Abstract
Background
Infection is a major cause of morbidity and mortality following liver transplants. We evaluated the risk factors of mortality within 1 month of liver transplantation caused by post-transplant infections.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 199 patients who underwent liver transplants from September 2005 to August 2010. We divided the enrolled patients into 3 groups. The first group, the Culture(-) group, was defined as those who had no significant culture results. The second group, the Culture(+)/survival group, was defined as those who tested positive for culture but survived longer than 1 month after transplantation. The third group, the Culture(+)/mortality group, was defined as those who died within 1 month of the transplant with positive culture test results.
Results
The culture(+)/mortality group consisted of more deceased donor liver transplants than other groups. Also, the Culture(+)/mortality group showed more evidence of pre-transplant infections, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, continuous post-transplant renal replacement therapy (CRRT), and a higher MELD score than other groups. The risk factors of early mortality combined with infection 1 month after liver transplantation are hospitalization in ICU before transplantation (HR=16.3, CI=2.6∼102.3, P=0.003) and the positive results of culture within 7 days of the operation (HR=38.7, CI=4.1∼368.8, P=0.001).
Go to : 
References
1). Varo Perez E, Castroagudin JF. The future of liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:613–6.
2). Razonable RR, Findlay JY, O'Riordan A, Burroughs SG, Ghobrial RM, Agarwal B, et al. Critical care issues in patients after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2011; 17:511–27.

3). Kim SI, Kim YJ, Jun YH, Wie SH, Kim YR, Choi JY, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for bacteremia in 144 consecutive living-donor liver transplant recipients. Yonsei Med J. 2009; 50:112–21.

4). Markin RS, Stratta RJ, Woods GL. Infection after liver transplantation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990; 14(Suppl 1):64–78.
5). Fishman JA, Rubin RH. Infection in organ-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1741–51.

6). Paya CV, Hermans PE. Bacterial infections after liver transplantation. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989; 8:499–504.

7). Kusne S, Dummer JS, Singh N, Iwatsuki S, Makowka L, Esquivel C, et al. Infections after liver transplantation. An analysis of 101 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1988; 67:132–43.
8). Reid GE, Grim SA, Sankary H, Benedetti E, Oberholzer J, Clark NM. Early intra-abdominal infections associated with orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2009; 87:1706–11.

9). Dehghani SM, Derakhshan A, Taghavi SA, Gholami S, Jalaeian H, Malek-Hosseini SA. Prevalence and risk factors of renal dysfunction after liver transplant: a singlecenter experience. Exp Clin Transplant. 2008; 6:25–9.
10). Nah YW, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, Hwang S, Choi DL, et al. Infection after adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2001; 15:93–105. (나양원, 이승규, 이영주, 박광민, 황신, 최동락 등. 성인대 성인간 생체 부분 간이식 후 감염. 대한이식학회지 2001;15: 93–105.).
11). Bekeris LG, Jones BA, Walsh MK, Wagar EA. Urine culture contamination: a College of American Pathologists Q-Probes study of 127 laboratories. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:913–7.

13). Corona A, Raimondi F. Prevention of nosocomial infection in the ICU setting. Minerva Anestesiol. 2004; 70:329–37.
14). Hanaoka N, Araki M. Problem of infection in the ICU. Masui. 2010; 59:46–55.
15). Valles J, Ferrer R. Bloodstream infection in the ICU. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009; 23:557–69.
16). Sun HY, Cacciarelli TV, Singh N. Identifying a targeted population at high risk for infections after liver transplantation in the MELD era. Clin Transplant. 2011; 25.

17). Benckert C, Quante M, Thelen A, Bartels M, Laudi S, Berg T, et al. Impact of the MELD allocation after its implementation in liver transplantation. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:941–8.

18). Selzner M, Kashfi A, Cattral MS, Selzner N, McGilvray ID, Greig PD, et al. Live donor liver transplantation in high MELD score recipients. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:153–7.

