Abstract
Background:
Triple immunosuppressant therapy including antimetabolites is the representative immunosuppressive therapy after renal transplantation. This study is to evaluate the factors that influence Mycophenolate sodium (MPS, Myfortic, Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) dosage patterns in renal transplantation patients who take MPS as an inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) among antimetabolites.
Methods:
From May 2007 to April 2008, 16 clinical departments of 14 transplantation centers in Korea retrospectively per-formed a survey on 650 renal transplantation recipients taking MPS. This survey collected personal information, clinical factors related to transplantation and immunosuppressive therapy.
Results:
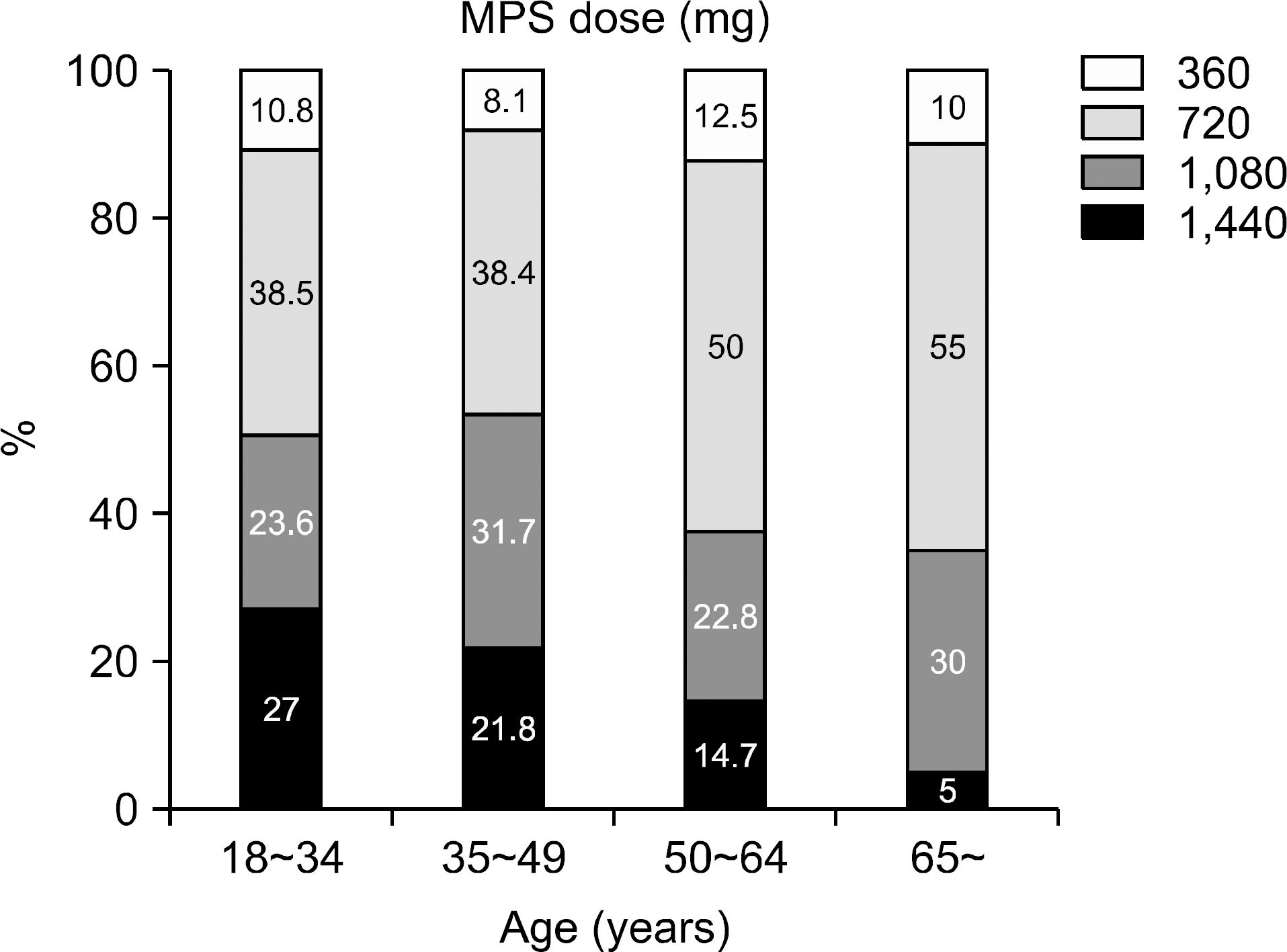
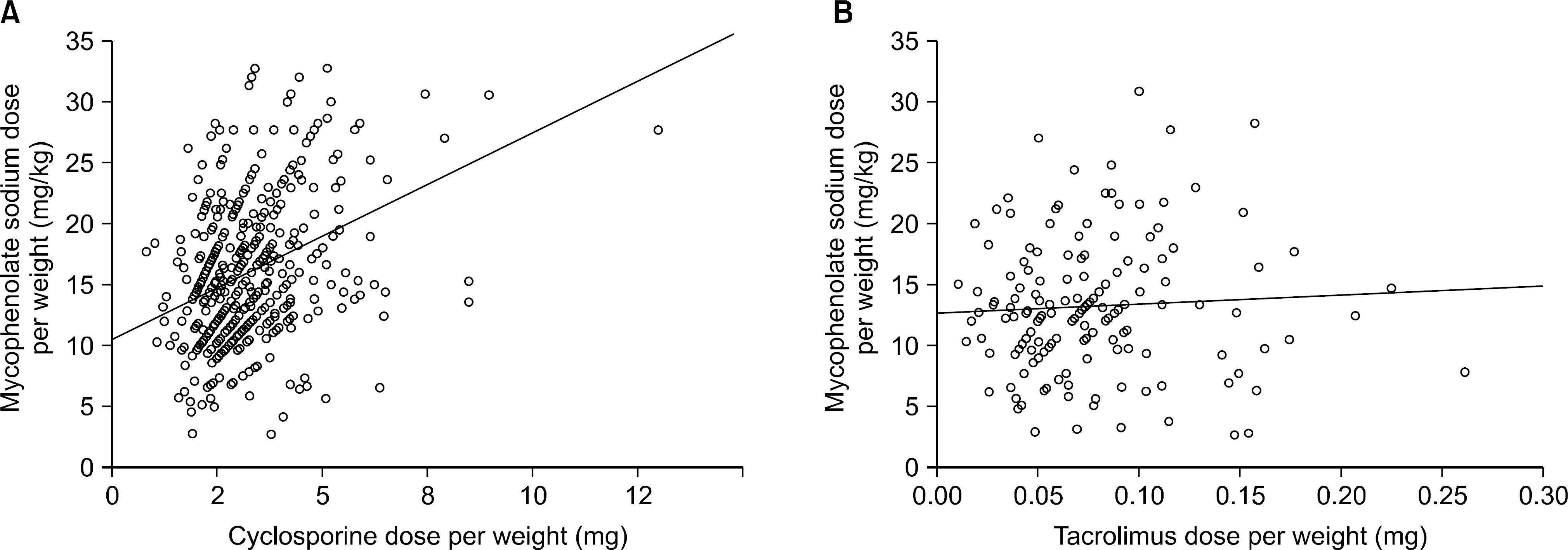
The mean age of the patients was 43.0±12.0 (7∼75) and the study included 364 males (56.0%) and 286 females (44.0%). The average follow up period after renal transplantation was 49.5±53.4 (1∼307) months. There were 366 (56.3%) living related cases, 145 (22.3%) living non-related cases and 139 (21.4%) deceased donor cases. Cyclosporine was the most common calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) used in combination therapy with MPS (476 cases, 73.2%) followed by tacrolimus (169 cases, 26.0%). The mean daily dose of MPS was 909.7±336.3 (180∼1,620)mg and the mean daily dose per kg was 15.3±5.9(2.65∼32.73)mg/kg. The daily dose showed significant positive correlation with patient body weight but the daily dose per kg showed negative correlation. The daily dose of MPS was significantly higher in the combination therapy with cyclosporine than that with tacrolimus. The daily dose and the dose per kg decreased with increment of recipient age and posttransplant period.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Sollinger HW. Mycophenolate mofetil for the prevention of acute rejection in primary cadaveric renal allograft recipients. U.S. Renal Transplant Mycophenolate Mofetil Study Group. Transplantation. 1995; 60:225–32.
2). Ekberg H, Tedesco-Silva H, Demirbas A, Vítko S, Nashan B, Gürkan A, et al. Reduced exposure to calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2562–75.

