Abstract
STATEMENT OF PROBLEM
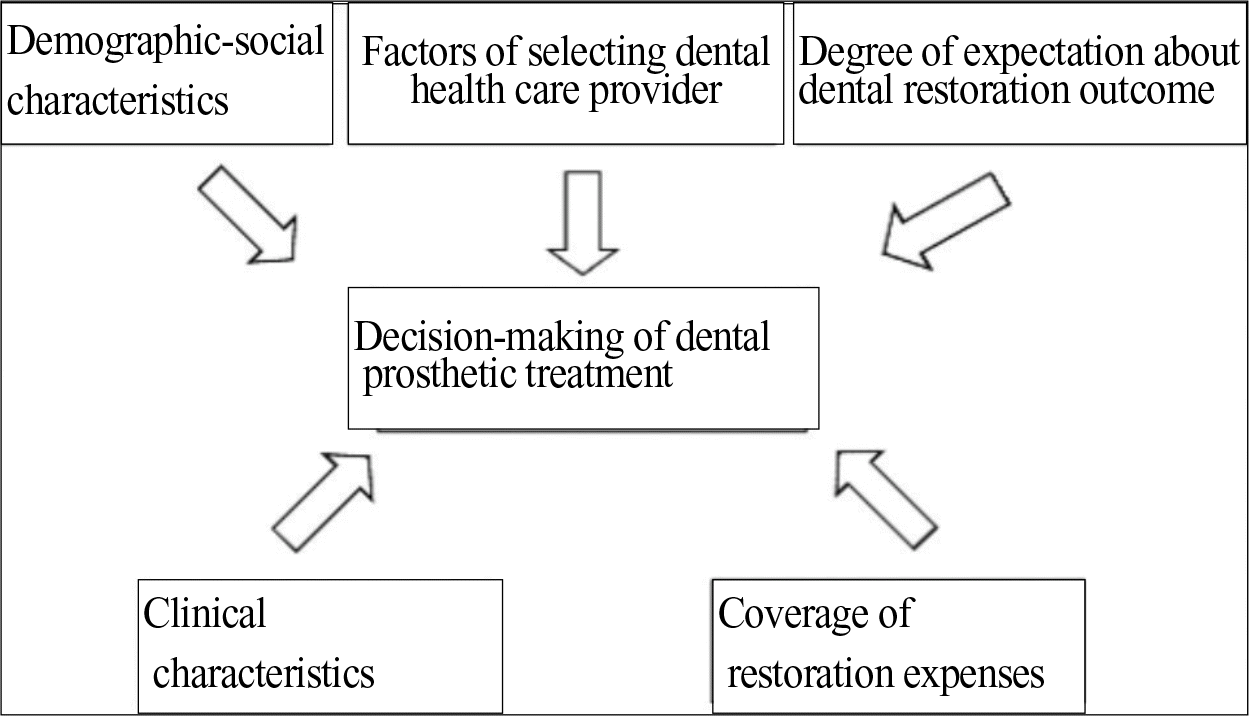
Factors affecting patients'decision-making for dental prosthetic treatment should be examined in terms of understanding improving patients'oral health.
PURPOSE
The main purpose of this dissertation was to investigate patients'dental prosthetic treatment and factors affecting patients'decision-making for dental prosthesis treatment in Deagu and Gyungbook areas.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This study was based on the preliminary survey of dental patients conducted from July 1 to August 31 in 2006. A total of 700 questionnaires had been distributed and 640 were collected. 629 questionnaires were used for the statistical analysis. Descriptive and inferential statistics, such as frequencies, cross tabulation analysis, correlation analysis, logistic regression analysis, and multiple regression analysis were introduced. In the multiple regression analysis and logistic regression analysis, twenty-two independent variables were employed to explore the factors which have impacts on decision-making and satisfaction.
RESULTS
The results of this dissertation are as follows: Logistic regression analysis turned out that monthly income, age, degree of expectation, marital status, and employer-insured policy of national insurance statistically increased the odds of decision-making of dental prosthesis treatment. But educational attainment decreased the odds ratio of the decision-making of dental prosthesis treatment. However, the rest independent variables do not have statistically significant impacts on the decision-making of dental prosthesis treatment
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Kim MA. A study on the Patient Satisfaction of Dental Outpatients of University Hospital. MA thesis, Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Youngnam University,. 2002.
2.Kim JS. Status of Dental Prosthetic Treatment in a Few Areas of Korea and Analysis of Related Factors. PhD thesis, Geimyoung University,. 2004.
3.Kim BO. Periodontology. Daehan Nara publishing;2004.
4.Sin SH. The Degree of Dental Caries and Related Factors in Children of an Elementary School. PhD thesis, Kyoungpook Univerisity,. 1989.
5.Lee HS. Object of Oral Health Education in School and Development of the Curriculum model. PhD thesis, Kyoung Nam University,. 2000.
6.Chang KY., Song GB., Lee CH., Cho GH. An Analysis on Dental Patients' Attitude and Satisfaction of the Treatment in Department of Prosthodontics, Kyoungpook University. Kor Acad Dent Health,. 1997. 21:605–20.
7.Choi WJ. Contemporary Public Oral Health,. Myoungmoon Publishing;2003.
8.Ivancevich JM. Stress and Work AM;. Foresman and Company;1980.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.Hypothetic research model about factors affecting decision-making of dental prosthetic treatment. |
Table I.
General characteristics of respondents N = 629
Table II.
Cross tabulation analysis between sex and decision-making of prosthetic treatment
Table III.
Cross tabulation analysis between age and prosthetic treatment
Table IV.
Cross tabulation analysis between marital status and decsion-making of prosthetic treatment
Table V.
Cross tabulation analysis between education and decision making of prosthetic treatment
Table VI.
Cross tabulation analysis between monthly income and decision-making of prosthetic treatment
Table VII.
Cross tabulation analysis between expectation and decision-making of prosthetic treatment
Table VIII.
Cross tabulation analysis of financial status and decision-making of prosthetic treatment
Table IX.
Logistic regression analysis of factors affecting decision-making of dental prosthetic treatment
| Characteristics | b | S.E. | Wald | Sig | Exp (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Income | 0.249 | 0.08 | 9.735 | 0.002∗∗ | 1.282 |
| Age | 0.05 | 0.011 | 19.13 | 0.000∗∗∗ | 1.051 |
| Sex (male = 1, female = 0) | 0.061 | 0.2 | 0.094 | 0.759 | 1.063 |
| Education | -0.09 | 0.043 | 4.451 | 0.035∗ | 0.914 |
| Marital status | 0.801 | 0.279 | 8.227 | 0.004∗∗ | 2.228 |
| (Married = 1, Unmarried = 0) | |||||
| Health status | -0.07 | 0.119 | 0.339 | 0.56 | 0.933 |
| Expectation | 0.272 | 0.129 | 4.443 | 0.035∗ | 1.312 |
| Dental insurance coverage | 0.353 | 0.2 | 3.128 | 0.077 | 1.424 |
| (employer covered = 1, other = 0) | |||||
| Financial status | 0.155 | 0.119 | 1.687 | 0.194 | 1.168 |
| Selection factor | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.072 | 0.789 | 1.003 |
| Constant | -3.939 | 1.277 | 9.517 | 0.002∗∗ | 0.019 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download