Abstract
Background
While the number of deceased donor donations has increased in Korea, the organ shortage remains a major limitation for kidney transplantation. Donation after circulatory death (DCD) can be an option to expand the donor pool. In this study we evaluated the short and long term survival of grafts and patients and assessed the risk factors for graft failure.
Methods
In a single center, from August 1997 to December 2013, 28 cases of recipients who received kidney transplantation from DCD were enrolled. Information about donor and recipient factors, graft conditions, and transplant outcomes was collected through review of medical records. We calculated overall graft and patient survival rates and the risk factors for graft failure according to donor criteria and whether or not delayed graft function (DGF) occurred.
Results
There was no primary non-function, but DGF developed in 67.9% (19/28). Graft losses occurred in five patients during a median follow-up period of 68.2 months (4∼204). There was no significant difference in graft survival rates depending on the donor criteria and the occurrence of DGF. In addition, there were no noteworthy risk factors for graft failure among donor age, donor creatinine, extended criteria donor, recipient age, warm ischemic time, cold ischemic time, and DGF.
Go to : 
References
1). Reich DJ, Mulligan DC, Abt PL, Pruett TL, Abecassis MM, D'Alessandro A, et al. ASTS recommended practice guidelines for controlled donation after cardiac death organ procurement and transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2009; 9:2004–11.

2). Kootstra G, Daemen JH, Oomen AP. Categories of non-heart-beating donors. Transplant Proc. 1995; 27:2893–4.
3). Abt PL, Fisher CA, Singhal AK. Donation after cardiac death in the US: history and use. J Am Coll Surg. 2006; 203:208–25.

4). Jochmans I, Darius T, Kuypers D, Monbaliu D, Goffin E, Mourad M, et al. Kidney donation after circulatory death in a country with a high number of brain dead donors: 10-year experience in Belgium. Transpl Int. 2012; 25:857–66.

5). Dominguez-Gil B, Haase-Kromwijk B, Van Leiden H, Neuberger J, Coene L, Morel P, et al. Current situation of donation after circulatory death in European countries. Transpl Int. 2011; 24:676–86.
6). Evrard P. Belgian Working Group on DCD National Protocol. Belgian modified classification of Maastricht for donors after circulatory death. Transplant Proc. 2014; 46:3138–42.

7). Bradley JA, Pettigrew GJ, Watson CJ. Time to death after withdrawal of treatment in donation after circulatory death (DCD) donors. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013; 18:133–9.

8). O'Connor KJ, Delmonico FL. Increasing the supply of kidneys for transplantation. Semin Dial. 2005; 18:460–2.
9). Jin DC. Current status of dialysis therapy for ESRD patients in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; 56:562–8. (진동찬. 우리나라 말기신부전 환자의 투석현황. 대한의사협회지 2013;56: 562–8.).

10). Summers DM, Watson CJ, Pettigrew GJ, Johnson RJ, Collett D, Neuberger JM, et al. Kidney donation after circulatory death (DCD): state of the art. Kidney Int. 2015; 88:241–9.

11). Gagandeep S, Matsuoka L, Mateo R, Cho YW, Genyk Y, Sher L, et al. Expanding the donor kidney pool: utility of renal allografts procured in a setting of uncontrolled cardiac death. Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:1682–8.

12). Singh RP, Farney AC, Rogers J, Zuckerman J, Reeves-Daniel A, Hartmann E, et al. Kidney transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors: lack of impact of delayed graft function on post-transplant outcomes. Clin Transplant. 2011; 25:255–64.

13). Mallon DH, Summers DM, Bradley JA, Pettigrew GJ. Defining delayed graft function after renal transplantation: simplest is best. Transplantation. 2013; 96:885–9.
15). Serur D, Saal S, Wang J, Sullivan J, Bologa R, Hartono C, et al. Deceased-donor kidney transplantation: improvement in longterm survival. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:317–24.

