Abstract
Apios americana Medik tubers are medicinal foods with anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities. However, mechanisms of immunostimulatory action of the Apios tuber extract (ATE) on macrophages have not been elucidated. In the present study, we investigated whether ATE could modulate immune responses, such as production of nitric oxide (NO), proinflammatory cytokines, and transcription factors, in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. ATE significantly increased the production of NO and proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and induced the mRNA and protein levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and proinflammatory cytokines in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, Western blot analysis revealed that ATE activated the transcription factor Nuclear Factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling cascades, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 kinase. In addition, we found that ATE induced the activation of macrophages through upregulation of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and TLR2. Taken together, these findings indicate that ATE possesses a potential as a functional food with immunostimulatory activity.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Hamsa TP, Kuttan G. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effect of Ipomoea obscura (L) and its mode of action through the inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide and COX-2. Inflammation. 2011; 34:171.
2). Zhang L, Zhu H, Lun Y, Yan D, Yu L, Du B, et al. Proteomic analysis of macrophages: a potential way to identify novel proteins associated with activation of macrophages for tumor cell killing. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007; 4:359–67.
4). Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000; 406:782–7.

5). Shi Z, Cai Z, Sanchez A, Zhang T, Wen S, Wang J, et al. A novel Toll-like receptor that recognizes vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:4517–24.

6). Rosadini CV, Kagan JC. Early innate immune responses to bacterial LPS. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016; 44:14–9.

7). Lee J, Kim SL, Lee S, Chung MJ, Park YI. Immunostimulating activity of maysin isolated from corn silk in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages. BMB Rep. 2014; 47:382–7.

8). Lee JS, Hong EK. Immunostimulating activity of the polysaccharides isolated from Cordyceps militaris. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011; 11:1226–33.

9). Ishii KJ, Koyama S, Nakagawa A, Coban C, Akira S. Host innate immune receptors and beyond: making sense of microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe. 2008; 3:352–63.

10). Takashima M, Nara K, Niki E, Yoshida Y, Hagihara Y, Stowe M, et al. Evaluation of biological activities of a groundnut (Apios americana Medik) extract containing a novel isoflavone. Food Chem. 2013; 138:298–305.
11). Kaneta H, Koda M, Saito S, Imoto M, Kawada M, Yamazaki Y, et al. Biological activities of unique isoflavones prepared from Apios americana Medik. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2016; 80:774–8.
12). Ichige M, Fukuda E, Miida S, Hattan J, Misawa N, Saito S, et al. Novel isoflavone glucosides in groundnut (Apios americana Medik) and their antiandrogenic activities. J Agric Food Chem. 2013; 61:2183–7.
13). Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM, Cross CE. Free radicals, anti-oxidants, and human disease: where are we now? J Lab Clin Med. 1992; 119:598–620.
14). Masilamani M, Wei J, Sampson HA. Regulation of the immune response by soybean isoflavones. Immunol Res. 2012; 54:95–110.

15). Mueller EA, Anderer FA. Chemical specificity of effector cell/tumor cell bridging by a Viscum album rhamnogalacturonan enhancing cytotoxicity of human NK cells. Immunopharmacology. 1990; 19:69–77.
16). Khwaja TA, Dias CB, Pentecost S. Recent studies on the anticancer activities of mistletoe (Viscum album) and its alkaloids. Oncology. 1986; 43(Suppl 1):42–50.
17). Yoon TJ, Yoo YC, Kang TB, Shimazaki K, Song SK, Lee KH, et al. Lectins isolated from Korean mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 1999; 136:33–40.
18). Hajto T, Hostanska K, Frei K, Rordorf C, Gabius HJ. Increased secretion of tumor necrosis factors alpha, interleukin 1, and interleukin 6 by human mononuclear cells exposed to beta-galactoside-specific lectin from clinically applied mistletoe extract. Cancer Res. 1990; 50:3322–6.
19). Kenmochi E, Kabir SR, Ogawa T, Naude R, Tateno H, Hirabayashi J, et al. Isolation and biochemical characterization of Apios tuber lectin. Molecules. 2015; 20:987–1002.
20). Fukao T, Koyasu S. PI3K and negative regulation of TLR signaling. Trends Immunol. 2003; 24:358–63.

21). Li X, Jiang S, Tapping RI. Toll-like receptor signaling in cell proliferation and survival. Cytokine. 2010; 49:1–9.

