Abstract
Background
To identify the optimum culture conditions by investigating isolated rat hepatocytes cultured in medium containing different growth factors.
Methods
Hepatocytes were isolated from rats using a two-step perfusion technique and divided into the following four groups cultured in medium containing different growth factors: control, epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin, and EGF+insulin. The viability of the cultured rat hepatocytes and liver function parameters, including albumin, ammonia, and urea in the culture medium, were measured. Hepatocyte morphology was examined by staining with hematoxylin and eosin, and albumin receptor expression was confirmed by immunofluorescence.
Results
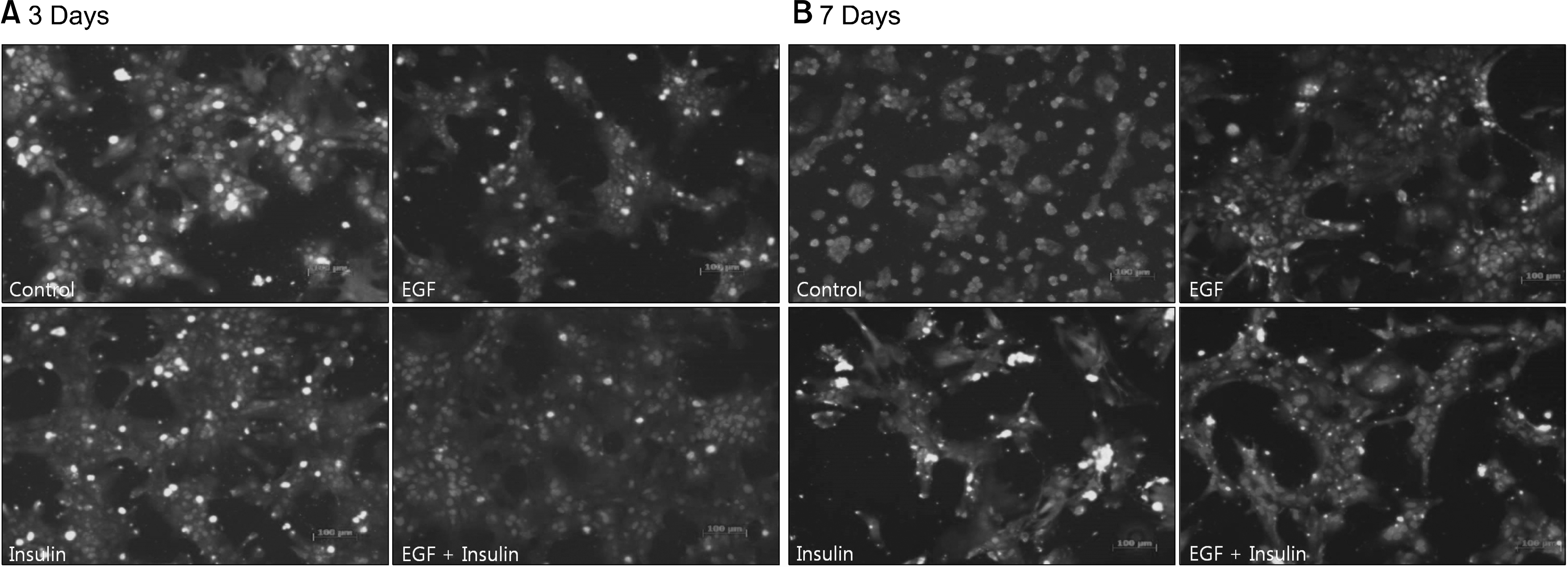
Slightly higher viability was observed in the growth factor groups than in the control group, although without significance (P=0.073). The levels of albumin (P=0.001), ammonia (P<0.001), and urea (P=0.041) differed significantly among the four groups. The functional parameters in the growth factor groups, particularly the EGF+insulin group, were significantly superior to those in the control group. The morphology of the hepatocytes in all growth factor groups was well maintained at 10 days. However, the control group showed deterioration in cell morphology by day 7.
Go to : 
References
1). O'Grady JG, Schalm SW, Williams R. Acute liver failure: redefining the syndromes. Lancet. 1993; 342:273–5.
3). O'Grady J. Timing and benefit of liver transplantation in acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 2014; 60:663–70.
4). Neuberger J, James O. Guidelines for selection of patients for liver transplantation in the era of donor-organ shortage. Lancet. 1999; 354:1636–9.