16). Ounissi M, Cherif M, Abdallah TB, Bacha M, Hedri H, Abderrahim E, et al. Risk factors and consequences of delayed graft function. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2013; 24:243–6.

17). Boom H, Mallat MJ, de Fijter JW, Zwinderman AH, Paul LC. Delayed graft function influences renal function, but not survival. Kidney Int. 2000; 58:859–66.

18). Ojo AO, Wolfe RA, Held PJ, Port FK, Schmouder RL. Delayed graft function: risk factors and implications for renal allograft survival. Transplantation. 1997; 63:968–74.
Go to : 
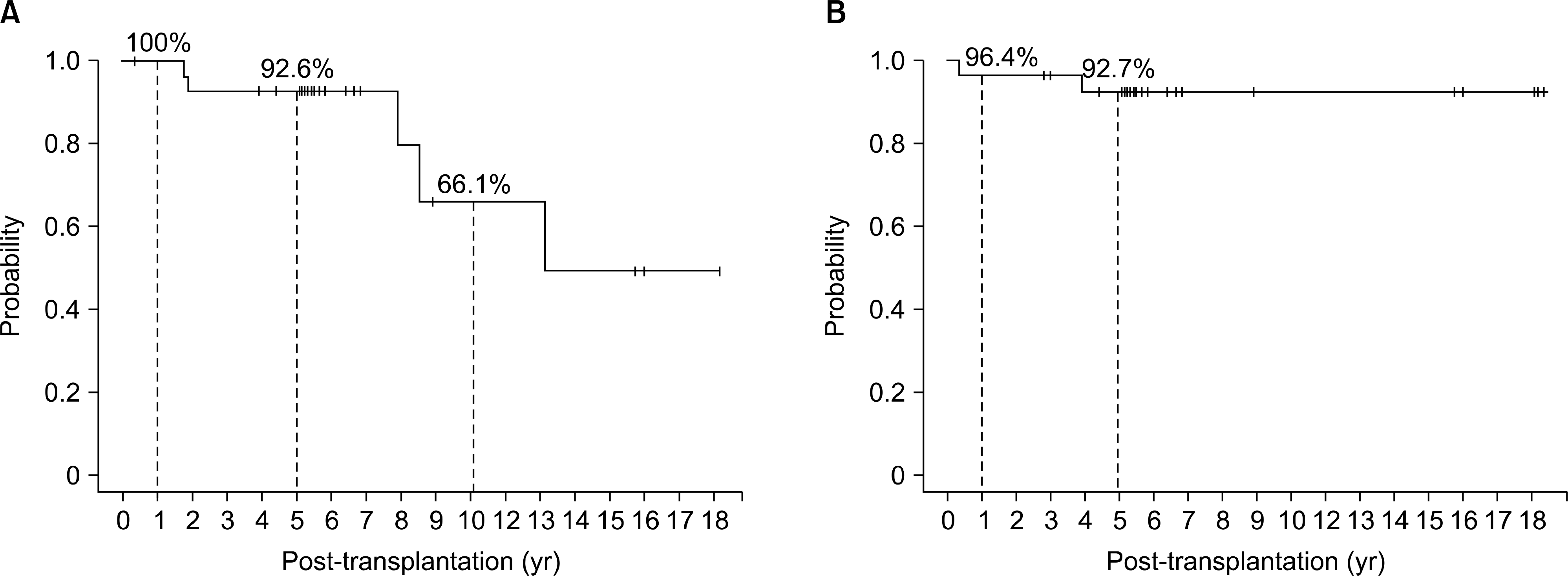 | Fig. 1.Overall survival. (A) Donation after circulatory death (DCD): overall graft survival. (B) DCD: overall patient survival. |
