Abstract
Background
The main factor limiting the increase in brain dead organ donors is low consent rates for organ donation.
Methods
This study is a retrospective analysis of donor records of Korea Organ Donation Agency from 2013 to 2015. Factors related before providing information about organ donation and process of explaining organ donation were analyzed.
Results
Donor gender, marital status, religious affiliation, residence area, knowledge of patients' wishes, understanding of brain death status, and the referring system, providing initial information about donation and initial medical staff providing information about donation had a significant influence on decision to donate. Organ donation greatly increased when the donor family knew the patient's intent to donate. As the degree of family understanding of brain death status and the referring system increased, organ donation rate significantly increased.
Figures and Tables
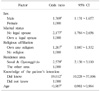
Table 4
Initial providing information about organ donation and the degree of family understanding (n=2,301)

References
1. Kim SC. Live organ transplants and autonomous decisions of patients: focusing on the discussions made in Japan. Law Rev. 2008; 29:125–158.
2. Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). KONOS waiting list [Internet]. Seoul: KONOS;2015. cited 2017 Aug 23. Available from: https://www.konos.go.kr.
3. IRODaT. Database [Internet]. Barcelona: IRODaT;2015. cited 2017 Aug 23. Available from: http://www.irodat.org/.
4. Siminoff LA, Gordon N, Hewlett J, Arnold RM. Factors influencing families' consent for donation of solid organs for transplantation. JAMA. 2001; 286:71–77.

5. Korea Organ Donation Agency (KODA). 2013 The referral of potential organ donors: KODA Annual Report. Seoul, KR: KODA;2013.
6. Korea Organ Donation Agency (KODA). 2014 The referral of potential organ donors: KODA Annual Report. Seoul, KR: KODA;2014.
7. Korea Organ Donation Agency (KODA). 2015 The referral of potential organ donors: KODA Annual Report. Seoul, KR: KODA;2015.
8. DeJong W, Franz HG, Wolfe SM, Nathan H, Payne D, Reitsma W, et al. Requesting organ donation: an interview study of donor and nondonor families. Am J Crit Care. 1998; 7:13–23.

9. Volz Wenger A, Szucs TD. Predictors of family communication of one's organ donation intention in Switzerland. Int J Public Health. 2011; 56:217–223.

10. Boulware LE, Ratner LE, Cooper LA, Sosa JA, LaVeist TA, Powe NR. Understanding disparities in donor behavior: race and gender differences in willingness to donate blood and cadaveric organs. Med Care. 2002; 40:85–95.

11. Brown CV, Foulkrod KH, Dworaczyk S, Thompson K, Elliot E, Cooper H, et al. Barriers to obtaining family consent for potential organ donors. J Trauma. 2010; 68:447–451.

12. Hong JJ. A study on experiences about organ donation of brain death donors' families [master's thesis]. Seoul, KR: Chung-Ang University;2001.
13. Hwangbo HM. A study on factors influencing families consent for donation of solid organs for transplantation [master's thesis]. Seoul, KR: Seoul National University;2004.
14. Franz HG, DeJong W, Wolfe SM, Nathan H, Payne D, Reitsma W, et al. Explaining brain death: a critical feature of the donation process. J Transpl Coord. 1997; 7:14–21.

15. Martinez JM, Lopez JS, Martin A, Martin MJ, Scandroglio B, Martin JM. Organ donation and family decision-making within the Spanish donation system. Soc Sci Med. 2001; 53:405–421.

16. Jeong YH. Factors associated with intention of family consent for organ donation by patients with brain death [dissertation]. Busan, KR: Inje University;2013.
17. Rodrigue JR, Cornell DL, Howard RJ. Organ donation decision: comparison of donor and nondonor families. Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:190–198.

18. Rodrigue JR, Cornell DL, Howard RJ. Does family disagreement affect donation decisions by next of kin? Prog Transplant. 2008; 18:179–184.

19. Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). Attitudes toward organ donation among the Public and Health care providers. Seoul, KR: KONOS;2009.
20. Schulz PJ, van Ackere A, Hartung U, Dunkel A. Prior family communication and consent to organ donation: using intensive care physicians' perception to model decision processes. J Public Health Res. 2012; 1:130–136.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download