Abstract
In previous decades, pediatric liver transplantation has become a state-of-the-art operation with excellent success and limited mortality. Graft and patient survival have continued to improve as a result of proper selection criteria for both donors and recipients, improvement in medical, surgical and anesthetic management, organ availability, balanced immunosuppression, and early identification and treatment of postoperative complications. Most of all, refinements of the technique has directly related to good outcome. Therefore rapid establishment of surgical knowhow is mandatory. In pediatric liver transplantation, the utilization of split-liver grafts and grafts for living donors has provided more organs for pediatric patients and has had a significant impact on graft and patient survival. This has been one of the brilliant outcomes of surgical evolution. In addition, new surgical technique of minimal invasive live donor surgery has been recently widening the living donor liver transplantation for children. Although the recent outcome has been rapidly improved and the volume of living donor liver transplantation has been larger and larger in Korea, pediatric liver transplantation has been performed in a very limited large volume centers. Therefore, this review focuses on surgical technique in order to share the experiences and to improve the outcome of pediatric liver transplantation.
Go to : 
References
1). Starzl TE. The puzzle people: memoirs of a transplant surgeon. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press;1992. p. 145–54.
2). Lee SK. Outline and state of liver transplantation. Park YH, Kim SH, editors. Hepato-biliaty-pancreatic surgery. 2nd ed.Seoul: Ŭ ihak Munhwasa;2006. p. 553–62. (이승규. 간이식의 개요 및 현황. In: 박용현, 김선희, 등. 간담췌외과학. 제2판. 서울: 의학문화사; 2006: 553–62.).
3). Spada M, Riva S, Maggiore G, Cintorino D, Gridelli B. Pediatric liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:648–74.

4). Guiteau JJ, Cotton RT, Karpen SJ, O' Mahony CA, Goss JA. Pediatric liver transplantation for primary malignant liver tumors with a focus on hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: the UNOS experience. Pediatr Transplant. 2010; 14:326–31.

5). Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). 2009 Annual Data Report [Internet]. Seoul: KONOS;2010. [cited 2010 Sep 20]. Available from:. http://www.konos.go.kr.
6). Cho JW. Cadevaric liver transplantation. Park YH, Kim SH, editors. Hepato-biliaty-pancreatic surgery. 2nd ed.Seoul: Ŭ ihak Munhwasa;2006. p. 563–72. (조재원. 사체간이식. In: 박용현, 김선희, 등. 간담췌외과학. 제2판. 서울: 의학문화사; 2006: 563–72.).
7). Jin US, Chang H, Minn KW, Yi NJ, Suh KS. Microvascular anastomosis of hepatic artery in children undergoing liver tTransplantation. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 33:454–7. (진웅식, 장학, 민경원, 이남준, 서경석. 소아 간이식에서 간동맥의 미세혈관 문합술. 대한성형외과학회지 2006;33: 454–7.).
8). Ueda M, Oike F, Kasahara M, Ogura Y, Ogawa K, Haga H, et al. Portal vein complications in pediatric living donor liver transplantation using left-side grafts. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8:2097–105.

9). Egawa H, Tanaka K, Kasahara M, Takada Y, Oike F, Ogawa K, et al. Single center experience of 39 patients with preoperative portal vein thrombosis among 404 adult living donor liver transplantations. Liver Transpl. 2006; 12:1512–8.

10). Lee SG, Moon DB, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Hwang S, Park KM, et al. Ligation of left renal vein for large spontaneous splenorenal shunt to prevent portal flow steal in adult living donor liver transplantation. Transpl Int. 2007; 20:45–50.

11). Sakamoto S, Egawa H, Ogawa K, Ogura Y, Oike F, Ueda M, et al. The technical pitfalls of duct-to-duct biliary reconstruction in pediatric living-donor left-lobe liver transplantation: the impact of stent placement. Pediatr Transplant. 2008; 12:661–5.

12). Bismuth H, Houssin D. Reduced-sized orthotopic liver graft in hepatic transplantation in children. Surgery. 1984; 95:367–70.
13). Yi NJ, Suh KS. Technical evolution in living donor liver transplantation. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2006; 20:149–59. (이남준, 서경석. 생체 간이식 술기의 변화와 발전. 대한이식학회지 2006;20: 149–59.).
14). Suh KS. Technical variations in living donor liver transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transpl. 2004; 9:90–8.

16). Strong RW, Lynch SV, Ong TH, Matsunami H, Koido Y, Balderson GA. Successful liver transplantation from a living donor to her son. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:1505–7.

17). Pichlmayr R, Ringe B, Gubernatis G, Hauss J, Bunzendahl H. [Transplantation of a donor liver to 2 recipients (splitting transplantation)–a new method in the further development of segmental liver transplantation]. Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1988; 373:127–30.
18). Rogiers X, Malago M, Gawad KA, Kuhlencordt R, Fröschle G, Sturm E, et al. One year of experience with extended application and modified techniques of split liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1996; 61:1059–61.
19). Suh KS, Lee KW, Koh YT, Roh HR, Chung JK, Minn KW, et al. First successful in situ split-liver transplantation in Korea. Transplant Proc. 2000; 32:2140.

