Abstract
STATEMENT OF PROBLEM
Proximal contact plays an important role in the stability and maintenance of the integrity of the dental arches. However, it is difficult to evaluate quantitatively the tightness of proximal tooth contact (TPTC).
MATERIAL AND METHODS
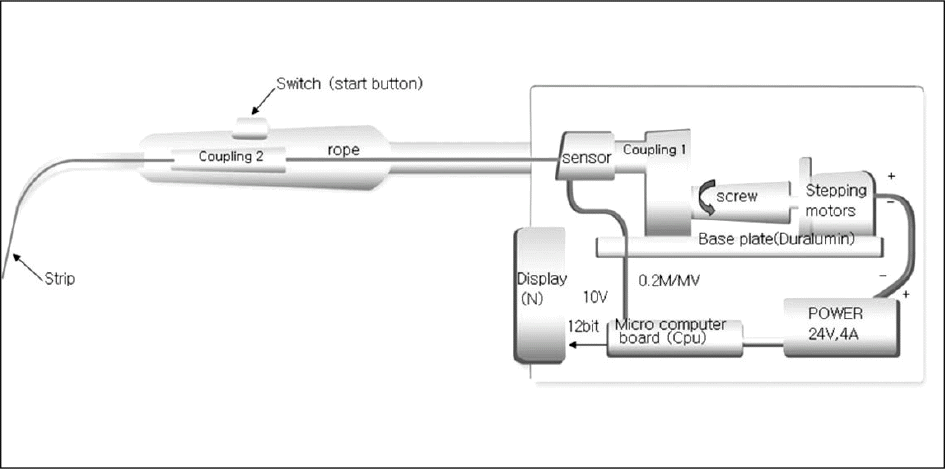
Ten young adult volunteers with healthy dentition participated in this experiment. The TPTC between the teeth of both the maxilla and the mandible was measured at rest state by a novel device which records the TPTC by pulling of a stainless steel strip (0.03 mm thick) using the electric motor. One-way ANOVA test was used to compare the values in all measured area. When a statistically significant difference was calculated, Bonferroni correction was applied. Independent samples t-test was used to compare the values in male and female.
RESULTS
The lowest TPTC and the highest TPTC was measured between the lower central incisors (0.87 ± 0.20 N), and between the lower left first molar and second molar (1.99 ± 0.68 N), respectively. All TPTC per quadrant demonstrated a similar pattern of a continuous increased gradient in an anterior-posterior direction. There are no significant difference between the maxilla and mandible.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.The academy of prosthodontics. The glossary of prostho-dontic terms 8th ed. (GPT-8) J Prosthet Dent. 2005. 94:46.
3.Wheeler RC. An atlas of tooth form,. 4th ed.Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co;1969. p. 12.
4.Sluder TB. Clinical dental anatomy, histology, physiology and occlusion. Studevant CM, editor. The art and science of operative dentistry,. 2nd ed.New York: McGraw-Hill;1985. p. 21.
5.Hirschfeld I. Food impaction. J Am Dent Assoc. 1930. 17:1504–28.
6.Gould MSE., Picton DCA. The relation between irregularities of the teeth and periodontal disease. Br Dent J. 1966. 121:20–3.
7.Hancock EB., Mayo CV., Schwab RR., Wirthlin MR. Influence of interdental contacts on periodontal status. J Periodontol. 1980. 51:445–9.

8.Nielson IM., Glavand L., Karring T. Interdental periodontal intrabony defects. Prevalence, localization and etiological factors. J Clin Periodontol. 1980. 7:187–98.
9.Jernberg GR., Bakdash MB., Keenan KM. Relationship between proximal tooth open contacts and periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1983. 54:529–33.

10.Vardimon AD., Matsaev E., Lieberman M., Brosh T. Tightness of dental contact points in spaced and non-spaced permanent dentitions. Eur J Orthod. 2001. 23:305–14.

11.Barnes DM., Blank LW., Thompson VP., Hoston AM., Gingell JC. A 5-and 8-year clinical evaluation of a posterior composite resin. Quintessence Int. 1991. 22:143–51.
12.Prakki A., Cilli R., Saad JOC., Rodrigues JR. Clinical evaluation of proximal contacts of Class II esthetic direct restoration. Quintessence Int. 2004. 35:785–9.
13.Campagni WV. The final touch in the delivery of a fixed prosthesis. CDA J. 1984. 12:21–9.
14.Lindquist JT. Thesis: A study of the intra-arch relationships in normal human dentitions, Indiana University School of Dentistry,. 1951.
15.Boice PA., Niles SM., Dubois LM. Evaluation of proximal contacts with shim stock. J Oral Rehabil. 1987. 14:91–4.