3). Pelletier RP, Akin B, Henry ML, Bumgardner GL, Elkhammas EA, Rajab A, et al. The impact of mycophenolate mofetil dosing patterns on clinical outcome after renal transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2003; 17:200–5.

4). Arns W, Breuer S, Choudhury S, Taccard G, Lee J, Binder V, et al. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium delivers bio-equivalent MPA exposure compared with mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Transplant. 2005; 19:199–206.

5). Sollinger H. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium: the-rapeutic equivalence to mycophenolate mofetil in de novo renal transplant patients. Transplant Proc. 2004; 36(Suppl 2S):517S–20S.

6). Offermann G. Five-year results of renal transplantation on immunosuppressive triple therapy with mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Transplant. 2003; 17:43–6.

7). Salvadori M, Holzer H, de Mattos A, Sollinger H, Arns W, Oppenheimer F, et al. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium is therapeutically equivalent to mycophenolate mofetil in de novo renal transplant patients. Am J Transplant. 2004; 4:31–6.
8). Nashan B, Suwelack B, Ivens K, Arns W, Lhotta K, Bourbigot B, et al. Conversion to enteric-coated myco-phenolate sodium from various doses of mycophenolate mofetil: results of a prospective international multicenter trial in maintenance renal transplant patients receiving cyclosporine. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:2856–9.

9). Budde K, Curtis J, Knoll G, Chan L, Neumayer HH, Seifu Y, et al. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium can be safely administered in maintenance renal transplant patients: results of a 1-year study. Am J Transplant. 2004; 4(2):237–43.

10). Budde K, Glander P, Krämer BK, Fischer W, Hoffmann U, Bauer S, et al. Conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium in maintenance renal transplant recipients receiving tacrolimus: clinical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic out-comes. Transplantation. 2007; 83:417–24.

11). Shehata M, Bhandari S, Venkat-Raman G, Moore R, D’Souza R, Riad H, et al. Effect of conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium on maximum tolerated dose and gastrointestinal symptoms following kidney transplantation. Transpl Int. 2009; 22:821–30.

12). Naito T, Shinno K, Maeda T, Kagawa Y, Hashimoto H, Otsuka A, et al. Effects of calcineurin inhibitors on pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid and its glucuronide metabolite during the maintenance period following renal transplantation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006; 29:275–80.

13). van Gelder T, Klupp J, Barten MJ, Christians U, Morris RE. Comparison of the effects of tacrolimus and cyclosporine on the pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid. Ther Drug Monit. 2001; 23:119–28.

14). Zucker K, Rosen A, Tsaroucha A, de Faria L, Roth D, Clancio G, et al. Unexpected augmentation of mycophenolic acid pharmacokinetics in renal transplant patients receiving tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil in combination therapy, and analogous in vitro findings. Transpl Immunol. 1997; 5:225–32.