20). Shirouzu Y, Ohya Y, Hayashida S, Yoshii T, Asonuma K, Inomata Y. Reduction of left-lateral segment from living donors for liver transplantation in infants weighing less than 7 kg: technical aspects and outcome. Pediatr Transplant. 2010; 14:709–14.

21). Lee SG. Living donor liver transplantation. Park YH, Kim SH, editors. Hepato-biliaty-pancreatic surgery. 2nd ed.Seoul: Ŭ ihak Munhwasa;2006. p. 573–85. (이승규. 생체부분간이식. In: 박용현, 김선희, 등. 간담췌외과학. 제2판. 서울: 의학문화사; 2006: 573–85.).
22). Suh KS, Kim TH, Shin WY, Yi NJ, Minn KW, Lee KU. Living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) using monosegment graft for a small infant. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2009; 23:85–8. (서경석, 김태훈, 신우영, 이남준, 민경원, 이건욱. 작은 유아에게 시행된 단일 분절 이식편을 이용한 생체 간이식. 대한이식학회지 2009;23: 85–8.).
23). Attia MS, Stringer MD, McClean P, Prasad KR. The reduced left lateral segment in pediatric liver transplantation: an alternative to the monosegment graft. Pediatr Transplant. 2008; 12:696–700.

24). Thomas N, Thomas G, Verran D, Stormon M, O' Loughlin E, Shun A. Liver transplantation in children with hyperreduced grafts – a singlecenter experience. Pediatr Transplant. 2010; 14:426–30.

25). Yoo JY, Yi NJ, Suh KS, Kwon CH, Choi SH, Lee KU. Donor quality of life in living donor liver transplantation. J Korean Soc Transpl. 2004; 18:73–80. (유진영, 이남준, 서경석, 권준혁, 이건욱. 생체 부분 간이식 공여자의 삶의 질에 관한 연구. 대한이식학회지 2004;18: 73–80.).
26). Cherqui D, Soubrane O, Husson E, Barshasz E, Vignaux O, Ghimouz M, et al. Laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy for liver transplantation in children. Lancet. 2002; 359:392–6.

27). Soubrane O, Cherqui D, Scatton O, Stenard F, Bernard D, Branchereau S, et al. Laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy in living donors: safety and reproducibility of the technique in a single center. Ann Surg. 2006; 244:815–20.
28). Kim KH, Jung DH, Park KM, Lee YJ, Kim DY, Kim KM, et al. Comparison of open and laparoscopic live donor left lateral sectionectomy. Br J Surg. 2011; 98:1302–8.

29). Lee KW, Kim SH, Han SS, Kim YK, Cho SY, You T, et al. Use of an upper midline incision for living donor partial hepatectomy: A series of 143 consecutive cases. Liver Transpl. 2011; 17:969–75.

30). Sakamoto S, Egawa H, Kanazawa H, Shibata T, Miyaga-wa-Hayashino A, Haga H, et al. Hepatic venous outflow obstruction in pediatric living donor liver transplantation using left-sided lobe grafts: Kyoto University experience. Liver Transpl. 2010; 16:1207–14.

