Abstract
The growing shortage of organs for orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) has led to an expanded donor pool with the use of marginal grafts. Recipients who receive liver grafts from HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc positive donors have an increased risk of developing de novo hepatitis B infection. This review covers several issues in liver transplantation using hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors: (1) the mechanism of de novo hepatitis B infection, (2) high risk groups, (3) prophylactic regimens and (4) clinical significance and a proposal for patients in Korea.
Go to : 
References
1). Wachs ME, Amend WJ, Ascher NL, Bretan PN, Emond J, Lake JR, et al. The risk of transmission of hepatitis B from HBsAg(−), HBcAb(+), HBIgM(−) organ donors. Transplantation. 1995; 59:230–4.

2). Donataccio D, Roggen F, del Reyck C, Verbaandert C, Bodeus M, Lerut J. Use of anti-HBc positive allografts in adult liver transplantation: toward a safer way to expand the donor pool. Transpl Int. 2006; 19:38–43.

3). Dickson RC, Everhart JE, Lake JR, Wei Y, Seaberg EC, Wiesner RH, et al. Transmission of hepatitis B by transplantation of livers from donors positive for antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Liver Transplantation Database. Gastroenterology. 1997; 113:1668–74.

4). Prieto M, Gómez MD, Berenguer M, C órdoba J, Ray ón JM, Pastor M, et al. De novo hepatitis B after liver transplantation from hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors in an area with high prevalence of anti-HBc positivity in the donor population. Liver Transpl. 2001; 7:51–8.

5). Liu CJ, Chen DS, Chen PJ. Epidemiology of HBV infection in Asian blood donors: emphasis on occult HBV infection and the role of NAT. J Clin Virol. 2006; 36(Suppl 1):S33–44.

6). Lo CM, Fan ST, Liu CL, Yong BH, Wong Y, Ng IO, et al. Safety and outcome of hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors in right-lobe living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2003; 9:827–32.

7). Chen YS, Wang CC, de Villa VH, Wang SH, Cheng YF, Huang TL, et al. Prevention of de novo hepatitis B virus infection in living donor liver transplantation using hepatitis B core antibody positive donors. Clin Transplant. 2002; 16:405–9.

8). Saab S, Waterman B, Chi AC, Tong MJ. Comparison of different immunoprophylaxis regimens after liver transplantation with hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors: a systematic review. Liver Transpl. 2010; 16:300–7.

9). Takemura N, Sugawara Y, Tamura S, Makuuchi M. Liver transplantation using hepatitis B core antibody-positive grafts: review and university of Tokyo experience. Dig Dis Sci. 2007; 52:2472–7.

10). Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV, Burroughs AK. Liver grafts from anti-hepatitis B core positive donors: a systematic review. J Hepatol. 2010; 52:272–9.

11). Sugauchi F, Orito E, Ohno T, Kato H, Suzuki T, Hashimoto T, et al. Liver transplantation-associated de novo hepatitis B virus infection: application of molecular evolutionary analysis. Intervirology. 2002; 45:6–10.

12). Raimondo G, Navarra G, Mondello S, Costantino L, Colloredo G, Cucinotta E, et al. Occult hepatitis B virus in liver tissue of individuals without hepatic disease. J Hepatol. 2008; 48:743–6.

13). Raimondo G, Pollicino T, Romanò L, Zanetti AR. A 2010 update on occult hepatitis B infection. Pathol Biol (Paris) [in press 2010 Mar 18].
14). Blackberg J, Kidd-Ljunggren K. Occult hepatitis B virus after acute self-limited infection persisting for 30 years without sequence variation. J Hepatol. 2000; 33:992–7.
15). Marusawa H, Uemoto S, Hijikata M, Ueda Y, Tanaka K, Shimotohno K, et al. Latent hepatitis B virus infection in healthy individuals with antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen. Hepatology. 2000; 31:488–95.

16). Kwon CH, Suh KS, Cho JY, Yi NJ, Jang JJ, Lee KU. Change of hepatitis B virus DNA status in anti-HBc positive liver graft. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:191–200. (권 준혁, 서 경 석, 조 재 영, 이 남 준, 장 자 준, 이 건 욱. Anti-HBc 양 성인 간 이 식 편 내 B형 간 염 바 이 러 스 DNA 발 현 의 변 화. 대 한간 학 회 지 2006;12: 191–200.).
17). Hu KQ. Occult hepatitis B virus infection and its clinical implications. J Viral Hepat. 2002; 9:243–57.

