Abstract
Background:
For various reasons, kidney transplant recipients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) often undergo native nephrectomy in preparation for the transplantation. Simultaneous nephrectomy can result in hypotensive events perioperatively and affect transplant outcome adversely. Our aim was to evaluate the effect of simultaneous native nephrectomy (SNx) on perioperative blood pressure and graft outcome compared to non-nephrectomy (NNx) in renal transplant recipients with ADPKD.
Methods:
Data regarding renal function and blood pressure were collected from 42 renal transplant recipients with ADPKD. The primary outcome was graft function over 1 year post-transplant. The secondary outcomes were patient and graft survival, postoperative hypotensive events, and blood pressure control. We compared units of antihypertensive medication used by transplanted ADPKD patients in the SNx and NNx groups.
Results:
Patients with SNx during kidney transplantation showed similar rates of patient and graft survival and renal function. Although they had significantly more hypotensive events during the perioperative period (69.2% vs. 37.5% in NNx, P=0.045), no harmful influence on renal function was observed. No difference in mean blood pressure during the 1-year post-transplant period was observed between the two groups; however, the SNx group required fewer units of antihypertensive medication.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Goncalves S., Guerra J., Santana A., Abreu F., Mil-Homens C., Gomes da Costa A. Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease and kidney transplantation: experience of a single center. Transplant Proc. 2009. 41:887–90.
2). Jin DC. Current status of dialysis therapy for ESRD patients in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013. 56:562–8. (진동찬. 우리 나라 말기신부전 환자의 투석현황. 대한의사협회지 2013;56: 562-8.).

3). Kirkman MA., van Dellen D., Mehra S., Campbell BA., Tavakoli A., Pararajasingam R, et al. Native nephrectomy for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: before or after kidney transplantation? BJU Int. 2011. 108:590–4.

4). Tabibi A., Simforoosh N., Abadpour P., Gholamrezaie HR., Nafar M. Concomitant nephrectomy of massively enlarged kidneys and renal transplantation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Transplant Proc. 2005. 37:2939–40.

5). Fuller TF., Brennan TV., Feng S., Kang SM., Stock PG., Freise CE. End stage polycystic kidney disease: indications and timing of native nephrectomy relative to kidney transplantation. J Urol. 2005. 174:2284–8.

6). Skauby MH., Oyen O., Hartman A., Leivestad T., Wadstrom J. Kidney transplantation with and without simultaneous bilateral native nephrectomy in patients with polycystic kidney disease: a comparative retrospective study. Transplantation. 2012. 94:383–8.
7). Song WL., Zheng JM., Mo CB., Wang ZP., Fu YX., Feng G, et al. Kidney transplant for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the superiority of concurrent bilateral nephrectomy. Urol Int. 2011. 87:54–8.

8). Drognitz O., Kirste G., Schramm I., Assmann A., Pohl M., Gobel H, et al. Kidney transplantation with concomitant unilateral nephrectomy: a matched-pair analysis on complications and outcome. Transplantation. 2006. 81:874–80.

9). Sulikowski T., Tejchman K., Zietek Z., Rozanski J., Domanski L., Kaminski M, et al. Experience with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in patients before and after renal transplantation: a 7-year observation. Transplant Proc. 2009. 41:177–80.

10). Brazda E., Ofner D., Riedmann B., Spechtenhauser B., Margreiter R. The effect of nephrectomy on the outcome of renal transplantation in patients with polycystic kidney disease. Ann Transplant. 1996. 1:15–8.
11). Alam A., Perrone RD. Management of ESRD in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010. 17:164–72.

12). Abramowicz D., Cochat P., Claas FH., Heemann U., Pascual J., Dudley C, et al. European Renal Best Practice Guideline on kidney donor and recipient evaluation and perioperative care. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015. 30:1790–7.
13). Medina A., Bell PR., Briggs JD., Brown JJ., Fine A., Lever AF, et al. Changes of blood pressure, renin, and angiotensin after bilateral nephrectomy in patients with chronic renal failure. Br Med J. 1972. 4:694–6.