Go to : 
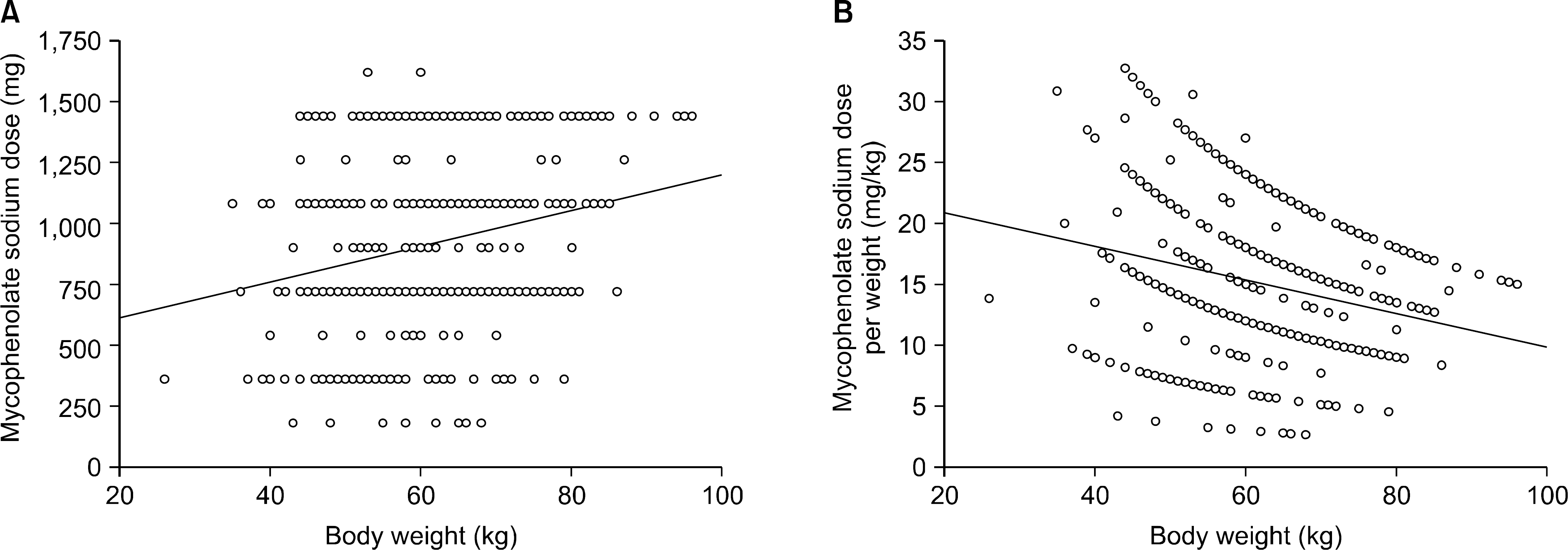 | Fig. 1.Correlation of mycophenolate sodium (MPS) dose and recipient body weight. The daily dose of MPS positively correlated with weight (Y=468.1+7.304∗X, P<0.0001, R2=0.053) (A), but the daily dose per weight negatively correlated with weight (Y=23.653−0.138∗X, P<0.0001, R2=0.061) (B). |
 | Fig. 2.Correlation of mycophenolate sodium (MPS) dose with combined immunosuppressants. MPS dose positively correlated with cyclosporine dose (P<0.0001) (A), but MPS dose showed no correlation with tacrolimus dose (P=0.668, P=0.481) (B). |
 | Fig. 3.Distribution of mycophenolate sodium (MPS) dose by recipient age (P<0.0001 by ANOVA test). |
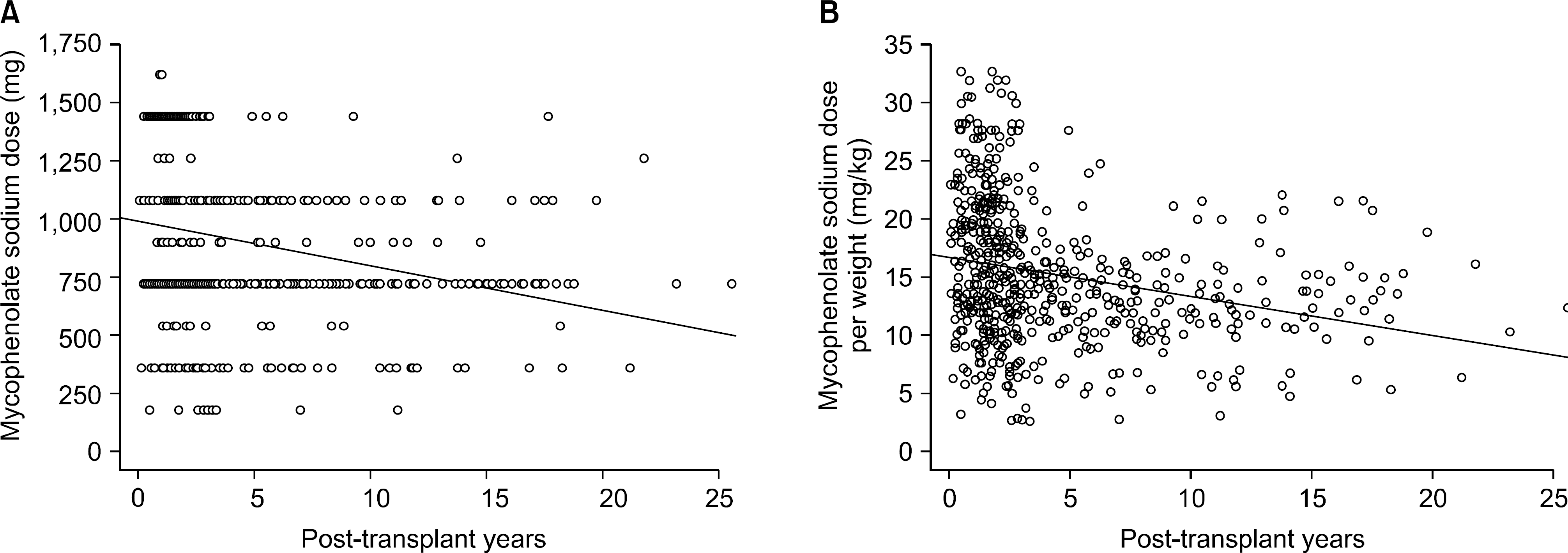 | Fig. 4.Correlation of mycophenolate sodium (MPS) dose and posttransplant period. Dose of MPS negatively correlated with posttransplant period (Y=986.291−1.583∗X, P<0.0001, R2=0.063). |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of study group
Table 2.
Variables affecting mycophenolate sodium dosage, uni-variate analysis
Table 3.
Variables affecting mycophenolate sodium dosage, multivariate analysis




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download