6). Hughes RD, Mitry RR, Dhawan A. Current status of hepatocyte transplantation. Transplantation. 2012; 93:342–7.

7). Bumgardner GL, Fasola C, Sutherland DE. Prospects for hepatocyte transplantation. Hepatology. 1988; 8:1158–61.

9). Strom SC, Fisher RA, Thompson MT, Sanyal AJ, Cole PE, Ham JM, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation as a bridge to orthotopic liver transplantation in terminal liver failure. Transplantation. 1997; 63:559–69.

10). Strom SC, Bruzzone P, Cai H, Ellis E, Lehmann T, Mitamura K, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation: clinical experience and potential for future use. Cell Transplant. 2006; 15(Suppl 1):S105–10.

11). Mitaka T. The current status of primary hepatocyte culture. Int J Exp Pathol. 1998; 79:393–409.

12). Seglen PO. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976; 13:29–83.
13). Fisher RA, Strom SC. Human hepatocyte transplantation: worldwide results. Transplantation. 2006; 82:441–9.

14). Matas AJ, Sutherland DE, Steffes MW, Mauer SM, Sowe A, Simmons RL, et al. Hepatocellular transplantation for metabolic deficiencies: decrease of plasms bilirubin in Gunn rats. Science. 1976; 192:892–4.
15). Mito M, Kusano M, Kawaura Y. Hepatocyte transplantation in man. Transplant Proc. 1992; 24:3052–3.

16). Dhawan A, Puppi J, Hughes RD, Mitry RR. Human hepatocyte transplantation: current experience and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 7:288–98.

17). Kobayashi N, Fujiwara T, Westerman KA, Inoue Y, Sakaguchi M, Noguchi H, et al. Prevention of acute liver failure in rats with reversibly immortalized human hepatocytes. Science. 2000; 287:1258–62.

18). Lagasse E, Connors H, Al-Dhalimy M, Reitsma M, Dohse M, Osborne L, et al. Purified hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into hepatocytes in vivo. Nat Med. 2000; 6:1229–34.

19). Demetriou AA, Brown RS Jr, Busuttil RW, Fair J, McGuire BM, Rosenthal P, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:660–7.

20). Berry MN, Friend DS. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969; 43:506–20.
21). Hughes RD, Mitry RR, Dhawan A. Hepatocyte transplantation for metabolic liver disease: UK experience. J R Soc Med. 2005; 98:341–5.

22). Richman RA, Claus TH, Pilkis SJ, Friedman DL. Hormonal stimulation of DNA synthesis in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976; 73:3589–93.

Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.(A) Operative view of a cannulation in portal vein and (B) an infusion of collagenase solution with whitish discoloration of liver. |
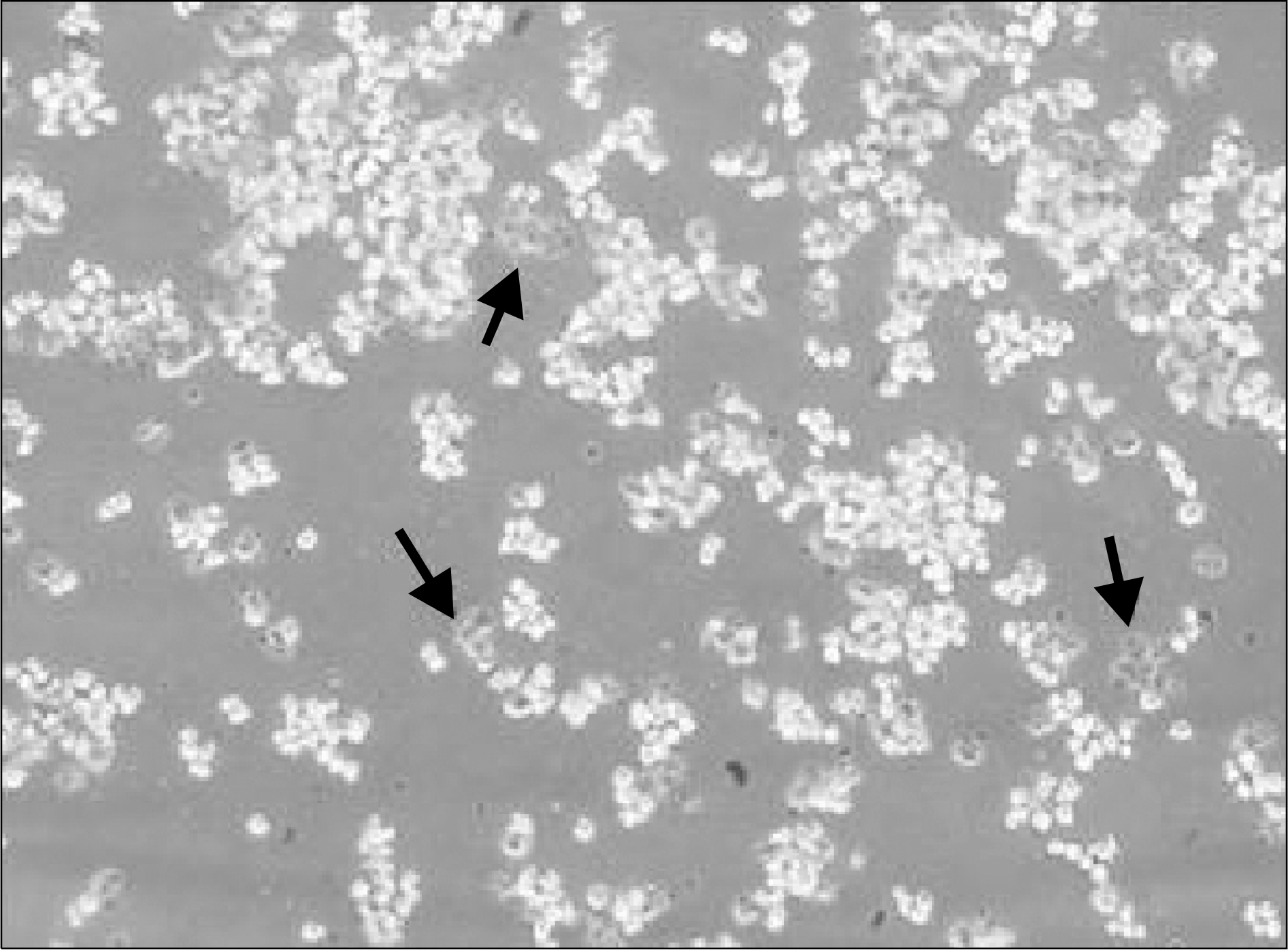 | Fig. 2.Evaluation of cell viability by trypan blue exclusion test (×200). Viable cells with an intact plasma membrane exclude dyes such as trypan