22). Peroval MY, Boyd AC, Young JR, Smith AL. A critical role for MAPK signalling pathways in the transcriptional regulation of toll like receptors. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e51243.

23). Sohn SH, Lee SY, Cui J, Jang HH, Kang TH, Kim JK, et al. Apios americana Medik Extract Alleviates Lung Inflammation in Influenza Virus H1N1- and Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015; 25:2146–52.
Go to : 
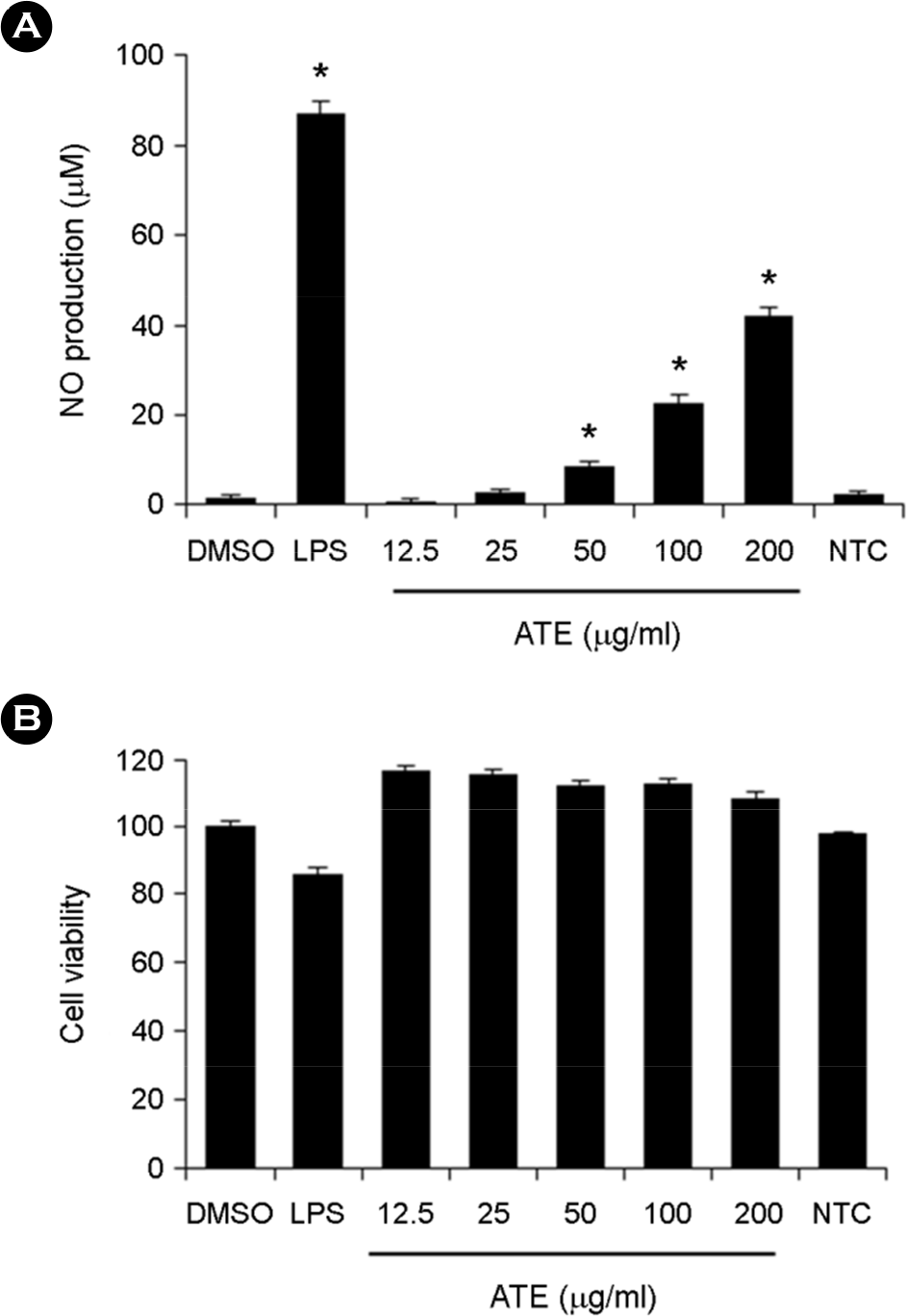 | Figure 1.Effect of ATE on nitric oxide (NO) production and cell viability of RAW264.7 cells. (A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentrations (12.5, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ml) of ATE or LPS (1 μg/ml) and then incubated for 24 h. Nitrite levels in the culture media were determined using the Griess reagent and