18). Hui CK, Cheung WW, Zhang HY, Au WY, Yueng YH, Leung AY, et al. Kinetics and risk of de novo hepatitis B infection in HBsAg-negative patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:59–68.

19). Matsue K, Aoki T, Odawara J, Fujiwara H, Iwama K, Kimura S, et al. High risk of hepatitis B-virus reactivation after hematopoietic cell transplantation in hepatitis B core antibody-positive patients. Eur J Haematol. 2009; 83:357–64.

20). Hollinger FB, Sood G. Occult hepatitis B virus infection: a covert operation. J Viral Hepat. 2010; 17:1–15.

21). Yeo W, Chan TC, Leung NW, Lam WY, Mo FK, Chu MT, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in lymphoma patients with prior resolved hepatitis B undergoing anticancer therapy with or without rituximab. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:605–11.

22). Samuel D, Forns X, Berenguer M, Trautwein C, Burroughs A, Rizzetto M, et al. Report of the monothematic EASL conference on liver transplantation for viral hepatitis (Paris, France, January 12–14, 2006). J Hepatol. 2006; 45:127–43.
23). Mindikoglu AL, Regev A, Schiff ER. Hepatitis B virus reactivation after cytotoxic chemotherapy: the disease and its prevention. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:1076–81.

24). Yeo W, Johnson PJ. Diagnosis, prevention and management of hepatitis B virus reactivation during anticancer therapy. Hepatology. 2006; 43:209–20.

25). Kusumoto S, Tanaka Y, Mizokami M, Ueda R. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus following systemic chemotherapy for malignant lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2009; 90:13–23.

26). Dhédin N, Douvin C, Kuentz M, Saint Marc MF, Reman O, Rieux C, et al. Reverse seroconversion of hepatitis B after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a retrospective study of 37 patients with pretransplant an-ti-HBs and anti-HBc. Transplantation. 1998; 66:616–9.
27). Seth P, Alrajhi AA, Kagevi I, Chaudhary MA, Colcol E, Sahovic E, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation with clinical flare in allogeneic stem cell transplants with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002; 30:189–94.

28). Natov SN, Pereira BJ. Transmission of viral hepatitis by kidney transplantation: donor evaluation and transplant policies (Part 1: hepatitis B virus). Transpl Infect Dis. 2002; 4:117–23.
29). Hartwig MG, Patel V, Palmer SM, Cantu E, Appel JZ, Messier RH, et al. Hepatitis B core antibody positive donors as a safe and effective therapeutic option to increase available organs for lung transplantation. Transplantation. 2005; 80:320–5.

30). Veroux M, Puliatti C, Gagliano M, Cappello D, Macarone M, Vizcarra D, et al. Use of hepatitis B core antibody-positive donor kidneys in hepatitis B surface antibody-positive and -negative recipients. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37:2574–5.

31). Dhillon GS, Levitt J, Mallidi H, Valentine VG, Gupta MR, Sista R, et al. Impact of hepatitis B core antibody positive donors in lung and heart-lung transplantation: an analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing Database. Transplantation. 2009; 88:842–6.

32). Chang SH, Suh KS, Yi NJ, Choi SH, Lee HJ, Seo JK, et al. Active immunization against de novo hepatitis B virus infection in pediatric patients after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2003; 37:1329–34.

33). Kim SJ, Hwang SJ, Park SE, Choi YH, Lee SK, Joe JW, et al. Efficacy of hepatitis b immune globulin for prevention of de novo hepatitis b in living-related liver transplantation. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003; 6:32–8. (김 상 종, 황 수 정, 박 성 은, 최 연 호, 이 석 구, 조 재 원, 등. 생 체 부 분 간 이 식에 서 de novo hepatitis B에 대 한 B형 간 염 면 역 글로 불 린 의 예 방 적 효 과. 대 한 소 아 소 화 기 영 양 학 회 지 2003;6: 32–8.).