31). Mathes SJ, Hentz VR. Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier;2006.
32). Cheong HI, Lee BS, Kang HG, Hahn H, Suh KS, Ha IS, et al. Attempted treatment of factor H deficiency by liver transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2004; 19:454–8.
33). Suh KS. Auxiliary partial orthotopic liver transplantation. Park YH, Kim SH, editors. Hepato-biliaty-pancreatic surgery. 2nd ed.Seoul: Ŭ ihak Munhwasa;2006. p. 586–9. (서경석. 보조간이식. In: 박용현, 김선희, 등. 간담췌외과학. 제2판. 서울: 의학문화사; 2006: 586–9.).
Go to : 
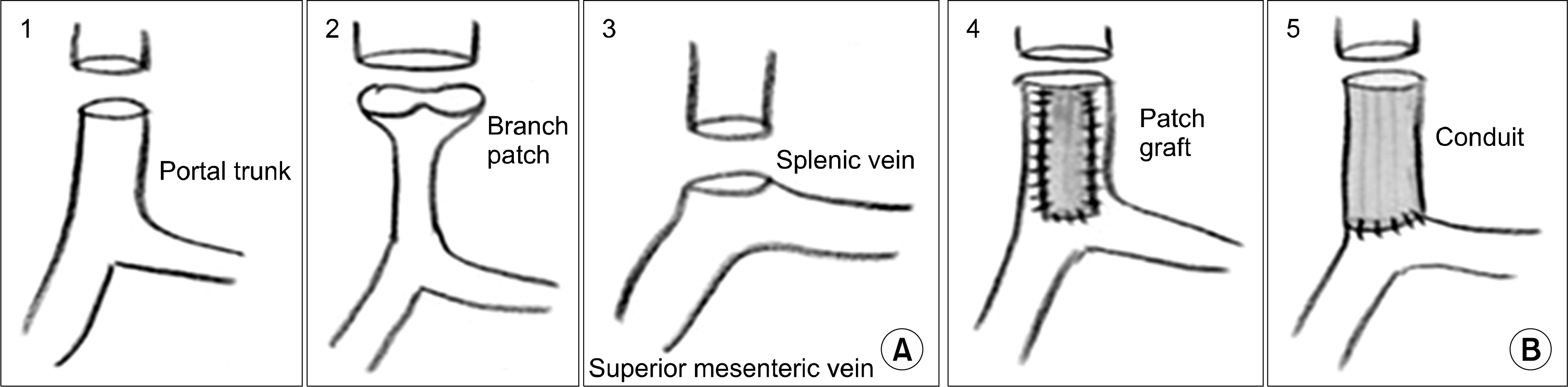 | Fig. 1.Portal vein reconstruction. (A) Portal vein reconstruction without vein graft, (B) Portal vein reconstruction with vein conduit from donor. Reprinted from reference (7). |
