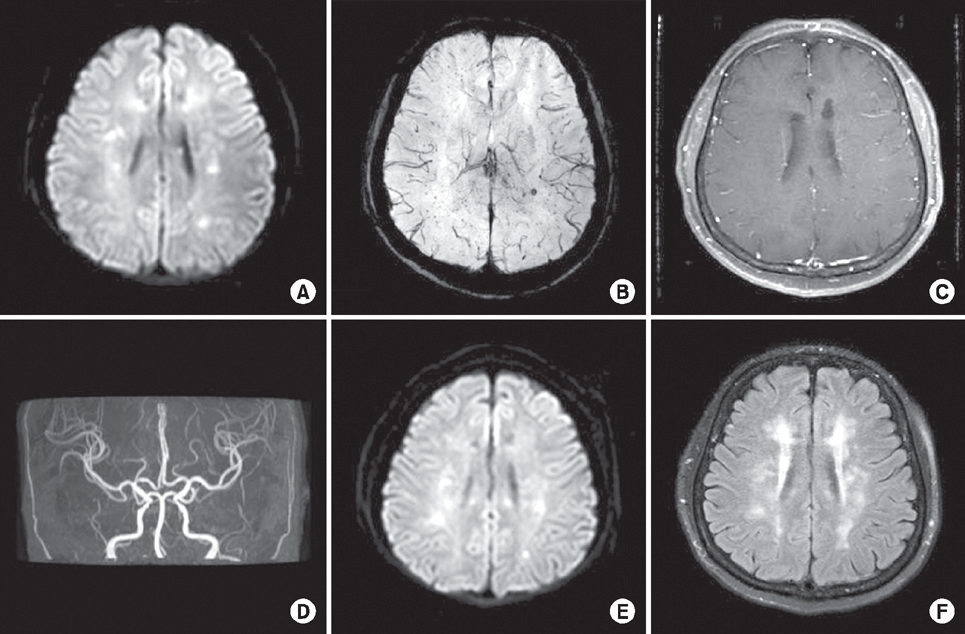
 | Fig. 1.Initial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including (A) diffusion-weighted sequence and (B) susceptibility-weighted sequence shows multiple infarctions involving bilateral corona radiata. (C) Enhanced T1-weighted image and (D) intracranial angiography are normal. Follow-up MRI on re-admission shows (E) recurred acute infarctions involving brain stem and bilateral subcortical white matters from diffusion-weighted sequence and (F) increased white matter changes from fluid attenuated inversion recovery sequence. |
Abstract
Tacrolimus is the most commonly used immunosuppressant after kidney transplantation. Here, we report a patient with multiple cerebral infarctions during tacrolimus treatment after kidney transplantation. A 54-year-old female was admitted due to sudden onset right leg weakness. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed multiple acute infarctions but normal vasculature. Evaluations of cardiac embolism were unremarkable. After 8 months, her weakness progressed and follow-up brain MRI showed additional multiple infarctions. We changed here medication from tacrolimus to mycophenolate mofetil, and her symptoms improved gradually.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Kim Y, Lee SH, Lee DW, Jung H, Oh TS, Kim MJ, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome improved by changing immunosuppressant from calcineurin inhibitor to sirolimus in a kidney transplantation recipient. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2015; 29:166–9.

2. Wu Q, Marescaux C, Wolff V, Jeung MY, Kessler R, Lauer V, et al. Tacrolimus-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after solid organ transplantation. Eur Neurol. 2010; 64:169–177.

3. Chegounchi M, Hanna MG, Neild GH. Progressive neurological disease induced by tacrolimus in a renal transplant recipient: case presentation. BMC Nephrol. 2006; 7:7.

4. Senzolo M, Ferronato C, Burra P. Neurologic complications after solid organ transplantation. Transpl Int. 2009; 22:269–278.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download