34). Douglas DD, Rakela J, Wright TL, Krom RA, Wiesner RH. The clinical course of transplantation-associated de novo hepatitis B infection in the liver transplant recipient. Liver Transpl Surg. 1997; 3:105–11.

35). Uemoto S, Sugiyama K, Marusawa H, Inomata Y, Asonuma K, Egawa H, et al. Transmission of hepatitis B virus from hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors in living related liver transplants. Transplantation. 1998; 65:494–9.

36). Avelino-Silva VI, D Albuquerque LA, Bonazzi PR, Song AT, Miraglia JL, de Brito Neves A, et al. Liver transplant from Anti-HBc-positive, HBsAg-negative donor into HBsAg-negative recipient: is it safe? A systematic review of the literature. Clin Transplant [in press 2010 Apr 28].
37). de Villa VH, Chen YS, Chen CL. Hepatitis B core antibody-positive grafts: recipient's risk. Transplantation. 2003; 75(3 Suppl):S49–53.

38). Roque-Afonso AM, Feray C, Samuel D, Simoneau D, Roche B, Emile JF, et al. Antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen prevent viral reactivation in recipients of liver grafts from anti-HBC positive donors. Gut. 2002; 50:95–9.

39). Tur-Kaspa R, Laub O. Corticosteroids stimulate hepatitis B virus DNA, mRNA and protein production in a stable expression system. J Hepatol. 1990; 11:34–6.

40). Lee JP, Heo NJ, Joo KW, Yi NJ, Suh KS, Moon KC, et al. Risk factors for consequent kidney impairment and differential impact of liver transplantation on renal function. Nephrol Dial Transplant [in press 2010 Mar 5].
41). Lee KW, Lee DS, Lee HH, Kim SJ, Joh JW, Seo JM, et al. Prevention of de novo hepatitis B infection from HbcAb-positive donors in living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2004; 36:2311–2.

42). Lim YA, Yoon S. An experience of the use of Anti-HBc and Anti-HBs for blood donor screening tests at a tertiary hospital blood center in Korea]. Korean J Lab Med. 2009; 29:59–65. (임 영 애, 윤 석 호. 일 개 삼 차 의 료 기 관 혈 액 원 에 서 헌 혈 자 선 별 검 사 로 서 의 anti-HBc와 anti-HBs 검 사 의 시 행 경 험. 일 개 삼 차 의 료 기 관 혈 액 원 에 서 헌 혈 자 선 별 검 사 로 서의 anti-HBc와 anti-HBs 검 사 의 시 행 경 험. 대 한 진 단 검 사의 학 회 지 2009;29: 59–65.).

43). Kwon CH, Suh KS, Yi NJ, Chang SH, Cho YB, Cho JY, et al. Long-term protection against hepatitis B in pediatric liver recipients can be achieved effectively with vaccination after transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2006; 10:479–86.

44). Radomski JS, Moritz MJ, Armenti VT, Munoz SJ. Hepatitis B transmission from a liver donor who tested negative for hepatitis B surface antigen and positive for hepatitis B core antibody. Liver Transpl Surg. 1996; 2:130–1.

45). Dodson SF, Bonham CA, Geller DA, Cacciarelli TV, Rakela J, Fung JJ. Prevention of de novo hepatitis B infection in recipients of hepatic allografts from anti-HBc positive donors. Transplantation. 1999; 68:1058–61.

46). Holt D, Thomas R, van Thiel D, Brems JJ. Use of hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors in orthotopic liver transplantation. Arch Surg. 2002; 137:572–5. discussion 5–6.

47). Jain A, Orloff M, Abt P, Kashyap R, Mohanka R, Lansing K, et al. Use of hepatitis B core antibody-positive liver allograft in hepatitis C virus-positive and -negative recipients with use of short course of hepatitis B immunoglobulin and lamivudine. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37:3187–9.

48). Suehiro T, Shimada M, Kishikawa K, Shimura T, Soejima Y, Yoshizumi T, et al. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection from hepatitis B core antibody-positive donor graft using hepatitis B immune globulin and lamivudine in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Int. 2005; 25:1169–74.

