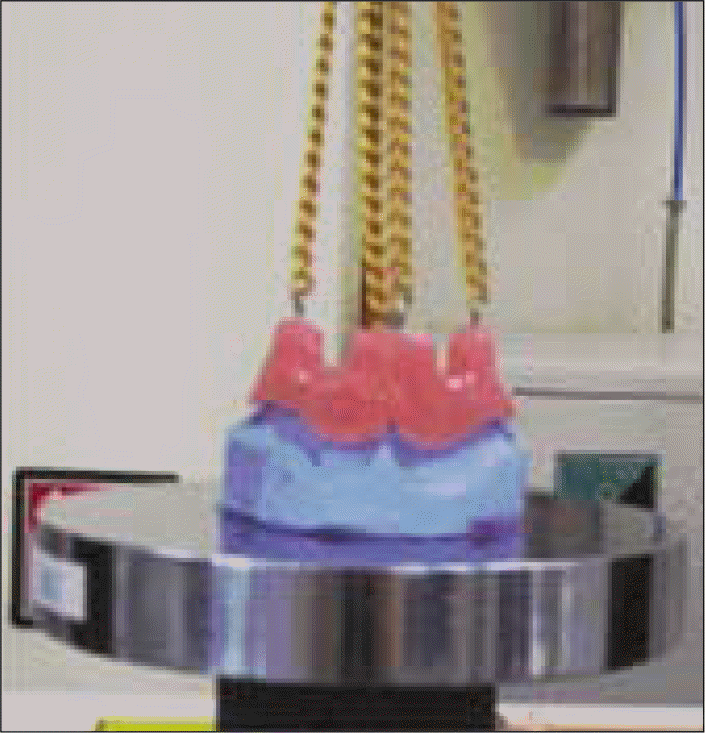
The experimental groups were used two denture adhesives and classified into 5 subgroups each. Subgroups were divided by the number of times the saliva sprayed. The control group was used synthetic saliva only. Dislodging tensile strengths were applied to the resin denture base using Instron in 3 directions : vertical, lateral, and anterior-posterior.
Results
The retention of two denture adhesives was increased significantly than saliva alone (P < .05). In each denture adhesives, the retention of saliva sprayed first was decreased than denture adhesive alone, but it didn't have significant differences. Whenever saliva sprayed repeated, the retention was decreased significantly than saliva sprayed first (P < .05). In each denture adhesives, vertical retentive force was highest than lateral and anterior-posterior retentive forces, and anterior-posterior retentive force was higher than lateral retentive force. This results were significantly different (P < .05). Significant differences of the retentive ability among two denture adhesives were not observed.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.Ozcan M., Kulak Y., Arikan A., Silahtar E. The attitude of complete denture wearers towards denture adhesives in Istanbul. J Oral Rehabil. 2004. 31:131–4.
5.Chew CL. Retention of denture adhesives-an in vitro study. J Oral Rehabil. 1990. 17:425–34.
6.Zarb GA., Bolender CL., Carlsson GE., Boucher CO. Boucher' s Prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients. 11th ed.St. Louis: CV Mosby;1997. p. 400–11.
7.Tarbet WJ., Silverman G., Schmidt NF. Maximum incisal biting force in denture wearers as influenced by adequacy of denture-bearing tissues and the use of an adhesive. J Dent Res. 1981. 60:115–9.

8.Tarbet WJ., Boone M., Schmidt NF. Effect of a denture adhesive on complete denture dislodgement during mastication. J Prosthet Dent. 1980. 44:374–8.

9.Ozcan M., Kulak Y., de Baat C., Arikan A., Ucankale M. The effect of a new denture adhesive on bite force until denture dislodgement. J Prosthodont. 2005. 14:122–6.

10.Kelsey CC., Lang BR., Wang RF. Examining patients' responses about the effectiveness of five denture adhesive pastes. J Am Dent Assoc. 1997. 128:1532–8.
11.Uysal H., Altay OT., Alparslan N., Bilge A. Comparison of four different denture cushion adhesives-a subjective study. J Oral Rehabil. 1998. 25:209–13.
13.de Baat C., van' t Hof M., van Zeghbroeck L., Ozcan M., Kalk W. An international multicenter study on the effectiveness of a denture adhesive in maxillary dentures using disposable gnathometers. Clin Oral Investig. 2007. 11:237–43.