blue, whereas damaged cells (arrows) become stained, particularly intensively in the nucleus. The viability of isolated hepatocytes in this photograph was about 85%. |
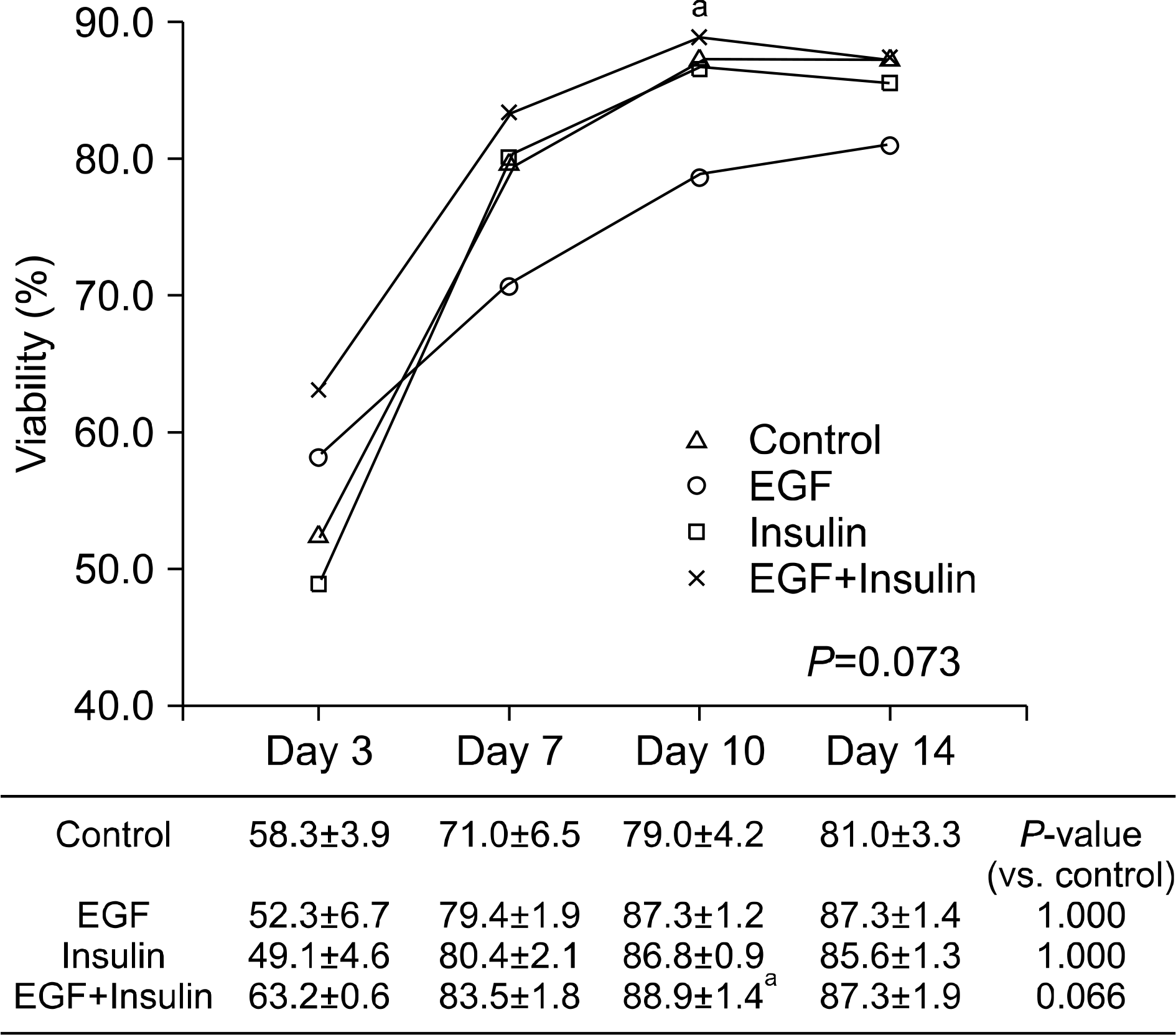 | Fig. 3.The change of viability according to growth factor supplement in culture medium. Data are average value±SEM. Abbreviation: EGF, epidermal growth factor. a P<0.05 vs. control on each day. |
