Abstract
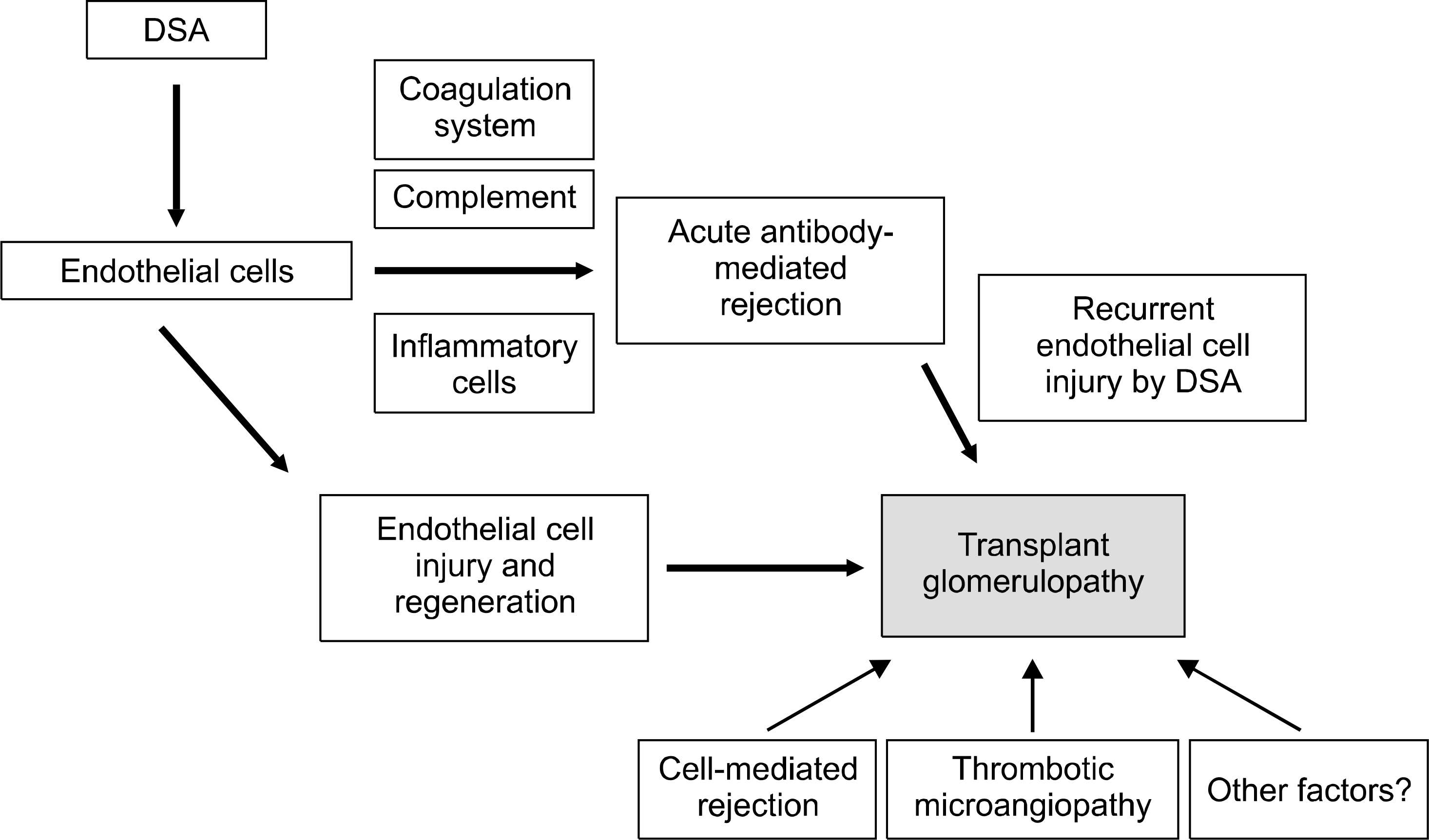
Transplant glomerulopathy is a late complication of renal transplantation. The characteristic morphology of transplant glomerulopathy includes thickening of glomerular capillary loops with double contour, and duplication of glomerular basement membrane on electron microscopy. Clinical and experimental evidences support the role of antibody-mediated immune mechanism in the development of transplant glomerulopathy. Antibody-induced endothelial cell injury is the key pathogenesis of transplant glomerulopathy. The evolution of transplant glomerulopathy in the context of immunologic injury is briefly reviewed.
Go to : 
References
1). Hamburger J, Crosnier J, Dormont J. Observations in patients with a well-tolerated homotransplanted kidney: possibility of a new secondary disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964; 120:558–77.

2). Fotheringham J, Angel CA, McKane W. Transplant glomerulopathy: morphology, associations and mechanism. Nephron Clin Pract. 2009; 113:c1–7. discussion c7.

3). Wavamunno MD, O'Connell PJ, Vitalone M, Fung CL, Allen RD, Chapman JR, et al. Transplant glomerulopathy: ultrastructural abnormalities occur early in longitudinal analysis of protocol biopsies. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:2757–68.

4). Feucht HE, Felber E, Gokel MJ, Hillebrand G, Nattermann U, Brockmeyer C, et al. Vascular deposition of complement-split products in kidney allografts with cell-mediated rejection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991; 86:464–70.

5). Feucht HE, Schneeberger H, Hillebrand G, Burkhardt K, Weiss M, Riethmüller G, et al. Capillary deposition of C4d complement fragment and early renal graft loss. Kidney Int. 1993; 43:1333–8.

