Abstract
Background
Two of the most sensitive methods for detecting donor-specific HLA antibodies (DSAs) are solid phase panel reactive antibody (PRA) assay using Luminex platform (Luminex-PRA), and a cell-based flow cytometric crossmatch (FCXM) test. We evaluated FCXM results in relation to DSAs detected by the Luminex-PRA method in solid organ transplantation candidates or post-transplant follow-up patients.
Methods
A total of 171 donor-recipient pairs were evaluated by Luminex-PRA (LIFECODES Class I and Class II ID kits; Gen-Probe, USA) and FCXM (T- and B-cells) tests. DSA levels were analyzed using a sum of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) values, and FCXM results were analyzed using MFI ratios.
Results
Class I and II DSAs were detected in 11.7% (20/171) and 11.1% (19/171) of tested sera, respectively. T-FCXM was negative in 97.4% (147/151) of Class I DSA negative sera, and B-FCXM was negative in 99.3% (137/138) of Class I and II DSA negative sera. T-FCXM was positive in 91.7% (11/12) of sera with moderate to strong Class I DSAs and B-FCXM was positive in 88.9% (16/18) of sera with moderate to strong Class II and/or Class I DSAs in the evaluation of sensitivities of FCXM in relation to DSA. There were significant correlations between FCXM ratios and DSA levels for both T-FCXM (P=0.008) and B-FCXM (P<0.001).
Figures and Tables
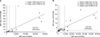 | Fig. 1Relationship between DSA intensity (MFI sum) and FCXM strength (MFI ratio). (A) T-FCXM results in patients with Class I DSA (n=20), and (B) B-FCXM results in patients with Class I or Class II DSA (n=33). Abbreviations: DSA, donor-specific antibody; FCXM, flow cytometric crossmatch; MFI, median fluorescence intensity. |
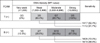 | Fig. 2Relationship between DSA intensity and flow cytometric crossmatch (FCXM) results. Sensitivities of FCXM tests detecting DSA-positive samples of different intensities are shown. Abbreviations: DSA, donor-specific antibody; MFI, median fluorescence intensity. |
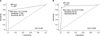 | Fig. 3Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis of DSA intensity (MFI sum) for FCXM positivity. MFI sum values of Class I DSAs were used for T-FCXM (A), and those of Class I and Class II were used for B-FCXM (B). Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; DSA, donor-specific antibody; FCXM, flow cytometric crossmatch; MFI, median fluorescence intensity. |
References
1. Patel R, Terasaki PI. Significance of the positive crossmatch test in kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1969. 280:735–739.

2. Süsal C, Döhler B, Sadeghi M, Ovens J, Opelz G. HLA antibodies and the occurrence of early adverse events in the modern era of transplantation: a collaborative transplant study report. Transplantation. 2009. 87:1367–1371. Erratum in Transplantation. 2009;88(2):293.

3. Fernández-Fresnedo G, Pastor JM, López-Hoyos M, Ruiz JC, Zubimendi JA, Gonzalez-Cotorruelo J, et al. ELISA after kidney transplantation on the development of acute rejection and graft survival. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003. 18:990–995.
4. Gebel HM, Bray RA, Nickerson P. Pre-transplant assessment of donor-reactive, HLA-specific antibodies in renal transplantation: contraindication vs. risk. Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:1488–1500.

5. Worthington JE, Martin S, Al-Husseini DM, Dyer PA, Johnson RW. Posttransplantation production of donor HLA-specific antibodies as a predictor of renal transplant outcome. Transplantation. 2003. 75:1034–1040.

6. Cardarelli F, Pascual M, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Delmonico FL, Wong W, Schoenfeld DA, et al. Prevalence and significance of anti-HLA and donor-specific antibodies long-term after renal transplantation. Transpl Int. 2005. 18:532–540.

7. Leffell MS, Zachary AA. Antiallograft antibodies: relevance, detection, and monitoring. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010. 15:2–7.