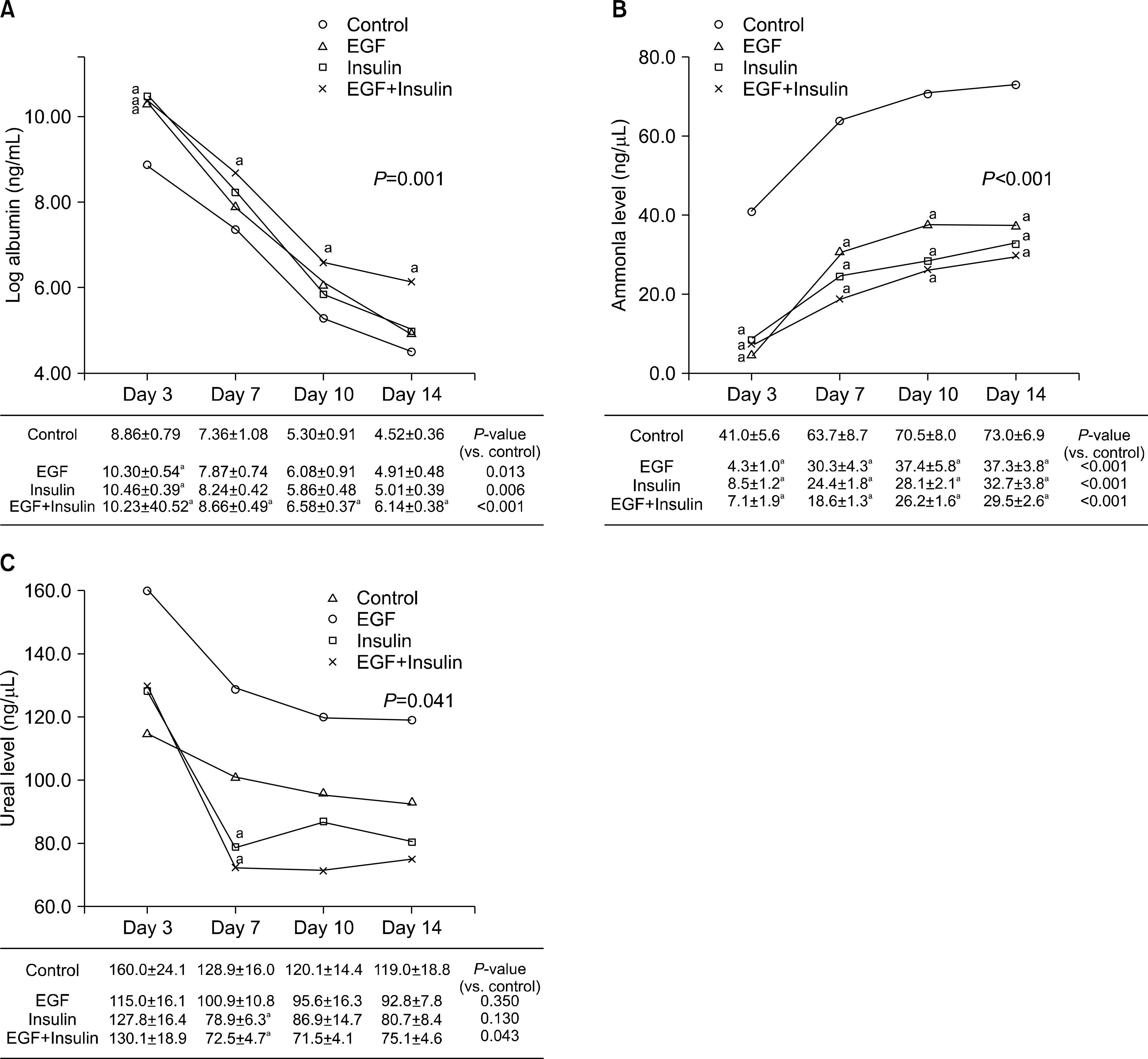 | Fig. 4.The change of liver function test including (A) albumin, (B) ammonia, and (C) urea according to growth factor supplement in culture medium. Data are average value±SEM. Abbreviation: EGF, epidermal growth factor. a P<0.05 versus control on each day. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download