Go to : 
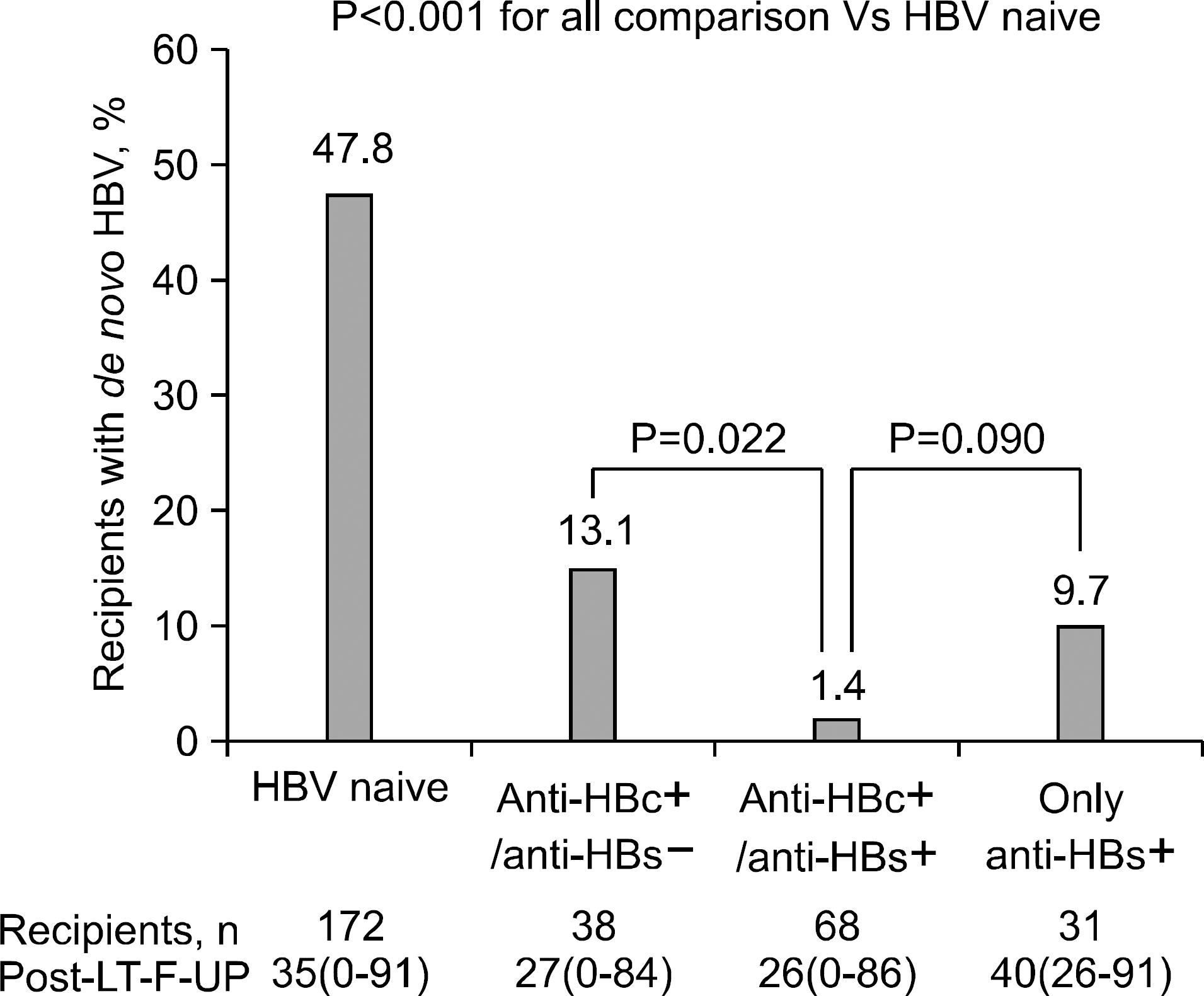 | Fig. 1.Risk of de novo hepatitis B infection in HBsAg-negative recipients after liver transplantation using anti-HBc positive liver graft without HBV prophylaxis in relation to pretransplant HBV serology of recipient. Abbreviations: HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; anti-HBc, hepatitis B core antibody; HBV, hepatitis B virus; LT, liver transplantation. Reprinted from Fig. 1 of reference [10]. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download