8. Eng HS, Bennett G, Bardy P, Coghlan P, Russ GR, Coates PT. Clinical significance of anti-HLA antibodies detected by Luminex: enhancing the interpretation of CDC-BXM and important post-transplantation monitoring tools. Hum Immunol. 2009. 70:595–599.

9. Zeevi A, Lunz JG 3rd, Shapiro R, Randhawa P, Mazariegos G, Webber S, et al. Emerging role of donor-specific anti-human leukocyte antigen antibody determination for clinical management after solid organ transplantation. Hum Immunol. 2009. 70:645–650.

10. Terasaki PI, McClelland JD. Microdroplet assay of human serum cytotoxins. Nature. 1964. 204:998–1000.

11. Zachary AA, Houp JA, et al. Detrick B, Hamilton RG, editors. Evaluation of the humoral response in transplantation. Manuals of molecular and clinical laboratory immunology. 2006. 7th ed. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press;1215–1227.

12. Colombo MB, Haworth SE, Poli F, Nocco A, Puglisi G, Innocente A, et al. Luminex technology for anti-HLA antibody screening: evaluation of performance and of impact on laboratory routine. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2007. 72:465–471.

13. Vaidya S, Cooper TY, Avandsalehi J, Barnes T, Brooks K, Hymel P, et al. Improved flow cytometric detection of HLA alloantibodies using pronase: potential implications in renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2001. 71:422–428.

14. Rodey GE, Neylan JF, Whelchel JD, Revels KW, Bray RA. Epitope specificity of HLA Class. I. alloantibodies I Frequency analysis of antibodies to private versus public specificities in potential transplant recipients. Hum Immunol. 1994. 39:272–280.

15. Rodey GE, Revels K, Fuller TC. Epitope specificity of HLA Class I alloantibodies: II. Stability of cross-reactive group antibody patterns over extended time periods. Transplantation. 1997. 63:885–893.
16. Reinsmoen NL, Lai CH, Vo A, Cao K, Ong G, Naim M, et al. Acceptable donor-specific antibody levels allowing for successful deceased and living donor kidney transplantation after desensitization therapy. Transplantation. 2008. 86:820–825.

17. Zachary AA, Leffell MS. Detecting and monitoring human leukocyte antigen-specific antibodies. Hum Immunol. 2008. 69:591–604.

18. Gebel HM, Moussa O, Eckels DD, Bray RA. Donor-reactive HLA antibodies in renal allograft recipients: considerations, complications, and conundrums. Hum Immunol. 2009. 70:610–617.

19. Tait BD, Hudson F, Brewin G, Cantwell L, Holdsworth R. Solid phase HLA antibody detection technology - challenges in interpretation. Tissue Antigens. 2010. 76:87–95.

20. Muro M, Llorente S, Marín L, Moya-Quiles MR, Gonzalez-Soriano MJ, Prieto A, et al. Acute vascular rejection mediated by HLA antibodies in a cadaveric kidney recipient: discrepancies between FlowPRA, ELISA and CDC vs luminex screening. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005. 20:223–226.

21. Lee PC, Ozawa M, Hung CJ, Lin YJ, Chang SS, Chou TC. Reappraisal of HLA antibody analysis and cross-matching in kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009. 41:95–98.

22. Morris GP, Phelan DL, Jendrisak MD, Mohanakumar T. Virtual crossmatch by identification of donor-specific anti-human leukocyte antigen antibodies by solid-phase immunoassay: a 30-month analysis in living donor kidney transplantation. Hum Immunol. 2010. 71:268–273.

23. Lee YS, Won DI. Analysis of positive flow cytometric crossmatch in organ transplantation. Lab Med Online. 2011. 1:43–50.

24. Christiaans MH, Overhof-de Roos R, Nieman F, van Hooff JP, van den Berg-Loonen EM. Donor-specific antibodies after transplantation by flow cytometry: relative change in fluorescence ratio most sensitive risk factor for graft survival. Transplantation. 1998. 65:427–433.

25. Riethmüller S, Ferrari-Lacraz S, Müller MK, Raptis DA, Hadaya K, Rüsi B, et al. Donor-specific antibody levels and three generations of crossmatches to predict antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2010. 90:160–167.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download