Abstract
Background:
In this era of donor shortage, use of organs from living donors has increased significantly. Nonetheless, less than 1% of pancreas transplantations involve living donors, despite the immunological benefits, reduced cold ischemic time, and decreased waiting time. One reason for the paucity of donors is the high morbidity after open surgery. Using hand-assisted laparo-scopic donor surgery (HALDS) can be a favorable technique for living donors.
Methods:
Using HALDS, we performed three Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantations (SPKs) involving living donors. Two donors were women; one was a man.
Results:
Their mean age was 34.3±4.7 years, and their body mass index was 23.2±2.36 kg/m2. The mean operation time was 241±19.0 minutes and the mean cold-ischemic time of the kidney was 42.7±9.8 minutes, while that of the pancreas was 64.3±5.2 minutes. One donor developed a pancreatic fistula, which was controlled using conservative management. The donors’ pancreatic and renal functions were well preserved postoperatively.
REFERENCES
1). You WP., Henneberg M. Type 1 diabetes prevalence increasing globally and regionally: the role of natural selection and life expectancy at birth. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2016. 4:e000161.

2). Sutherland DE., Gruessner RW., Dunn DL., Matas AJ., Humar A., Kandaswamy R, et al. Lessons learned from more than 1,000 pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann Surg. 2001. 233:463–501.

3). Zielinski A., Nazarewski S., Bogetti D., Sileri P., Testa G., Sankary H, et al. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant from living related donor: a single-center experience. Transplantation. 2003. 76:547–52.
4). Sutherland DE., Radosevich D., Gruessner R., Gruessner A., Kandaswamy R. Pushing the envelope: living donor pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2012. 17:106–15.
5). Sutherland DE., Goetz FC., Najarian JS. Living-related donor segmental pancreatectomy for transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1980. 12(4 Suppl 2):19–25.
6). Reynoso JF., Gruessner CE., Sutherland DE., Gruessner RW. Short- and long-term outcome for living pancreas donors. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010. 17:92–6.

7). Wolf JS Jr., Tchetgen MB., Merion RM. Hand-assisted laparo-scopic live donor nephrectomy. Urology. 1998. 52:885–7.

8). Gruessner RW., Kandaswamy R., Denny R. Laparoscopic simultaneous nephrectomy and distal pancreatectomy from a live donor. J Am Coll Surg. 2001. 193:333–7.
9). Gruessner RW., Sutherland DE., Drangstveit MB., Bland BJ., Gruessner AC. Pancreas transplants from living donors: short- and long-term outcome. Transplant Proc. 2001. 33:819–20.

10). Kim J., Zimmerman MA. Technical aspects for live-donor organ procurement for liver, kidney, pancreas, and intestine. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2015. 20:133–9.

11). Pruett TL., Tibell A., Alabdulkareem A., Bhandari M., Cronin DC., Dew MA, et al. The ethics statement of the Vancouver Forum on the live lung, liver, pancreas, and intestine donor. Transplantation. 2006. 81:1386–7.

12). Gruessner RW., Leone JP., Sutherland DE. Combined kidney and pancreas transplants from living donors. Transplant Proc. 1998. 30:282.

13). Tan M., Kandaswamy R., Sutherland DE., Gruessner RW. Laparoscopic donor distal pancreatectomy for living donor pancreas and pancreas-kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2005. 5:1966–70.

14). Slakey DP., Wood JC., Hender D., Thomas R., Cheng S. Laparoscopic living donor nephrectomy: advantages of the hand-assisted method. Transplantation. 1999. 68:581–3.
15). Lindstrom P., Haggman M., Wadstrom J. Hand-assisted lapa-roscopic surgery (HALS) for live donor nephrectomy is more time- and cost-effective than standard laparoscopic nephrectomy. Surg Endosc. 2002. 16:422–5.

16). Matsumoto I., Shinzeki M., Asari S., Goto T., Shirakawa S., Ajiki T, et al. Evaluation of glucose metabolism after distal pancreatectomy according to the donor criteria of the living donor pancreas transplantation guidelines proposed by the Japanese Pancreas and Islet Transplantation Association. Transplant Proc. 2014. 46:958–62.

