Abstract
Background:
This study was conducted in order to evaluate the propriety of expanded donor criteria in Korea and to identify the preoperative factors influencing allograft survival and function.
Methods:
We studied 404 patients who received deceased renal transplants from five transplantation centers of 2, 3 territory from 2000 to 2010. Differences in 1-year graft function, delayed graft function (DGF) rate, and graft survival rate between the standard criteria donor (SCD) and expanded criteria donor (ECD) were compared retrospectively. The preoperative factors influencing graft function and graft survival were analysed.
Results:
SCD showed significantly better 1-year graft function than ECD (P=0.011). No differences in 1-year acute rejection rate were observed between SCD (13.2%) and ECD (16.9%) (P=0.449). Significantly higher DGF rate was observed for ECD (25.4%) than for SCD (14.1%) (P=0.022). Graft type had no significant influence on 5-year graft survival (SCD 94.5% vs. ECD 93.7%) (P=0.835). Advanced donor age (P=0.001), donor hypertension history (P=0.047), high serum creatinine (P=0.002), and cerebral infarction as cause of death (P=0.004) had a negative influence on 1-year allograft function. Significantly low graft survival was observed for advanced donor age (P=0.002).
Conclusions:
Graft function, DGF rates of ECD were poorer than those of SCD. Graft survival rate of ECD was comparable to that of SCD kidney. Korean Network for Organ Sharing expanded criteria may underestimate the organ quality of deceased kidney and modification may be needed in order to expand the potential donor pool through nationwide study.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). 2012 KONOS Annual Report [Internet]. Seoul: KONOS;2012. [cited 2013 Jul 13]. Available from. http://www.konos.go.kr.
2). Crew RJ, Ratner LE. ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation: current practice and the decade ahead. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010; 15:526–30.

3). Evenson AR. Utilization of kidneys from donation after circulatory determination of death. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011; 16:385–9.

4). Schold JD, Segev DL. Increasing the pool of deceased donor organs for kidney transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012; 8:325–31.

5). Tso PL, Dar WA, Henry ML. With respect to elderly patients: finding kidneys in the context of new allocation concepts. Am J Transplant. 2012; 12:1091–8.

6). Warren DS, Montgomery RA. Incompatible kidney transplantation: lessons from a decade of desensitization and paired kidney exchange. Immunol Res. 2010; 47:257–64.

7). Zbroch E, Mał yszko J, Myś liwiec M, Przybył owski P, Durlik M. Hypertension in solid organ transplant recipients. Ann Transplant. 2012; 17:100–7.

8). Ojo AO, Hanson JA, Meier-Kriesche H, Okechukwu CN, Wolfe RA, Leichtman AB, et al. Survival in recipients of marginal cadaveric donor kidneys compared with other recipients and wait-listed transplant candidates. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:589–97.

9). Rosengard BR, Feng S, Alfrey EJ, Zaroff JG, Emond JC, Henry ML, et al. Report of the Crystal City meeting to maximize the use of organs recovered from the cadaver donor. Am J Transplant. 2002; 2:701–11.

10). Pascual J, Zamora J, Pirsch JD. A systematic review of kidney transplantation from expanded criteria donors. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008; 52:553–86.

11). Lai Q, Nudo F, Levi Sandri GB, Melandro F, Ferretti S, Grieco M, et al. Survival after kidney transplantation does not differ with 50-59- or over 60-year-old ex-panded-criteria donors. Transplant Proc. 2011; 43:1030–2.

12). Karatzas T, Gompou A, Bokos J, Dimitroulis D, Boletis J, Kostakis A, et al. Optimal utilization of expanded criteria deceased donors for kidney transplantation. Int Urol Nephrol. 2011; 43:1211–9.

13). Kim JM, Kim SJ, Joh JW, Kwon CH, Song S, Shin M, et al. Is it safe to use a kidney from an expanded criteria donor? Transplant Proc. 2011; 43:2359–62.

14). Park JY, Cho JH, Yoon YD, Song EJ, Jin MK, Yu CH, et al. Outcome of cadaveric kidney transplantation from expanded criteria donors. Korean J Med 2011;8:408-18. (박자용, 조장희, 윤영득, 송은주, 진미경, 류정훈, 등. 확장 범주 뇌사자의 신장이식 성적. 대한내과학회지. 2011; 80:408–18.
15). Metzger RA, Delmonico FL, Feng S, Port FK, Wynn JJ, Merion RM. Expanded criteria donors for kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003; 3(Suppl 4):114–25.