19). Brandao A, Fuchs SC, Gleisner AL, Marroni C, Zanotelli ML, Cantisani G. Liver Transplantation Group. MELD and other predictors of survival after liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2009; 23:220–7.
20). Schaub N, Frei R, Muller C. Addressing unmet clinical needs in the early diagnosis of sepsis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2011; 141:w13244.

21). Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:138–50.

Go to : 
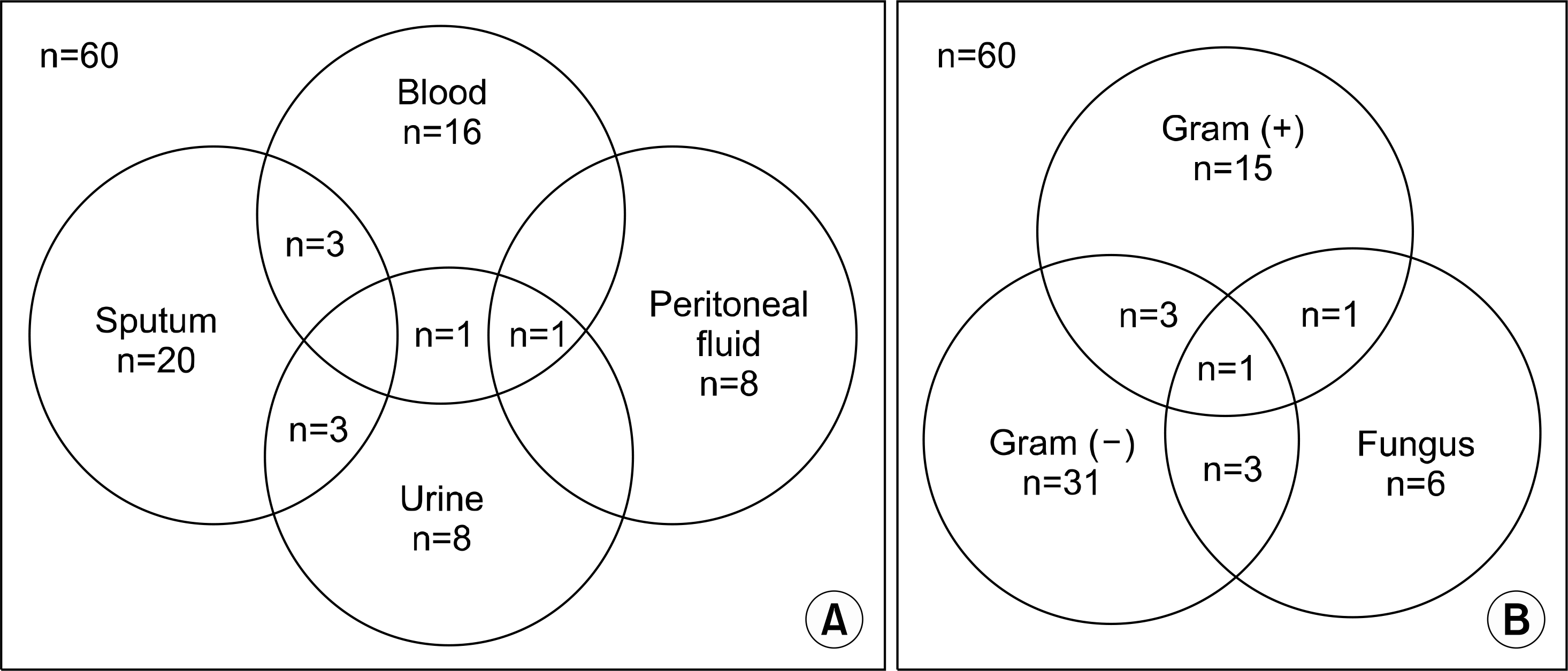 | Fig. 1.Sites and organisms of positive culture results within 7 days after liver transplantation. (A) Positive culture results of each sample. (B) Organism distribution of positive culture results. |