Fig. 2.
Exposed vessels during hand-assisted laparoscopic donor surgery. (A) Exposed renal artery and vein. (B) Splenic artery and vein were exposed when the pancreatic tail was lifted up using dissector and 2nd finger of operator.
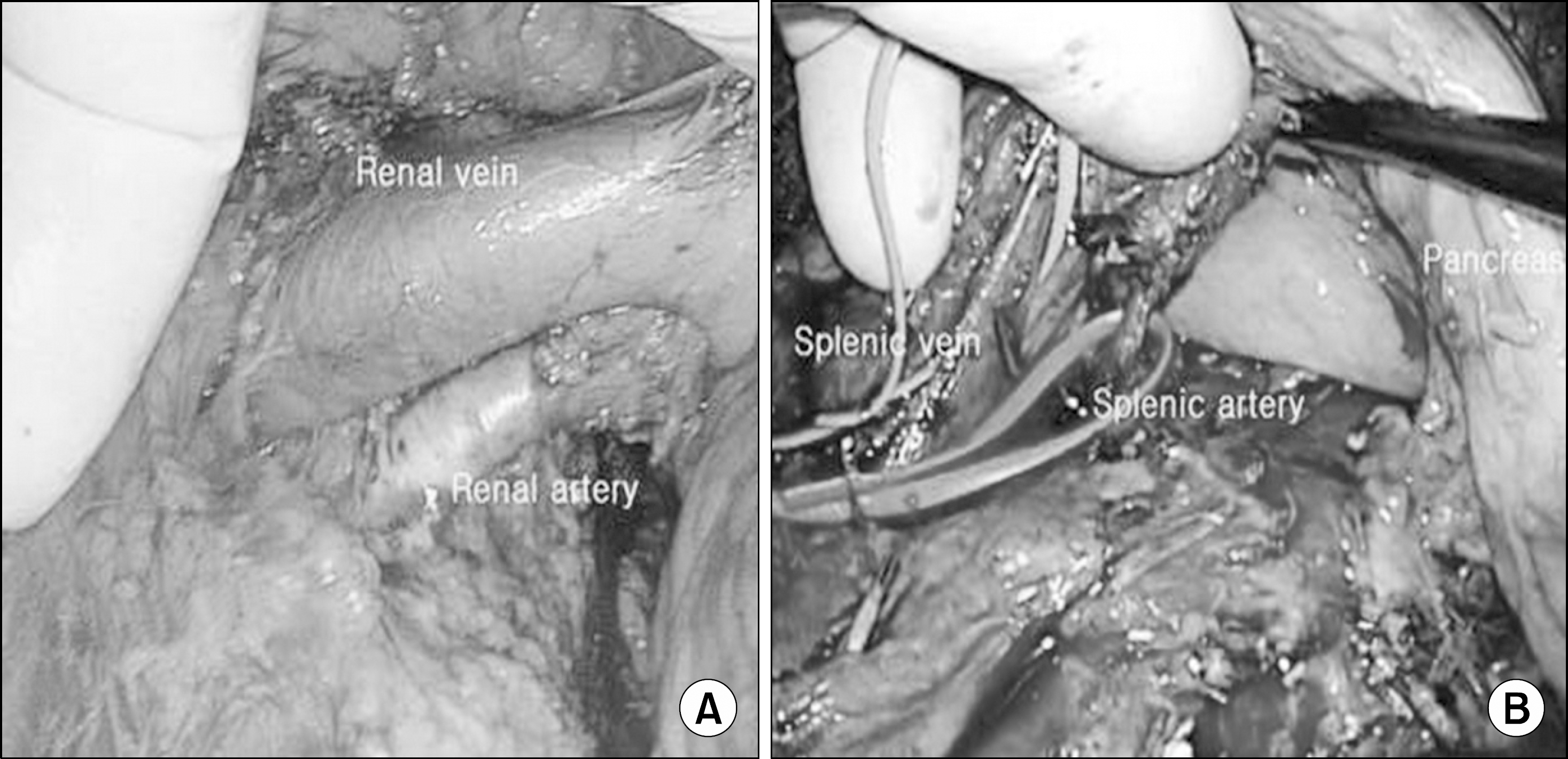
Fig. 3.
Benching of the pancreas graft. (A) Cold perfusion with preservation solution right after the pancreas brought out from the living donor. (B) Pancreas graft after completing benching.