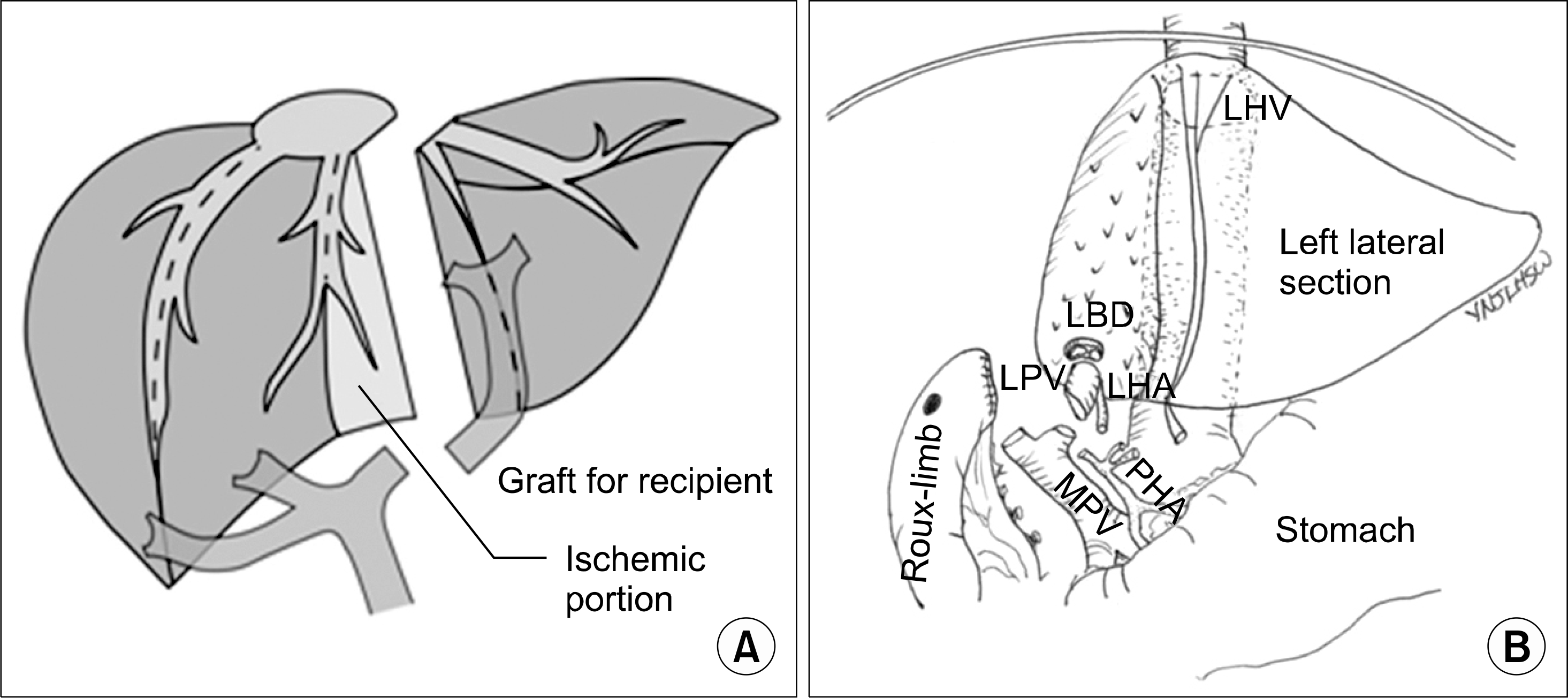 | Fig. 2.Living donor liver transplantation. (A) Left lateral sectionectomy in a live donor. There is usually no ischemia and congestion in the graft, but the left medial section and a part of caudate lobe become ischemic in the remnant liver of the donor. (B) Hepatic vein anastomosis and the position of the graft in transplantation of a left lateral section. Reprinted from reference (12,13). Abbreviations: LHV, left hepatic vein; LBD, left bile duct; LPV, left portal vein; MPV, main portal vein; PHA, proper hepatic artery. |
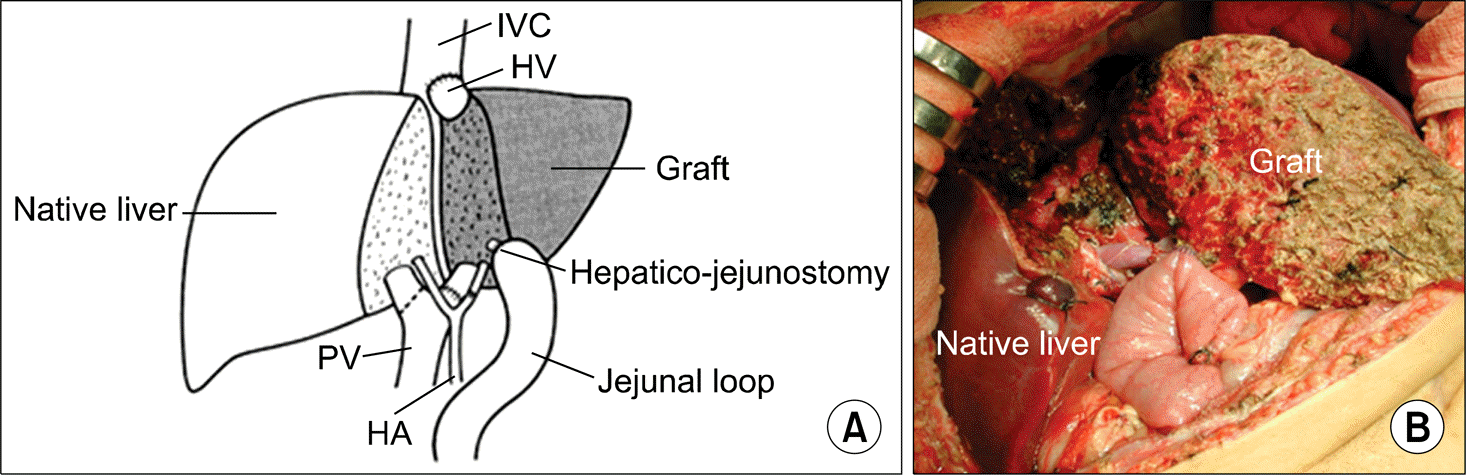
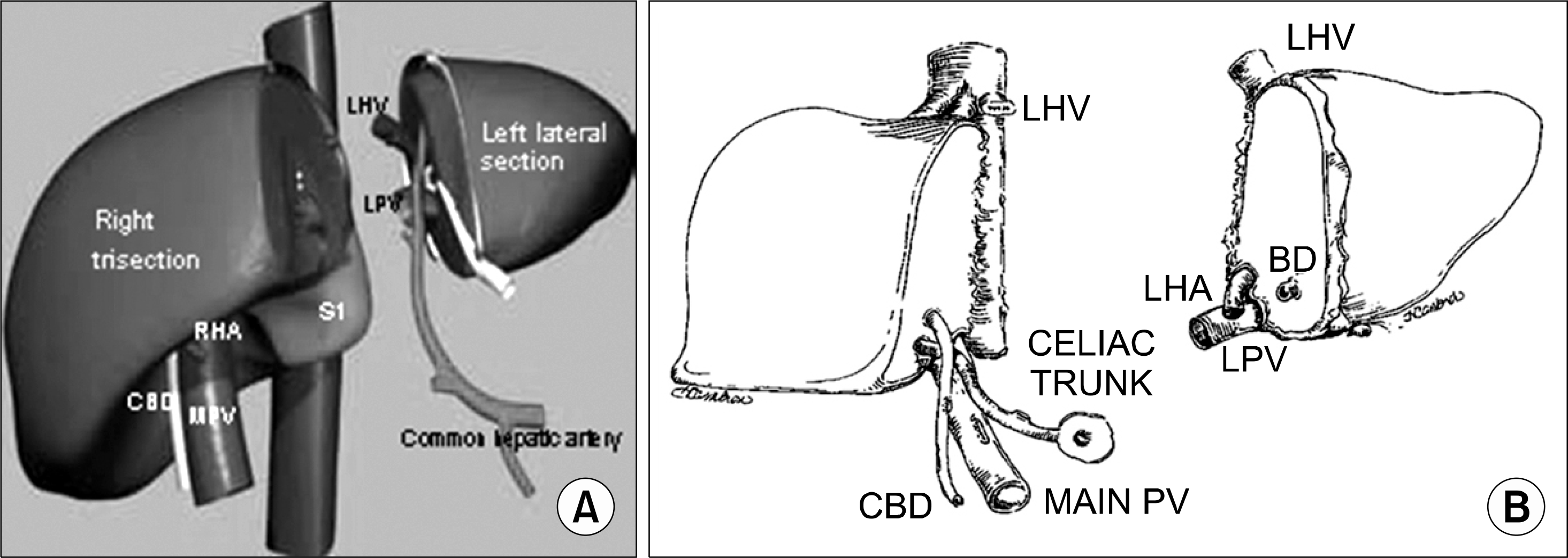 | Fig. 3.Split liver transplantation of left lateral section and right trisection. (A) Classic split technique. The left graft composed of segment 2 and 3 includes the left hepatic vein, the left portal vein, the left