16.Dubois LM., Niles SM., Boice PA. The magnitude of interproximal spaces between adjacent teeth. Am J Dent. 1993. 6:315–7.

17.Osborn JW. An investigation into the interdental forces occurring between the teeth of the same arch during clenching the jaws. Arch Oral Biol. 1961. 5:202–11.

18.Southard TE., Southard KA., Tolley EA. Variation of approximal tooth contact tightness with postural change. J Dent Res. 1990. 69:1776–9.

19.Oh SH., Nakano M., Bando E., Keisuke N., Shigemoto S., Jeong JH., Kang DW. Relationship between occlusal tooth contact patterns and tightness of proximal tooth contact. J Oral Rehabil. 2006. 33:749–53.

20.Do ¨ rfer CE., von Bethlenfalvy ER., Staehle HJ., Pioch T. Factors influencing proximal dental contact strength. Eur J Oral Sci. 2000. 108:368–77.
21.Kasahara K., Miura H., Kuriyama M., Kato H., Hasegawa S. Observations of interproximal contact relations during clenching. Int J Prosthodont. 2000. 13:289–94.
22.Choi WJ., Kim KH., Kim JA., Knag DW., Oh SH. Evaluation and development of digital device for measuring proximal tooth contact tightness. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2007. 45:687–95.
23.Picton DC. Some implications of normal tooth mobility during mastication. Arch Oral Biol. 1964. 9:565–73.

24.Southard TE., Southard KA., Tolley EA. Periodontal force: a potential cause of relapse. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1992. 101:221–7.

25.Eissmann HF. Wax pattern fabrication. Eissmann HF, Rudd KD, Morrow RM, editors. Dental Laboratory Procedure-fixed partial denture. St. Louis, MO, USA: C.V. Mosby Co.;1980. p. 144–6.
26.Sturdevant JR. & Sturdevant CM. Gold inlay and gold onlay restoration for ClassII cavity preparations. Sturdevant C, Barton R, Sockwell C, Strickland W, editors. The Art and Science of Operative Dentistry. St. Louis, MO, USA: C.V. Mosby Co.;1985. p. 490.
27.Malone WFP., Koth DL., Cavazos E Jr., Kaiser DA., Morgano SM. Laboratory support for fixed prosthodontics. Gregore H, editor. Theory and Practice of Fixed Prosthodontics,. 8th ed.St. Louis, MO, USA: Ishiyaku EuroAmerica;1993. p. 288–9.
28.Ko ¨rber KH. Periodontal Pulsation. J Periodontol. 1970. 41:382–90.
29.Kato H. The function of the tooth supporting structures. Part I. A method of measuring tooth displacement in two dimensions. J Jpn Prosthodont Soc. 1981. 25:733–45.
30.Kato H. The function of the tooth supporting structures. Part II. The dynamics of molars in function and at rest. J Jpn Prosthodont Soc. 1982. 26:133–47.
31.Miura H. A measurement of the physiological tooth displacement in horizontal plane in function. J Jpn Prosthodont Soc. 1985. 29:735–54.
32.Miura H. A study on the interdental proximal contact relation. J Jpn Prosthodont Soc. 1985. 29:1134–42.

33.Oh SH., Nakano M., Bando E., Shigemoto S., Kori M. Evaluation of proximal tooth contact tightness at rest and during clenching. J Oral Rehabil. 2004. 31:538–45.

34.Fuhrmann R., Grave C., Diedrich P. In vitro evaluation of a measurement method to analyze the interdental, mesially directed force. J Orofacial Orthop. 1998. 59:362–70.

35.Proffit WR. Equilibrium theory revisited: factors influencing position of the teeth. Angle Orthod. 1978. 48:175–86.
36.Kiliaridis S., Johansson A., Haraldson T., Omar R., Carlsson GE. Craniofacial morphology, occlusal traits and bite force in persons with advanced occlusal tooth wear. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995. 107:286–92.

37.Waltimo A., Ko ¨ no ¨ nen M. A novel bite force recorder and maximal isometric bite force values for healthy young adults. Scan J Dent Res. 1993. 101:171–5.