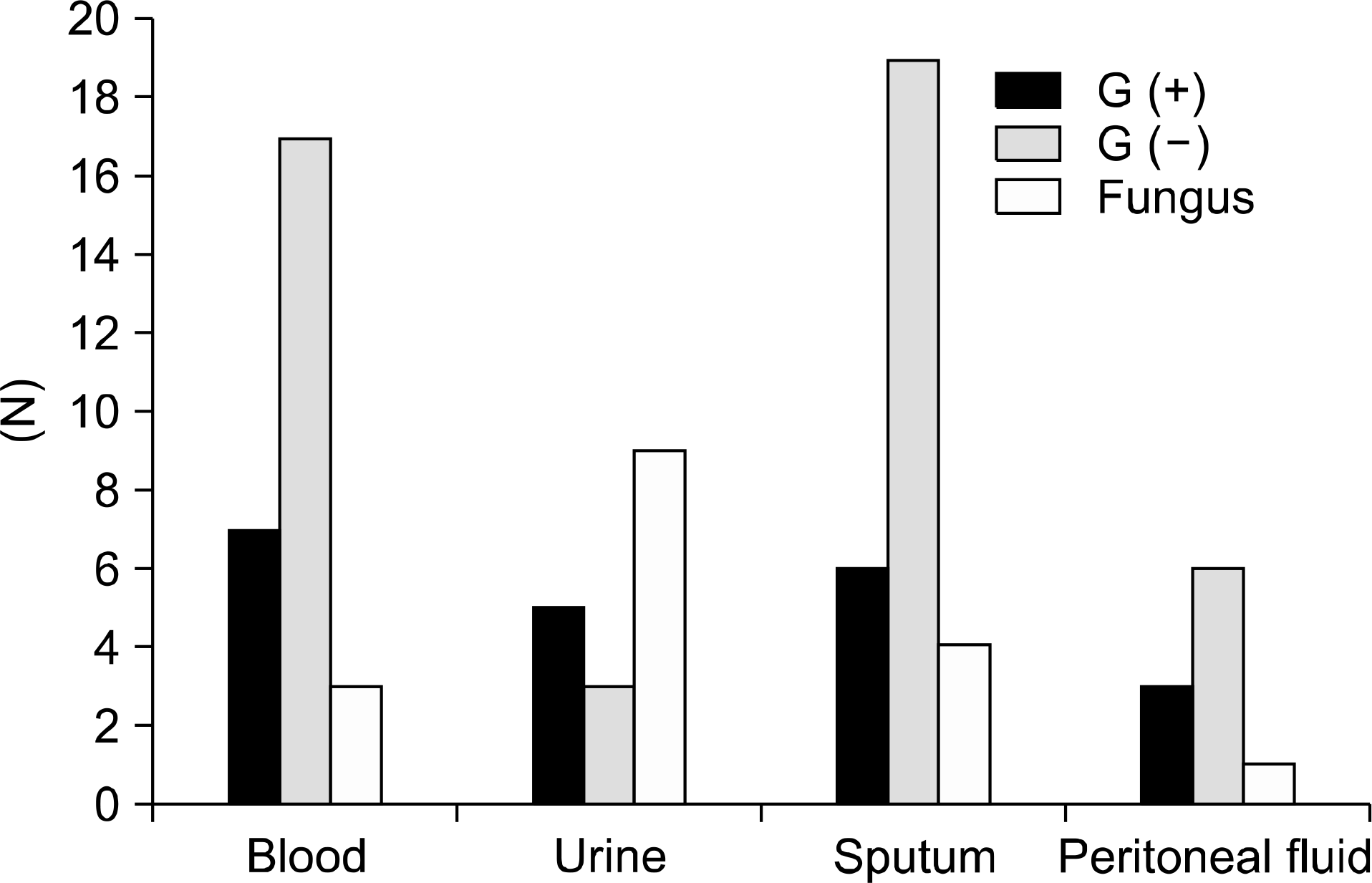 | Fig. 2.Organism distribution according to the culture site (n=60, data were duplicately included). |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics associated with significantly positive result of culture within 7 days after transplantation
Table 2.
Comparison of pre, intra, and postoperative clinical characteristics between three groups
Table 3.
Relation between the culture results of each sample and positive culture related mortality (data were overlaped)
Table 4.
Risk factor analysis of posttransplant mortality combined with infection within 1 month by logistic regression analysis




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download