hepatic artery from the common hepatic artery and the celiac triad, and the left hepatic duct. The right graft composed of segment 1 and 4∼8 includes the vena cava, the main portal vein, the right hepatic artery, and common bile duct. Reprinted from reference (3). Adapted split technique mimicking a graft from a live donor. The difference of the classical split liver graft is the arterial division level. Usually the left lateral graft includes only the left hepatic artery. Reprinted from reference (19). Abbreviations: BD, bile duct; CBD, common bile duct; PV, portal vein; LHV, left hepatic vein; LPV, left portal vein; S, segment. |
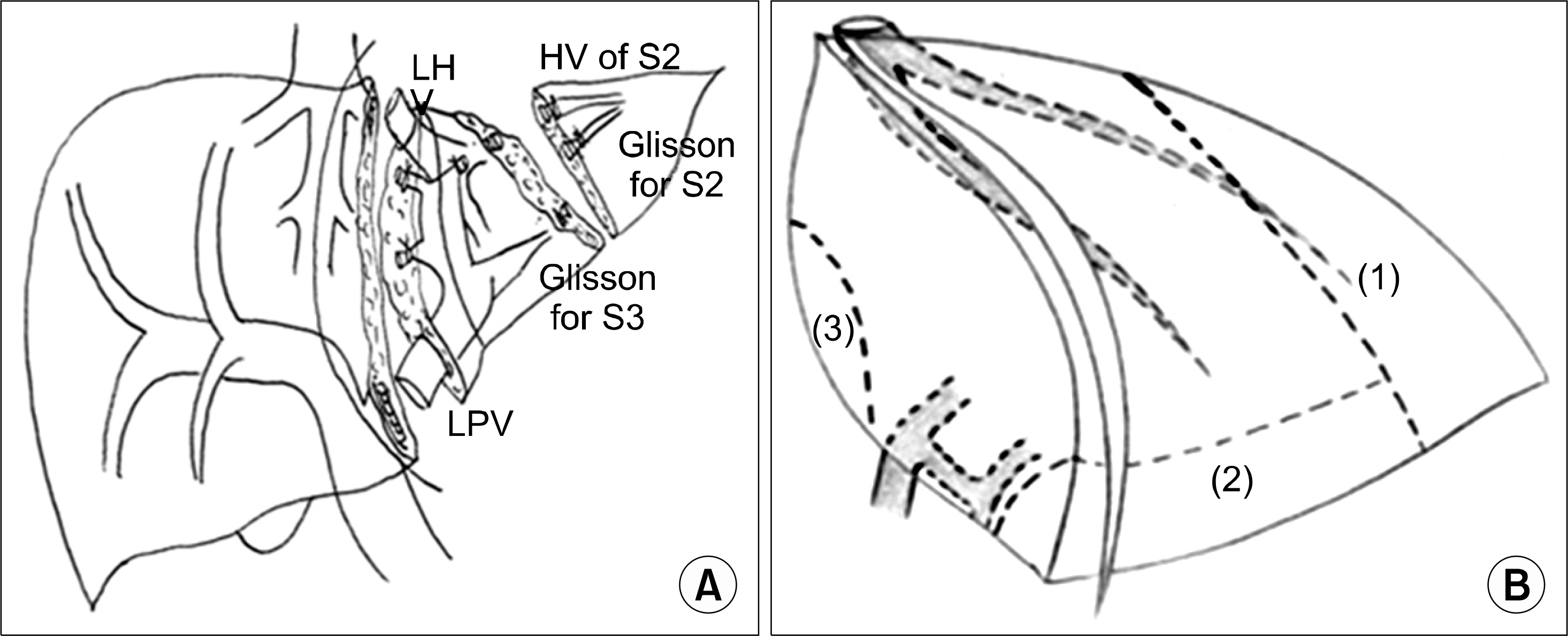 | Fig. 4.Reduced left lateral section. (A) Monosegment (Segment 3). Reprinted from reference (22). (B) Hyperreduced left lateral