16). Kauffman HM, Bennett LE, McBride MA, Ellison MD. The expanded donor. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 1997; 11:165–90.

17). Nyberg SL, Matas AJ, Kremers WK, Thostenson JD, Larson TS, Prieto M, et al. Improved scoring system to assess adult donors for cadaver renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003; 3:715–21.

18). Wijnen RM, Booster MH, Stubenitsky BM, de Boer J, Heineman E, Kootstra G. Outcome of transplantation of non-heart-beating donor kidneys. Lancet. 1995; 345:1067–70.

19). Cohen B, Smits JM, Haase B, Persijn G, Vanrenterghem Y, Frei U. Expanding the donor pool to increase renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005; 20:34–41.

20). Kootstra G, van Heurn E. Non-heartbeating donation of kidneys for transplantation. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007; 3:154–63.

21). Kimber RM, Metcalfe MS, White SA, Nicholson ML. Use of non-heart-beating donors in renal transplantation. Postgrad Med J. 2001; 77:681–5.

22). Kong PS, Lee KW, Choi IS, Kim SJ, Song GD, Lee SK, et al. The analysis of risk factors of donor affecting the graft survival in cadaveric kidney transplantation. J Korean Surg Soc 2001;60:281-7. (공필성, 이광웅, 최인석, 김성주, 송건도, 이석구, 등. 사체신이식에서 이식신생존율에 영향을 미치는 사체공여자의 위험인자 분석. 대한외과학회지. 2001; 60:281–7.
Go to : 
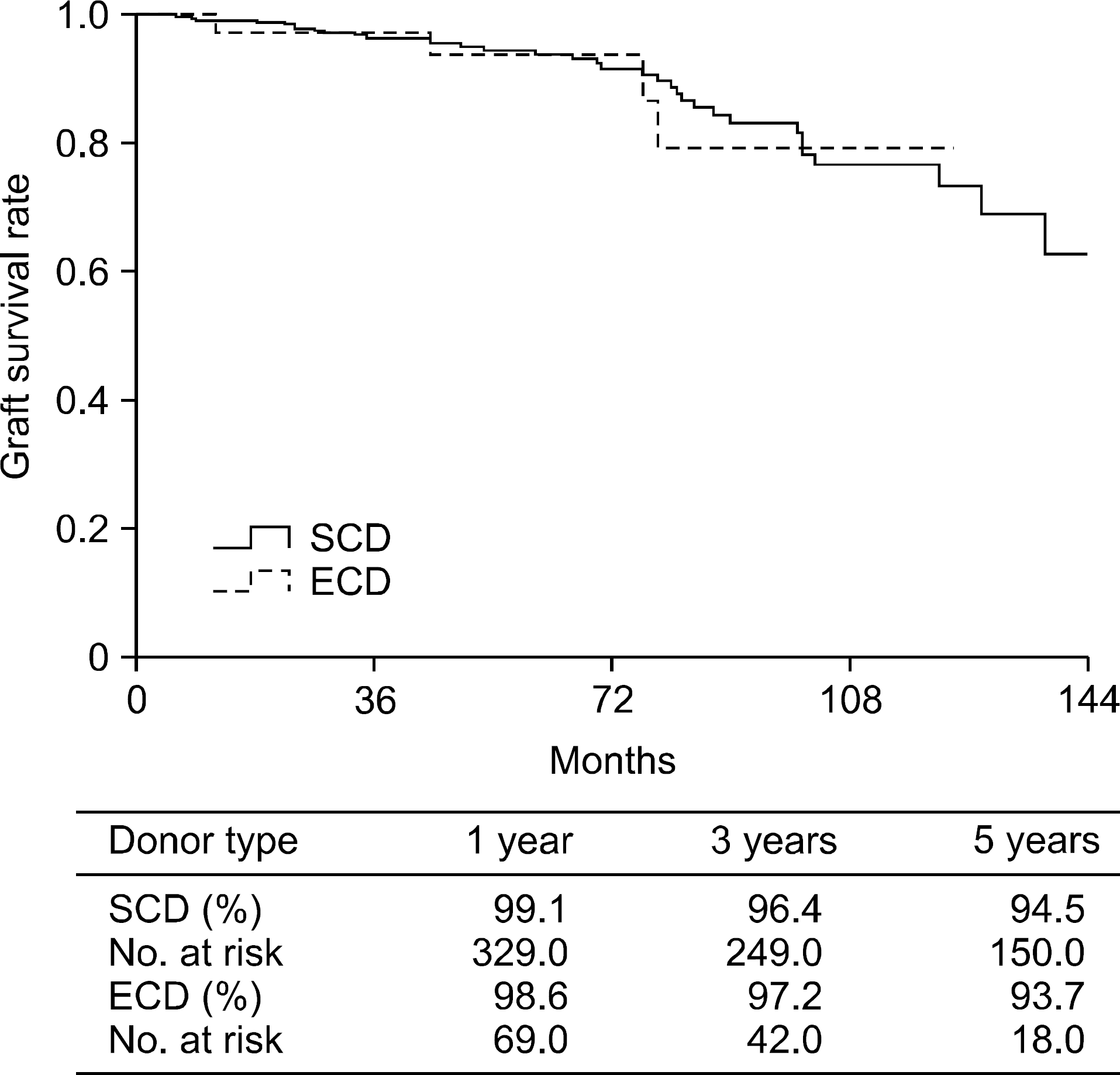 | Fig. 1.Renal allograft survival rate according to donor criteria: standard criteria donor (SCD) versus expanded criteria donor (ECD). |
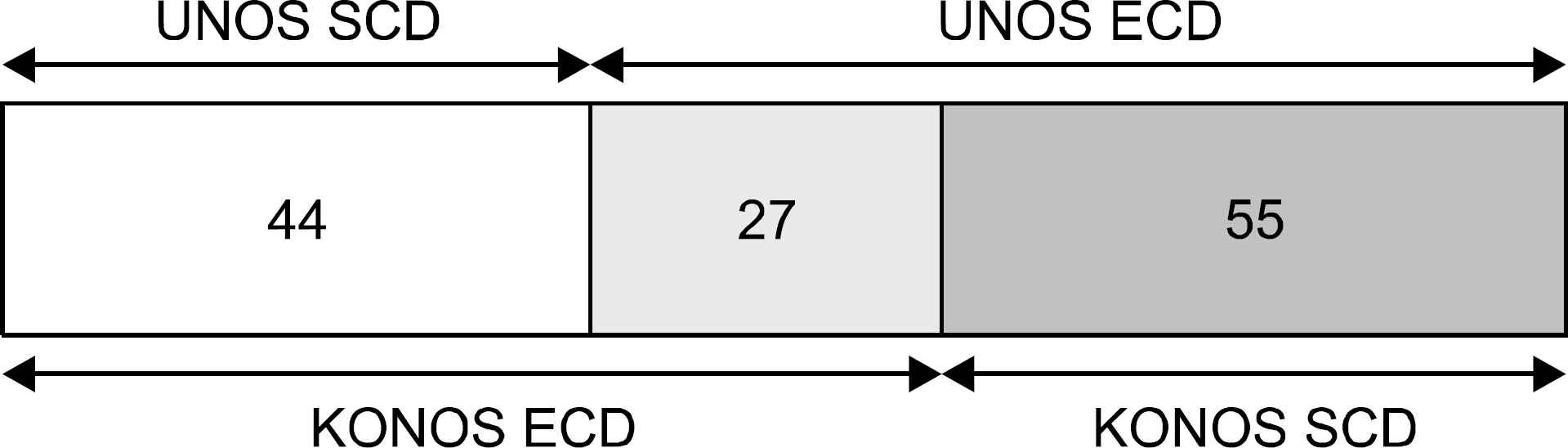 | Fig. 3.Total of 71 patients were assorted as expanded criteria donor (ECD) by Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS) criteria and only 27 patients (38.0%) of them were expanded donor by United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) criteria. Abbreviation: SCD, standard criteria donor. |
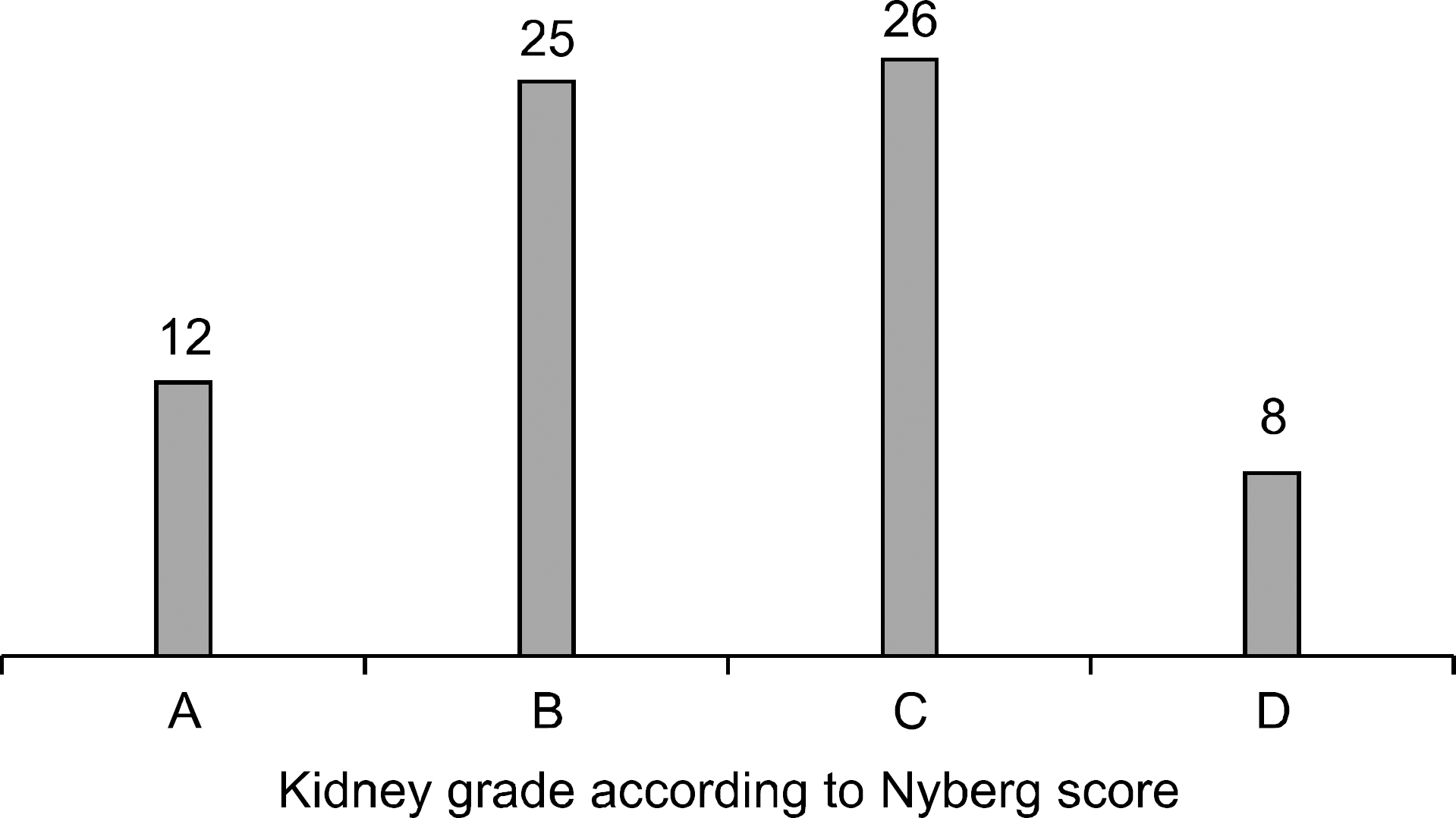 | Fig. 4.Kidney grade determined by Nyberg donor score in 71 patients of Korean Network for Organ Sharing expanded criteria donor. |
Table 1.
Comparison of recipient and donor characteristics
Table 2.
Causes which assorted deceased donor as expanded criteria donor
| Variable | ECD (n=71) |
|---|---|
| Nonheart beating donor | 3 (4.2) |
| Hypotensive attack a | 17 (23.9) |
| Age ≥60 years | 16 (22.5) |
| sCr ≥3.0 mg/dL or CrCl ≤60 mL/min | 24 (33.8) |
| Proteinuria (≥++) ≥2 times | 8 (11.3) |
| Proteinuria (≥++) ≥2 times+sCr ≥3.0 mg/dL | 2 (2.8) |
| Age ≥60 years+sCr ≥3.0 mg/dL | 1 (1.4) |
Table 3.
Comparison of clinical results in terms of estimated glomerular filtration rate, acute resection episode, and delayed graft function between standard criteria donor and expanded criteria donor
Table 4.
Donor variables associated with recipient estimated glomerular filtration rate at 1 year
Table 5.
Multivariate regression models for risk factors of 1-year estimated glomerular filtration rate after deceased donor kidney transplantation




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download