38.Miyamoto K., Yamada K., Ishizuka Y., Morimoto N., Tanne K. Masseter muscle activity during the whole day in young adults. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996. 110:394–8.
39.Southard TE., Behrents RG., Tolley EA. The anterior component of occlusal force: Part I. Measurement and distribution. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989. 96:493–500.
40.Omar R., Wise MD. Mandibular flexure associated with muscle force applied in the retruded axis position. J Oral Rehabil. 1981. 8:209–21.

41.Korioth TWP., Versluis A., Beyer JP. Numerical simulation of approximal dental contact forces during clenching. J Dent Res. 1997. 76:245–50.
Go to : 
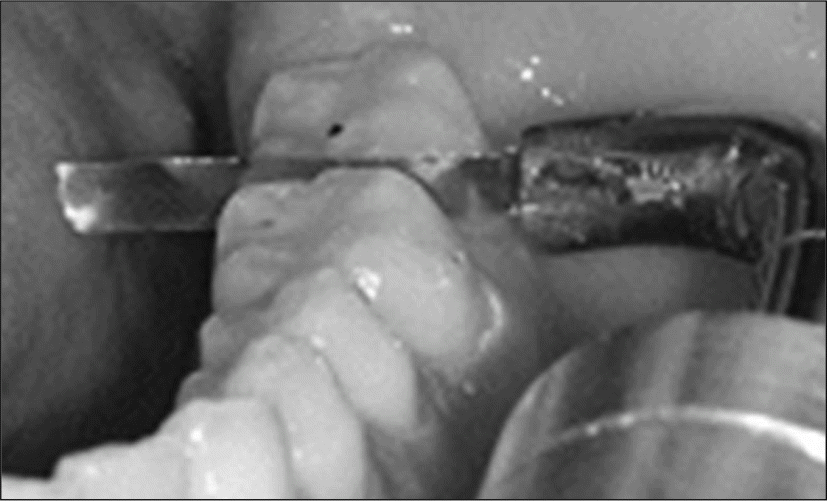 | Fig. 2.Measurement of the tightness of proximal tooth contact between the left first molar and second molar in mandible. |
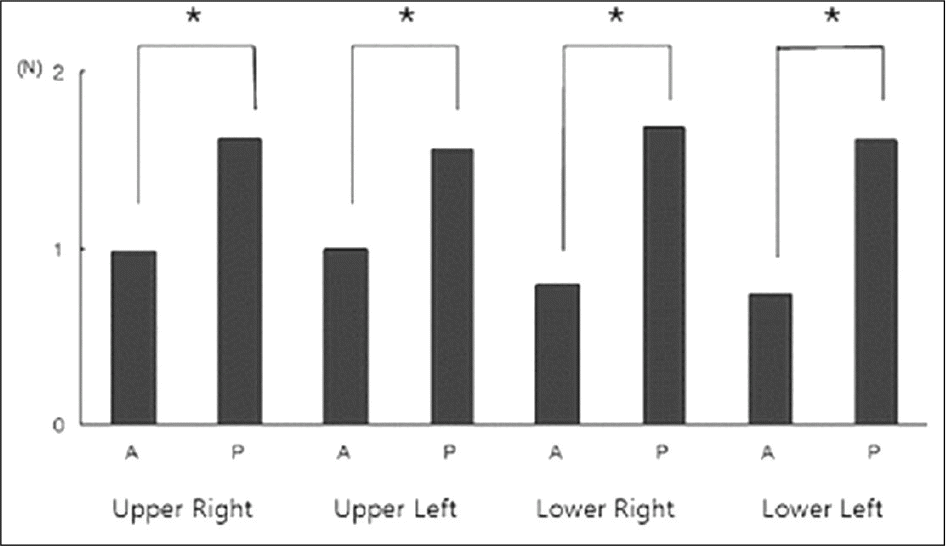 | Fig. 3.Comparison of the proximal contact tightness between anterior teeth (A: from mesial contact area of central incisor to mesial contact area of canine) and posterior teeth (P: from distal contact area of canine to mesial contact area of second molar). (∗P < .05, Independent samples t - test) |
Table I.
Tightness (N) of proximal tooth contact (left: maxilla, right: mandible)
Table II.
Tightness (N) of proximal tooth contact of male and female subjects in maxilla (∗P < .05, Independent samples t - test)
Table III.
Tightness (N) of proximal tooth contact of male and female subjects in mandible (∗P < .05, Independent samples t - test)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download