section (LLS). Cutting lines to reduce a LLS; (1) the lateral part of the LLS is resected first while preserving the medial branches of the LHV.(2) Further resection of the caudal part is performed without ligation of any portal branches of the S3. (3) The additional resection of the dorsal part is carried out, while preserving portal branches of the S2. Reprinted from reference (20). Abbreviations: HV, hepatic vein; LHV, left hepatic vein; LPV, left portal vein; S, segment. |
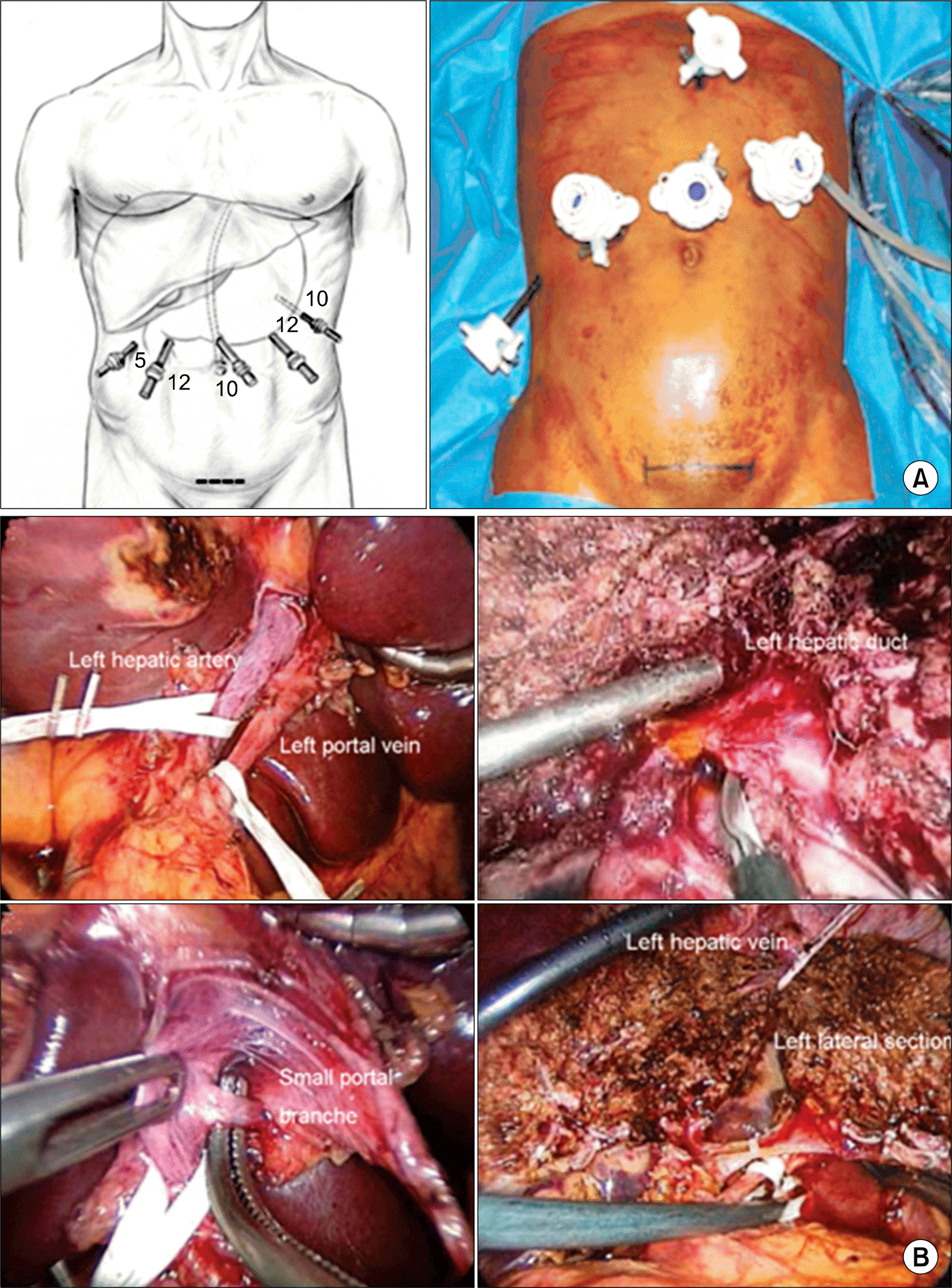 | Fig. 5.Laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy in a live donor. (A) Port placement (n=port size, mm) for laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy in a live donor. (B) Division of the left portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct, and hepatic vein for harvest of a left lateral section. Reprinted from reference (26,27). |