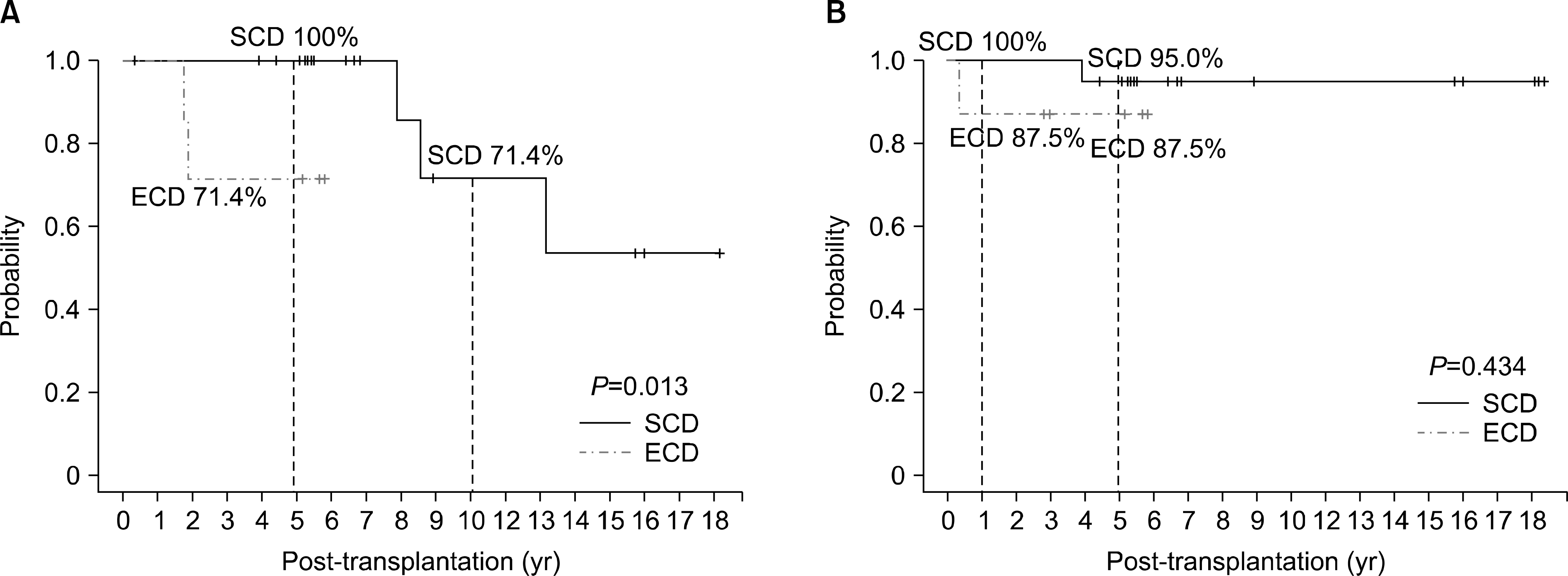 | Fig. 2.Survival according to donor criteria (standard criteria donor [SCD] vs. extended criteria donor [ECD]). (A) Donation after circulatory death (DCD): graft survival according to donor criteria (SCD vs. ECD). (B) DCD: patient survival according to donor criteria (SCD vs. ECD). |
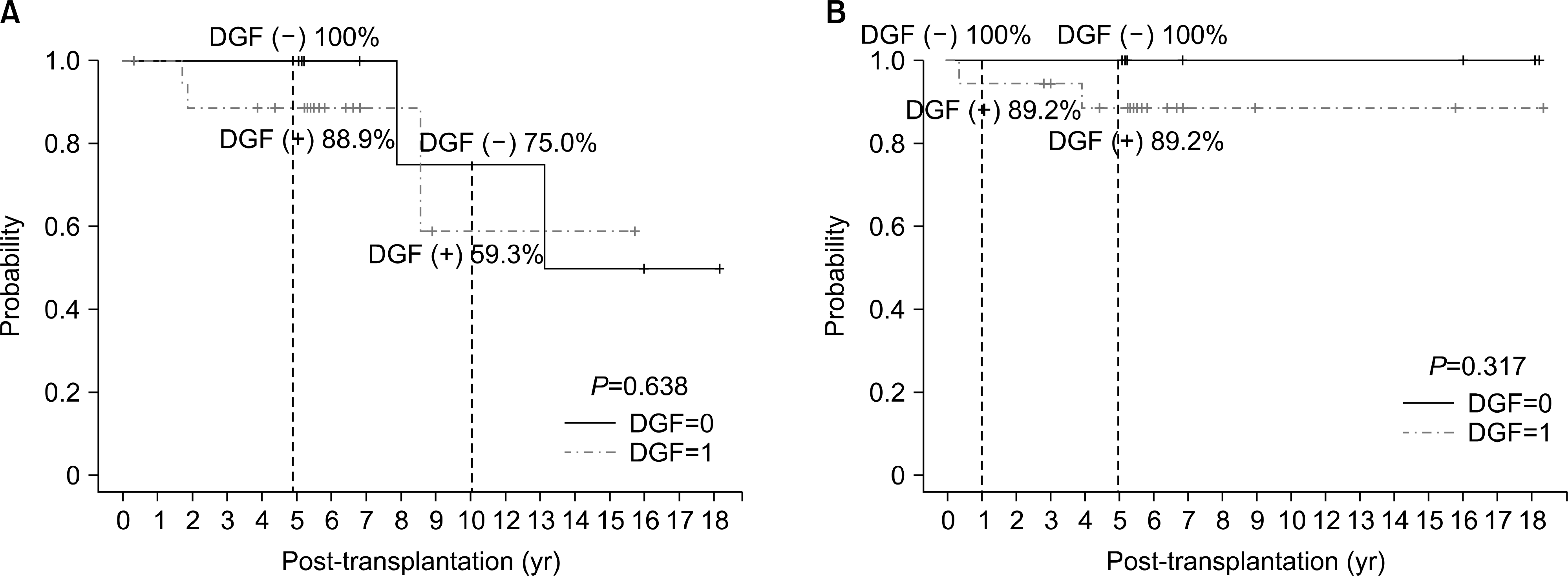 | Fig. 3.Survival according to delayed graft function (DGF) occurrence. (A) Graft survival according to DGF occurrence. (B) Patient survival according to DGF occurrence. |