14.Zhao K., Cheng XR., Chao YL., Li ZA., Han GL. Laboratory evaluation of a new denture adhesive. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:419–24.

15.Panagiotouni E., Pissiotis A., Kapari D., Kaloyannides A. Retentive ability of various denture adhesive materials: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 73:578–85.
16.Kulak Y., Ozcan M., Arikan A. Subjective assessment by patients of the efficiency of two denture adhesive pastes. J Prosthodont. 2005. 14:248–52.

17.Koppang R., Berg E., Dahm S., Real C., Fl � ystrand F. A method for testing denture adhesives. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 73:486–91.

18.Grasso JE., Rendell J., Gay T. Effect of denture adhesive on the retention and stability of maxillary dentures. J Prosthet Dent. 1994. 72:399–405.
19.Grasso J., Gay T., Rendell J., Baker R., Knippenberg S., Finkeldey J., Zhou X., Winston JL. Effect of denture adhesive on retention of the mandibular and maxillary dentures during function. J Clin Dent. 2000. 11:98–103.
20.Rendell JK., Gay T., Grasso JE., Baker RA., Winston JL. The effect of denture adhesive on mandibular movement during chewing. J Am Dent Assoc. 2000. 131:981–6.
21.Psillakis JJ., Wright RF., Grbic JT., Lamster IB. In practice evaluation of a denture adhesive using a gnathometer. J Prosthodont. 2004. 13:244–50.

22.Fujimori T., Hirano S., Hayakawa I. Effects of a denture adhesive on masticatory functions for complete denture wearers-consideration for the condition of denture-bearing tissues-. J Med Dent Sci. 2002. 49:151–6.
23.Hasegawa S., Sekita T., Hayakawa I. Effect of denture adhesive on stability of complete dentures and the masticatory function. J Med Dent Sci. 2003. 50:239–47.
Go to : 
Table I.
Denture adhesives used in this study
Table II.
Classification of the tested group
Table III.
Mean values of retentive forces on vertical direction (Unit: N/cm2)
| Abbr. | Mean | SD | Scheffe Grouping∗ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.30 | 0.02 | C |
| Px | 0.87 | 0.11 | A |
| P1 | 0.71 | 0.16 | B, A |
| P2 | 0.45 | 0.12 | B, C |
| P3 | 0.33 | 0.10 | C |
| P4 | 0.27 | 0.06 | C |
| Cx | 0.93 | 0.14 | A |
| C1 | 0.55 | 0.10 | B, C |
| C2 | 0.45 | 0.09 | B, C |
| C3 | 0.40 | 0.05 | C |
| C4 | 0.42 | 0.05 | C |
Table IV.
Mean values of retentive forces on lateral direction (Unit: N/cm2)
| Abbr. | Mean | SD | Scheffe Grouping∗ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.15 | 0.02 | D |
| Px | 0.35 | 0.05 | A |
| P1 | 0.28 | 0.03 | B, A, C |
| P2 | 0.20 | 0.04 | B, D, C |
| P3 | 0.18 | 0.04 | B, D, C |
| P4 | 0.18 | 0.04 | D, C |
| Cx | 0.28 | 0.02 | B, A |
| C1 | 0.27 | 0.05 | B, A, C |
| C2 | 0.23 | 0.01 | B, D, C |
| C3 | 0.23 | 0.03 | B, D, C |
| C4 | 0.20 | 0.05 | B, D, C |
Table V.
Mean values of retentive forces on anterior-posterior direction (Unit: N/cm2)
| Abbr. | Mean | SD | Scheffe Grouping∗ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.19 | 0.05 | A |
| Px | 0.35 | 0.06 | A |
| P1 | 0.30 | 0.08 | A |
| P2 | 0.22 | 0.10 | A |
| P3 | 0.21 | 0.08 | A |
| P4 | 0.20 | 0.09 | A |
| Cx | 0.33 | 0.07 | A |
| C1 | 0.37 | 0.06 | A |
| C2 | 0.38 | 0.11 | A |
| C3 | 0.32 | 0.10 | A |
| C4 | 0.30 | 0.07 | A |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download