14). Cohen SL. Hypertension in renal transplant recipients: role of bilateral nephrectomy. Br Med J. 1973. 3:78–81.

15). Rozanski J., Kozlowska I., Myslak M., Domanski L., Sienko J., Ciechanowski K, et al. Pretransplant nephrectomy in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Transplant Proc. 2005. 37:666–8.

Go to : 
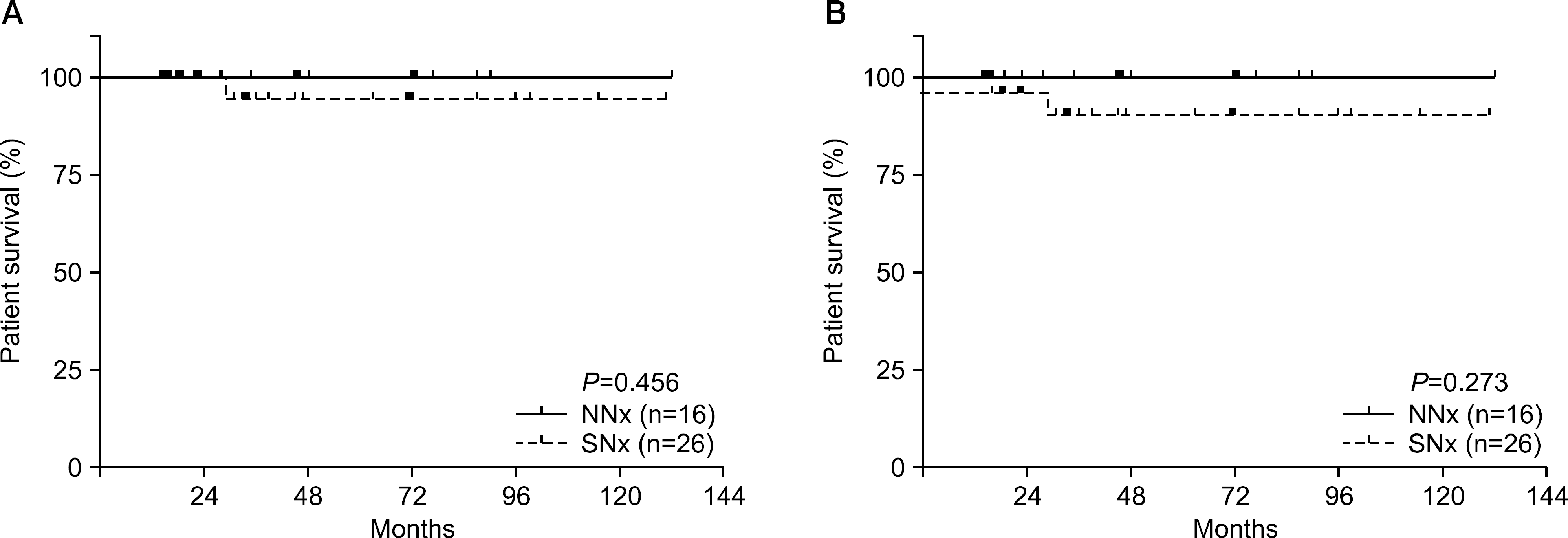 | Fig. 1.Kaplan-Meier curves for (A) patient survival and (B) graft survival between non-nephrectomy (NNx, n=16) and simultaneous native nephrectomy (SNx, n=26) groups. P-value is estimated by log-rank test. |