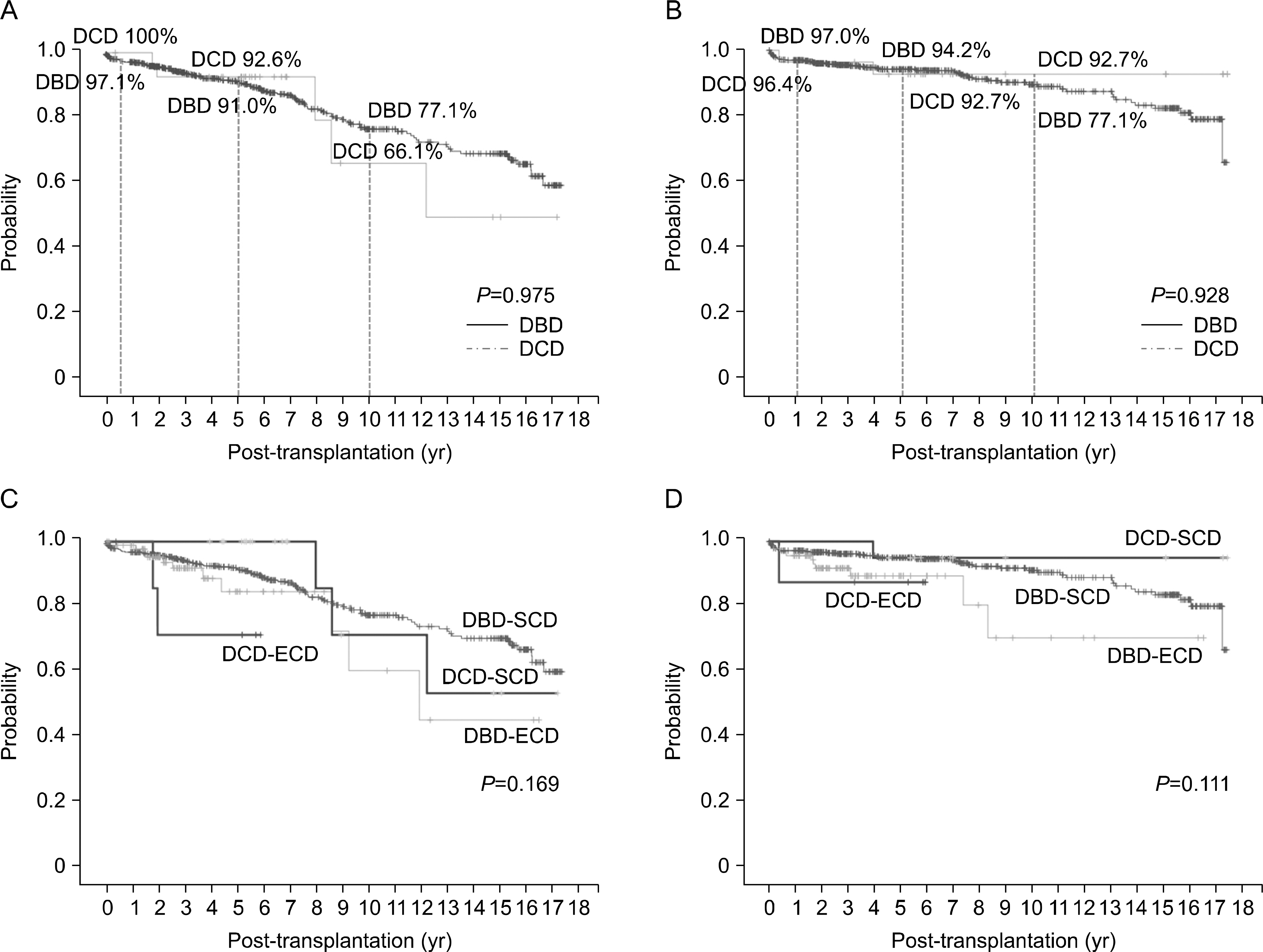 | Fig. 4.Overall survival (donation after circulatory death [DCD] vs. donation after brain death [DBD]). (A) Overall graft survival. (B) Overall patient survival. (C) Graft survival according to donor criteria (DCD-standard criteria donor [SCD] vs. DCD-extended criteria donor [ECD] vs. DBD-SCD vs. DBD-ECD). (D) Patient survival according to donor criteria (DCD-SCD vs. DCD-ECD vs. DBD-SCD vs. DBD-ECD). |
Table 1.
Basal characteristics of the patients
Table 2.
Subgroup analysis according to donor criteria
Table 3.
Subgroup analysis according to presence of delayed graft function
| Variable | DGF (+)(n=19) | DGF (−)(n=9) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm ischemic time (min) a | 7.8±4.3 | 11.4±9.3 | 0.560 |
| Cold ischemic time (min) | 515.7±185.4 | 390.3±128.0 | 0 0.084 |
| Sequential creatinine level | |||
| change (mo) | 2.00±0.74 | 1.31±0.33 | 0.006 |
| SCR 1∼3 | 1.67±0.40 | 1.27±0.21 | 0.009 |
| SCR 4∼6 | 1.56±0.43 | 1.27±0.23 | 0.101 |
| SCR 7∼9 | 1.55±0.50 | 1.28±0.30 | 0.247 |
| SCR 10∼12 | 2.03±1.88 | 1.22±0.35 | 0.145 |
| Last SCR | |||
| Graft survival (yr) | 0.638 | ||
| 1 | 100 | 100 | |
| 5 | 88.9 | 100 | |
| 10 | 59.3 | 75.0 | |
| Patient survival (yr) | 0.317 | ||
| 1 | 94.7 | 100 | |
| 5 | 89.2 | 100 | |
| 10 | 89.2 | 100 |
Table 4.
Risk factor analysis for graft failure (univariate analysis)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download