Abstract
Papular mucinosis (PM, scleromyxoedema) is a rare dermatologic disease. It is histologically characterized by a focal dermal deposit of mucin within the skin. Although PM is accepted as an idiopathic disease in most cases, some authors argued that it may be a cutaneous manifestation of a systemic disease. Here, we describe a 68-year-old male kidney transplantation recipient with a complaint of intractable itching sensation on the forehead. We diagnosed the skin lesions as PM, which were improved after cyclosporine dose reduction.
References
1). Dubreuilh W. Fibromes miliaris follicularis: sclerodemie consecutive. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1906; 7:569–70.
2). Arnold HL, Odom RB, James WD. Cutaneous focal mucinosis. Arnold HL, Odom RB, James WD, Andrews GC, editors. Andrews' diseases of the skin: clinical dermatology. 8th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;1990. p. 186–93.
3). Maize J, Metcalf J. Metabolic diseases of the skin. Lever WF, Elder DE, editors. Lever's histopathology of the skin. 8th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;1997. : 389.
5). Braue A, Dolianitis C, Varigos G. Spontaneous resolution of facial papular mucinosis in a transplant patient. Australas J Dermatol. 2008; 49:164–6.

6). Park J, Lee MG. A case of discrete papular mucinosis. Korean J Dermatol. 2003; 41:219–22.
8). Biro DE, Lynfield YC, Heilman ER. Papular mucinosis and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Cutis. 1995; 55:113–4.
9). Won YH, Lee SC, Kim SJ, Jeon SD. A case of papular mucinosis. Korean J Dermatol. 1999; 37:917–21.
10). Harper RA, Rispler J. Lichen myxedematosus serum stimulates human skin fibroblast proliferation. Science. 1978; 199:545–7.

11). Allam M, Ghozzi M. Scleromyxedema: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:168–75.

12). Phillips TE, McHugh J, Moore CP. Cyclosporine has a direct effect on the differentiation of a mucin-secreting cell line. J Cell Physiol. 2000; 184:400–8.

13). Saigoh S, Tashiro A, Fujita S, Matsui M, Shibata S, Takeshita H, et al. Successful treatment of intractable scleromyxedema with cyclosporin A. Dermatology. 2003; 207:410–1.

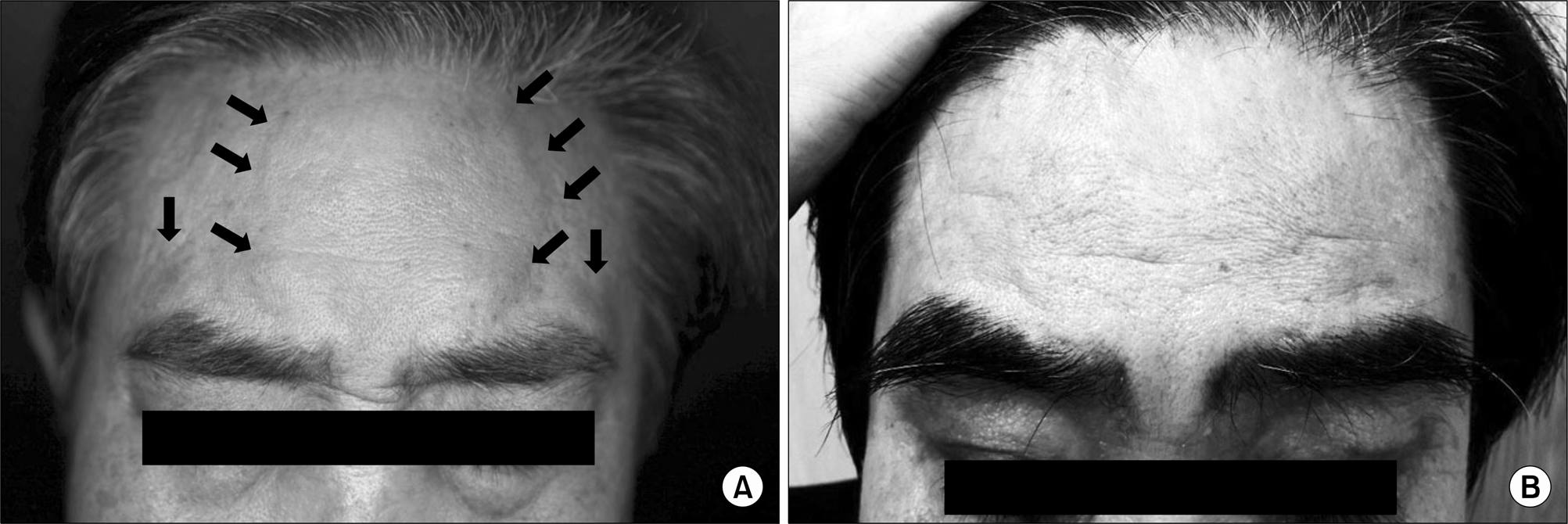
Fig. 1.
(A) Multiple, relatively well-demarcated, flesh or erythematous colored papules on the forehead. (B) Facial dome-shaped, skin-colored papules resolved 2 weeks after reduction of cyclosporine.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download