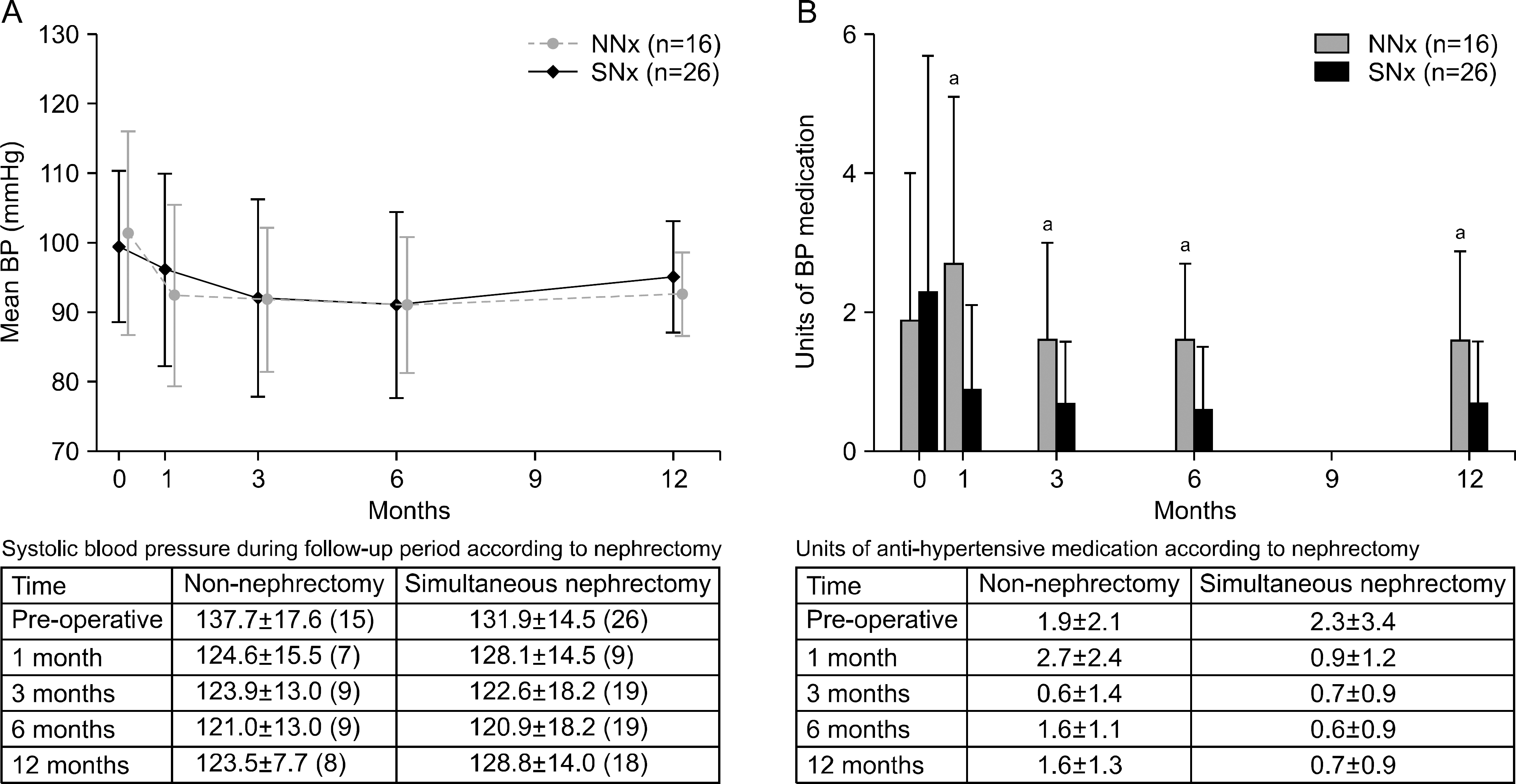 | Fig. 2.(A) Mean blood pressure (BP; mmHg, mean±SD [total no.]) and (B) units of antihypertensive medication during follow-up period after nephrectomy. Abbreviations: NNx, non-nephrectomy; SNx, simultaneous native nephrectomy. aP<0.05. |
Table 1.
Baseline demographic and transplant-related characteristics
Table 2.
Perioperative clinical outcomes
Table 3.
Demographic and transplant-related characteristics related to hypotensive events in the simultaneous native nephrectomy group
Supplementary Table 1.
Renal function outcomes related to hypotensive events in recipients with simultaneous nephrectomy




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download