were presumed to reflect the levels of NO. (B) RAW264.7 cells were treated with 12.5~200 μg/ml of ATE for 24 h. Cell viability was quantified using the EZ-CyTox cell viability assay kit. Data are presented as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗ p < 0.05 vs. control. |
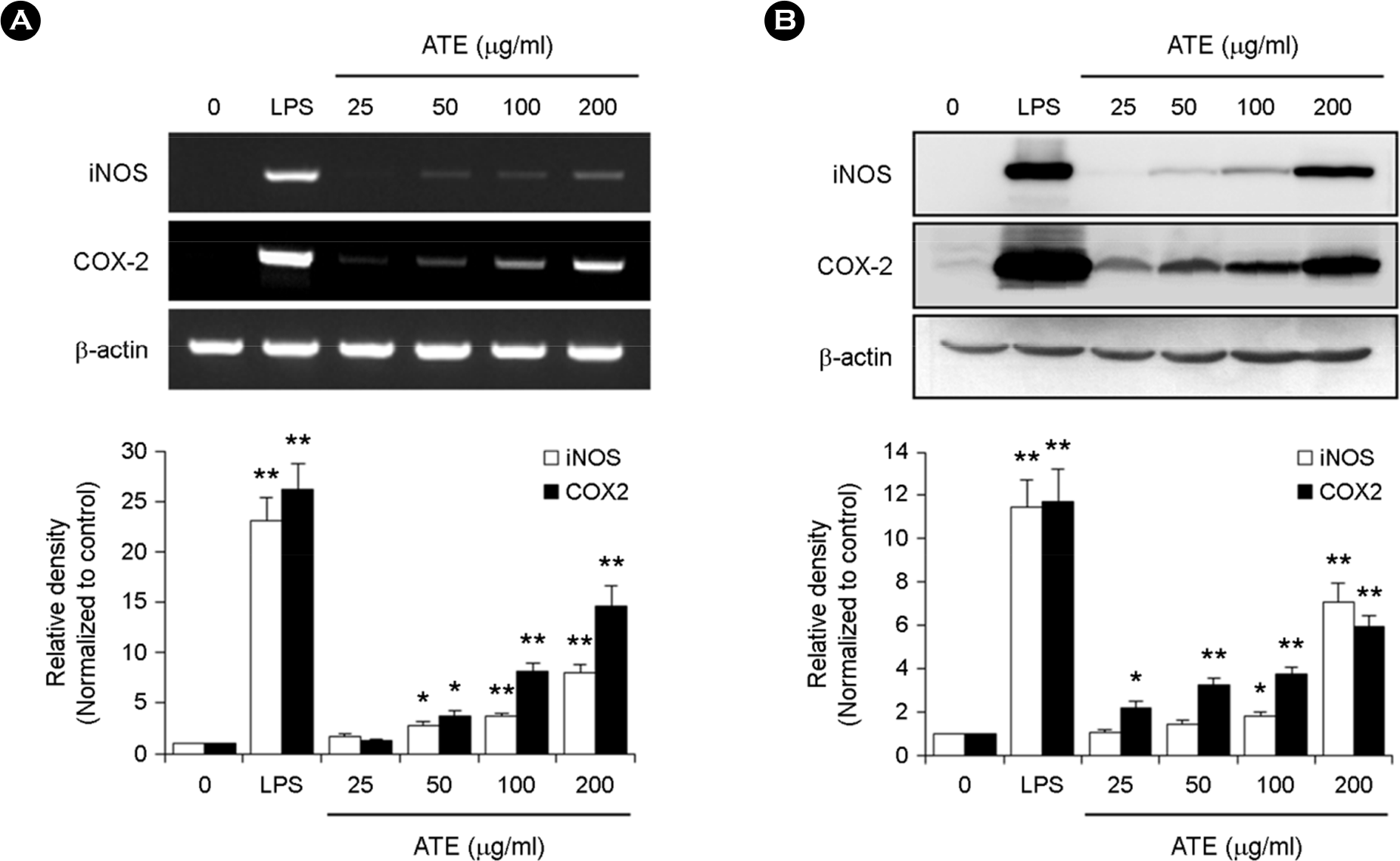 | Figure 2.Effect of ATE on the mRNA and protein expression of iNOS and COX-2 in RAW264.7 cells. (A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentrations (25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ml) of ATE or LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated for RT-PCR analysis of the expression of iNOS and COX-2. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. (B) RAW264.7 cells were treated as described above. iNOS and COX-2 protein levels were detected by Western blot analysis. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. |