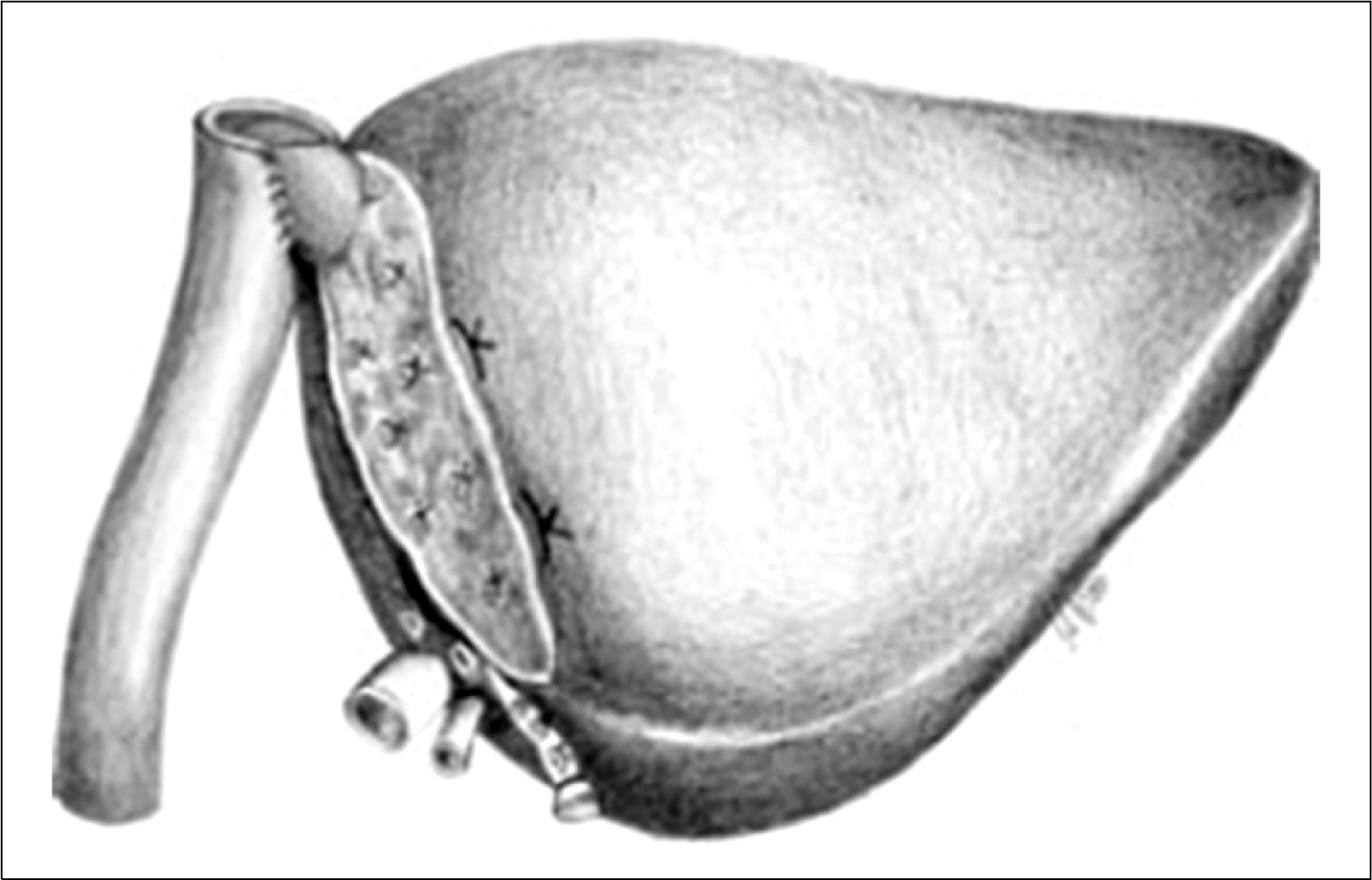 | Fig. 6.Use of a left lateral section graft to a recipient affected hepatic malignancy with replacement of the recipient's IVC using a cryopreserved iliac vein. Reprinted from reference (3). |
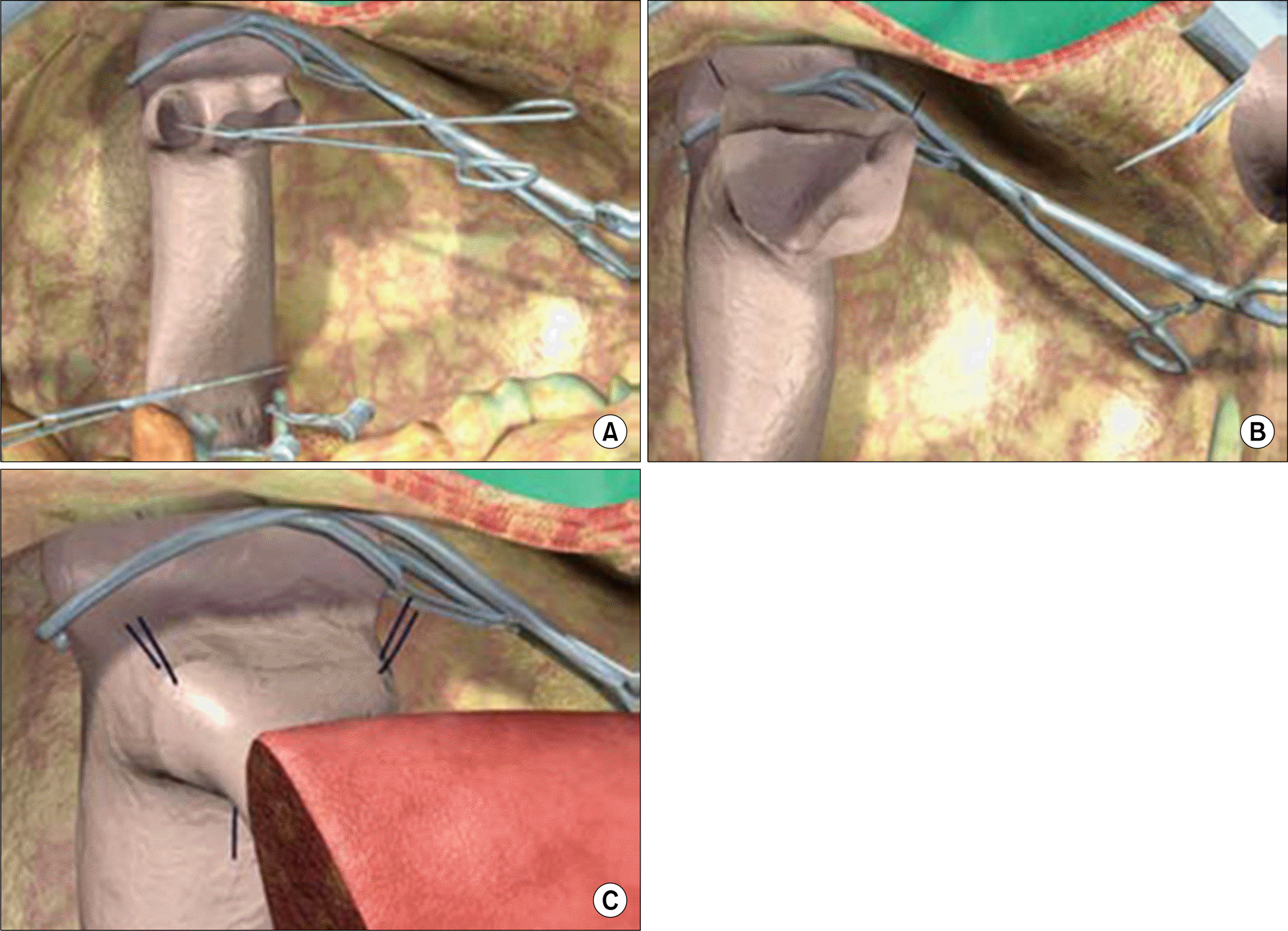 | Fig. 7.Anastomosis between the left hepatic vein of the graft and the inferior vena cava of the recipient, performed with the triangulation technique. (A) Total clamp of the IVC for reconstruction of hepatic vein. The bridge between the ostia of the right, middle, and left hepatic veins is cut to obtain a single opening. (B) Enlargement of IVC opening. The opening is further enlarged by cutting the anterior face of the vena cava to obtain a wide triangular orifice. (C) Anastomosis of the left hepatic vein to the IVC. Reprinted from reference (3). |