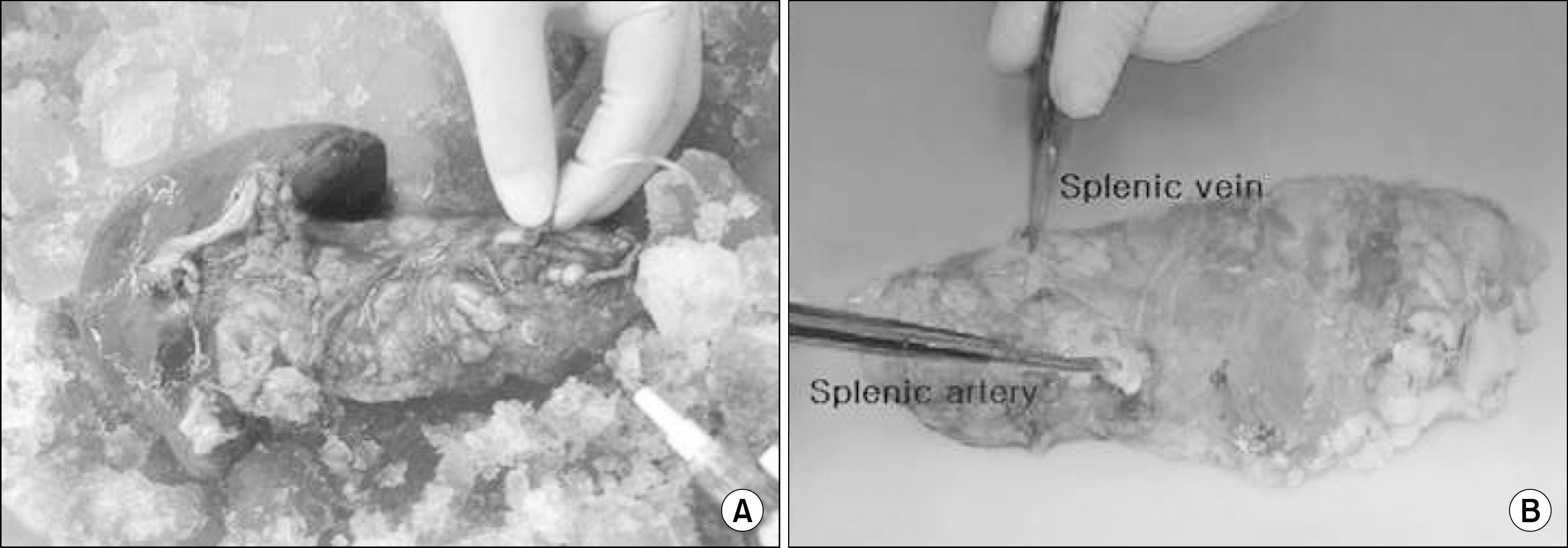
Fig. 4.
Abdominopelvic computer tomography. (A) Horizontal view. (B) Coronal view. Arrows indicate a cystic mass (pseudocyst) at the pancreatectomy site.
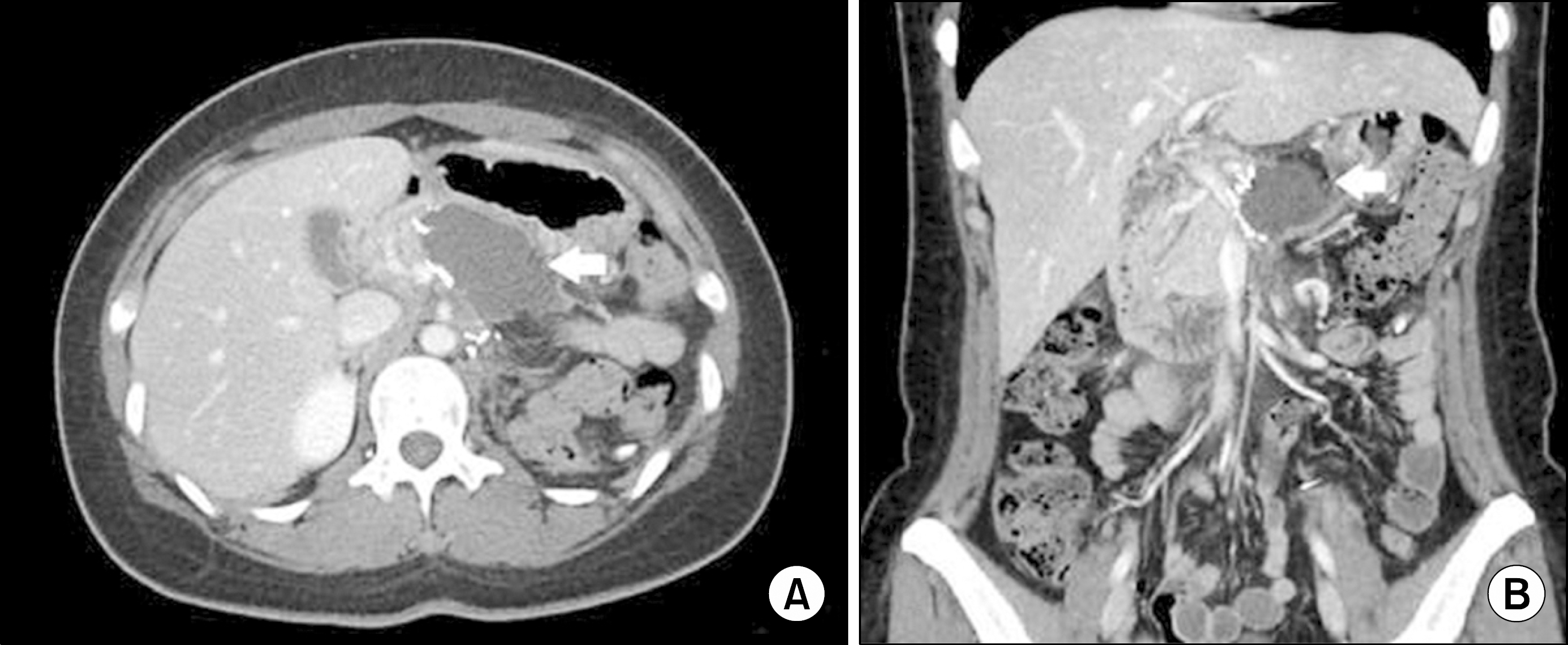
Table 1.
Characteristics and clinical outcomes of donors




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download