6). Collins AB, Schneeberger EE, Pascual MA, Saidman SL, Williams WW, Tolkoff-Rubin N, et al. Complement activation in acute humoral renal allograft rejection: diagnostic significance of C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:2208–14.
7). Mauiyyedi S, Pelle PD, Saidman S, Collins AB, Pascual M, Tolkoff-Rubin NE, et al. Chronic humoral rejection: identification of antibody-mediated chronic renal allograft rejection by C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:574–82.

8). Regele H, Böhmig GA, Habicht A, Gollowitzer D, Schillinger M, Rockenschaub S, et al. Capillary deposition of complement split product C4d in renal allografts is associated with basement membrane injury in peritubular and glomerular capillaries: a contribution of humoral immunity to chronic allograft rejection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:2371–80.

9). Sis B, Campbell PM, Mueller T, Hunter C, Cockfield SM, Cruz J, et al. Transplant glomerulopathy, late antibody-mediated rejection and the ABCD tetrad in kidney allograft biopsies for cause. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:1743–52.

10). Gloor JM, Sethi S, Stegall MD, Park WD, Moore SB, DeGoey S, et al. Transplant glomerulopathy: subclinical incidence and association with alloantibody. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:2124–32.

11). Joosten SA, Sijpkens YW, van Ham V, Trouw LA, van der Vlag J, van den Heuvel B, et al. Antibody response against the glomerular basement membrane protein agrin in patients with transplant glomerulopathy. Am J Transplant. 2005; 5:383–93.

12). Solez K, Colvin RB, Racusen LC, Sis B, Halloran PF, Birk PE, et al. Banff ‘05 Meeting Report: differential diagnosis of chronic allograft injury and elimination of chronic allograft nephropathy ('CAN'). Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:518–26.

13). Gloor JM, Cosio FG, Rea DJ, Wadei HM, Winters JL, Moore SB, et al. Histologic findings one year after positive crossmatch or ABO blood group incompatible living donor kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:1841–7.

14). Smith RN, Kawai T, Boskovic S, Nadazdin O, Sachs DH, Cosimi AB, et al. Chronic antibody mediated rejection of renal allografts: pathological, serological and immunologic features in nonhuman primates. Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:1790–8.

15). Smith RN, Kawai T, Boskovic S, Nadazdin O, Sachs DH, Cosimi AB, et al. Four stages and lack of stable accommodation in chronic alloantibody-mediated renal allograft rejection in Cynomolgus monkeys. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8:1662–72.

16). Haas M. C4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection in renal allografts: evidence for its existence and effect on graft survival. Clin Nephrol. 2011; 75:271–8.

17). Koch M, Joosten SA, Mengel M, van Kooten C, Paul LC, Nashan B. Adoptive transfer of primed CD4+ T-lymphocytes induces pattern of chronic allograft nephropathy in a nude rat model. Transplantation. 2005; 79:753–61.

18). Cosio FG, Gloor JM, Sethi S, Stegall MD. Transplant glomerulopathy. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8:492–6.

Go to : 
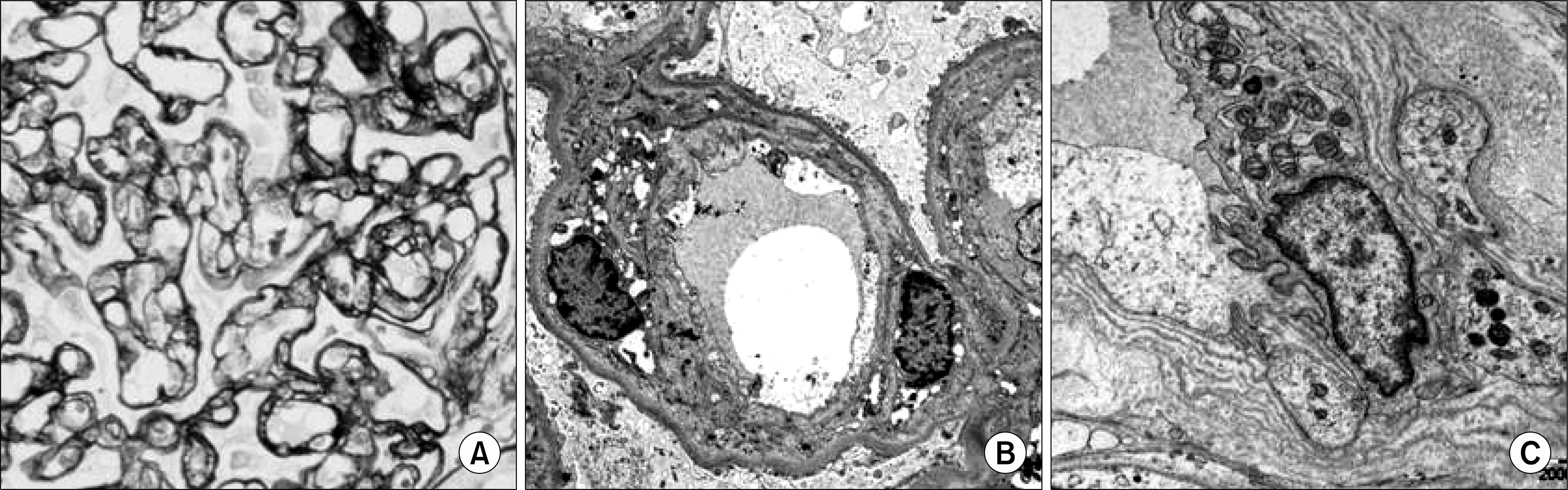 | Fig. 1.Morphologic changes of transplant glomerulopathy. Glomerular capillary loops are thickened and show double contour (A). Electron microscopy reveals the widening of lamina rara interna and newly formed lamina densa (B). The peritubular capillary basement membrane is also multilayered (C). (A; Methenamine silver stain, ×400, B; Electron microscopy, ×3,000, C; Electron microscopy, ×10,000) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download