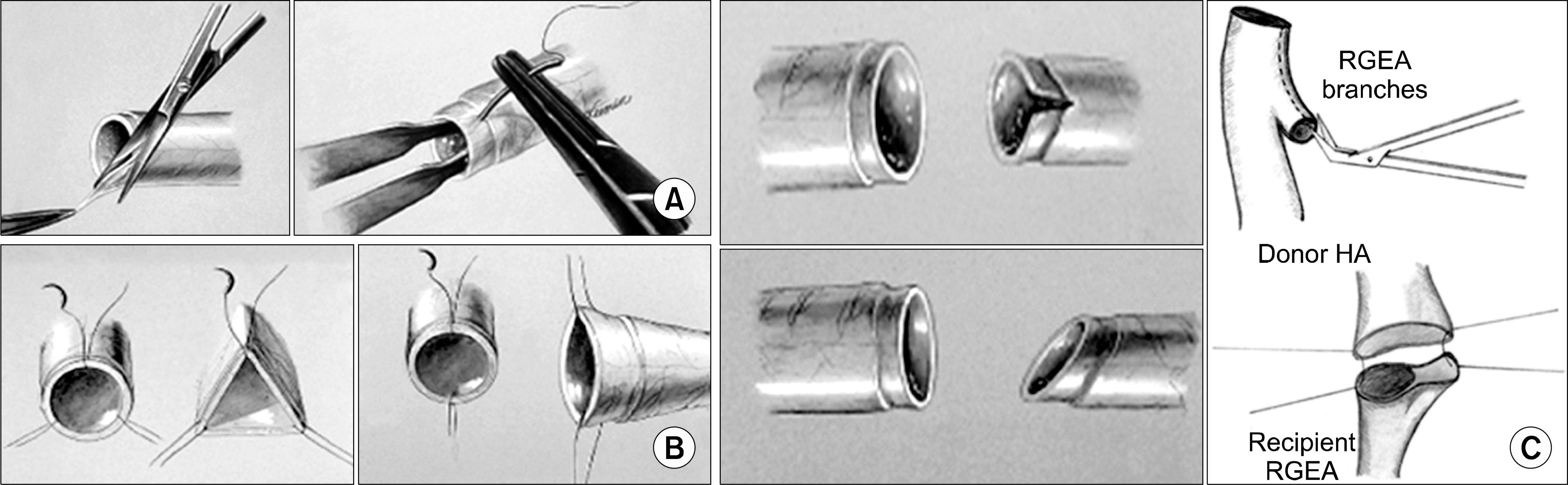 | Fig. 8.Microscopic technique of hepatic artery anastomosis. (A) Adventisectomoy of the end of the hepatic artery reducing thrombosis. ① Adventisectomoy of the end of the hepatic artery. ② Proper needling for hepatic artery anastomosis. (B) End-to-end anastomosis of hepatic artery. ① Carrel technique. ② Seidenberg technique. (C) Overcome size discrepancy of hepatic artery anastomosis. ① Fish mouth technique. ② Oblique technique. ③ Branch patch technique using the small right gastroepiploic artery of the recipient. Abbreviation: RGEA, right gastroepiploic artery. Reprinted from reference (31). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download