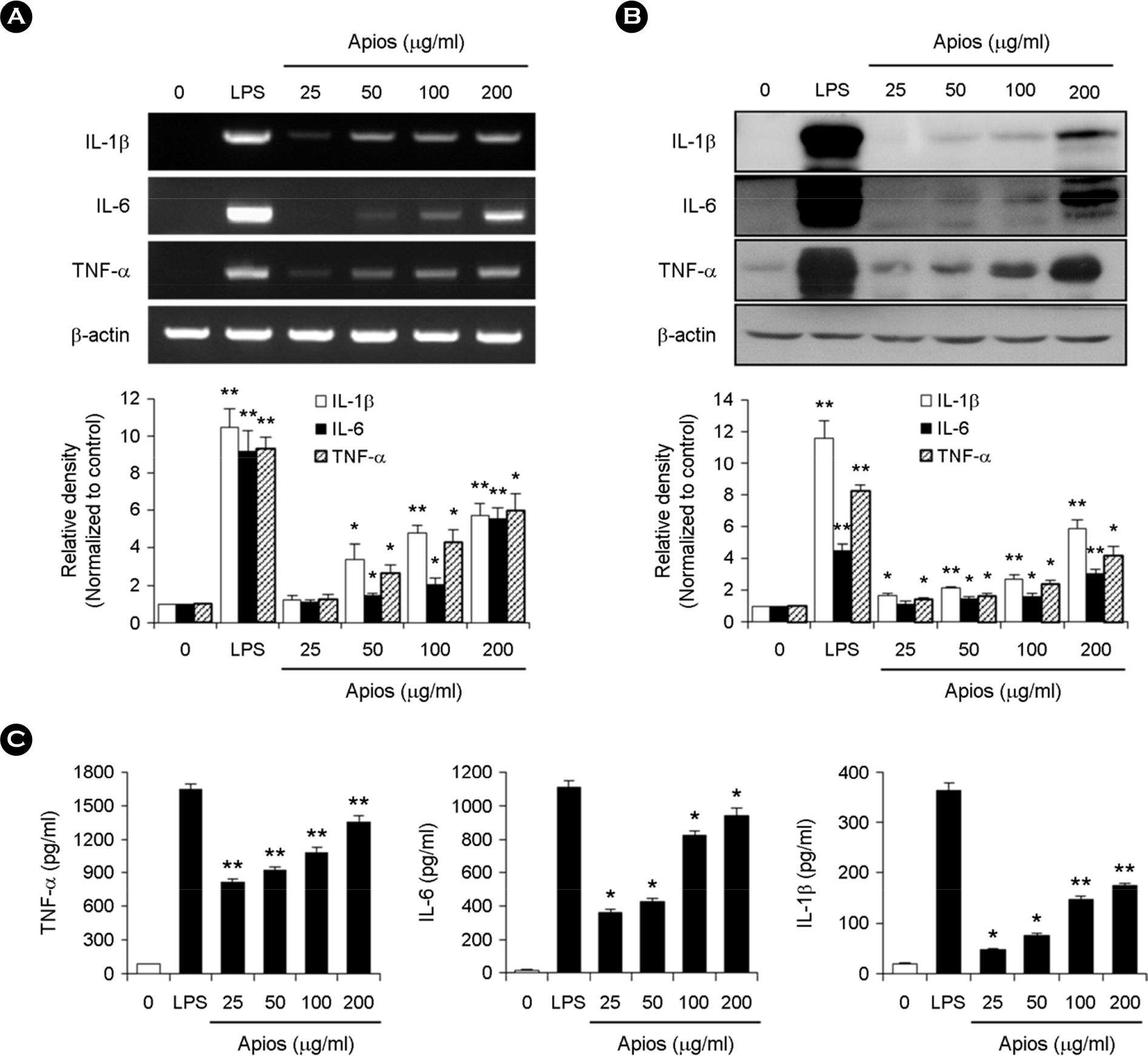 | Figure 3.Effect of ATE on cytokine production in RAW264.7 cells. (A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentrations (25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ml) of ATE or LPS for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted for RT-PCR analysis of the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. PCR of the β-actin gene was performed as a housekeeping control. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. (B) Protein expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α was assessed by Western blot analysis. The experiment was repeated in triplicate, and similar results were obtained in all three replicates. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. (C) RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentrations of ATE (25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ ml). The supernatants were collected, and the extracellular levels of cytokines were measured in the culture media using cytokine ELISA kits. The results are reported as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. |
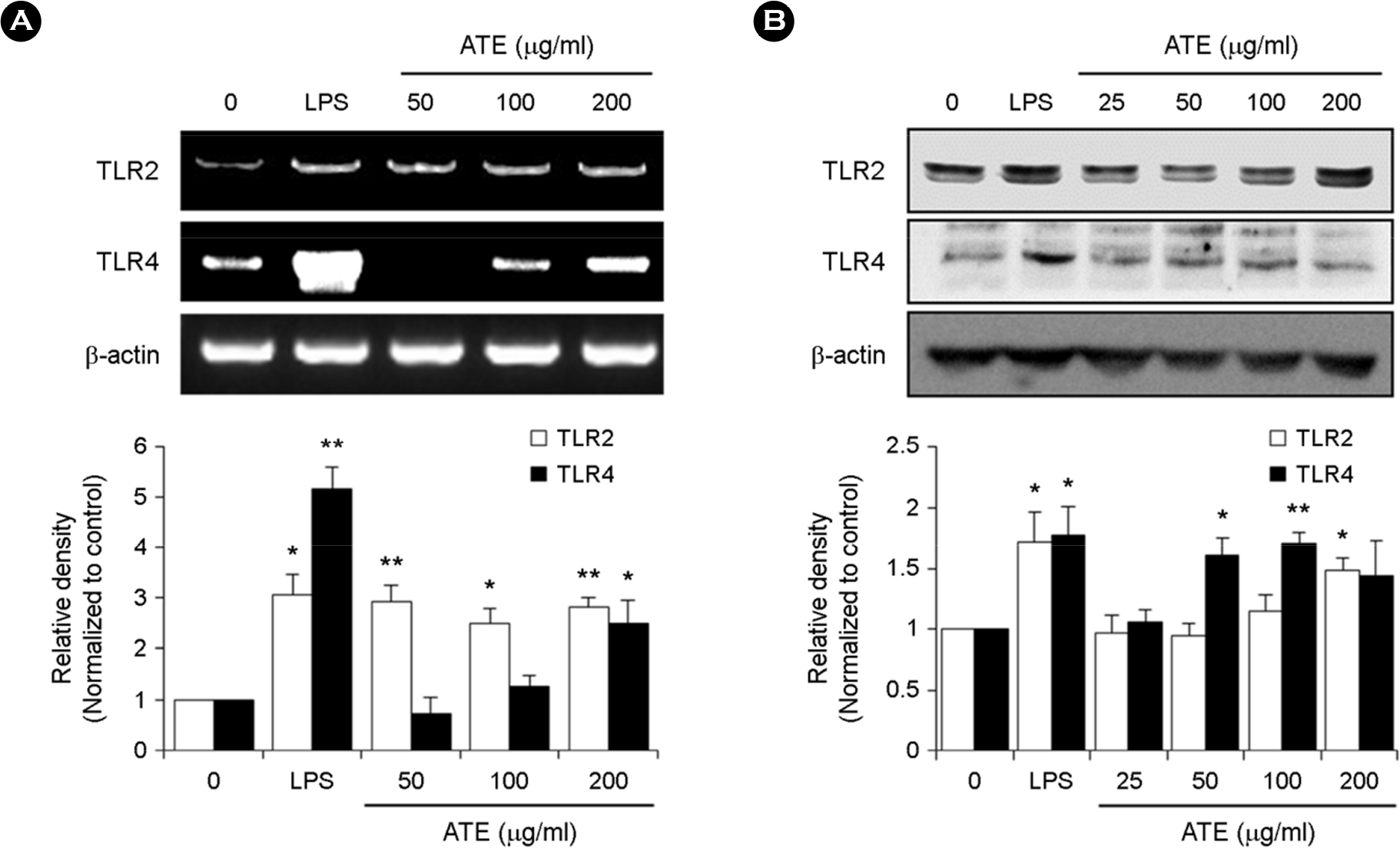 | Figure 4.Effect of ATE on the mRNA and protein expression of TLR2 and TLR4 in RAW264.7 cells. (A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of ATE (0, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ml) or LPS (1 μg/ml) for 6 h. The mRNA levels of TLR2 and TLR4 were detected by RT-PCR. (B) The protein levels of TLR2 and TLR4 were evaluated by Western blot analysis. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. |
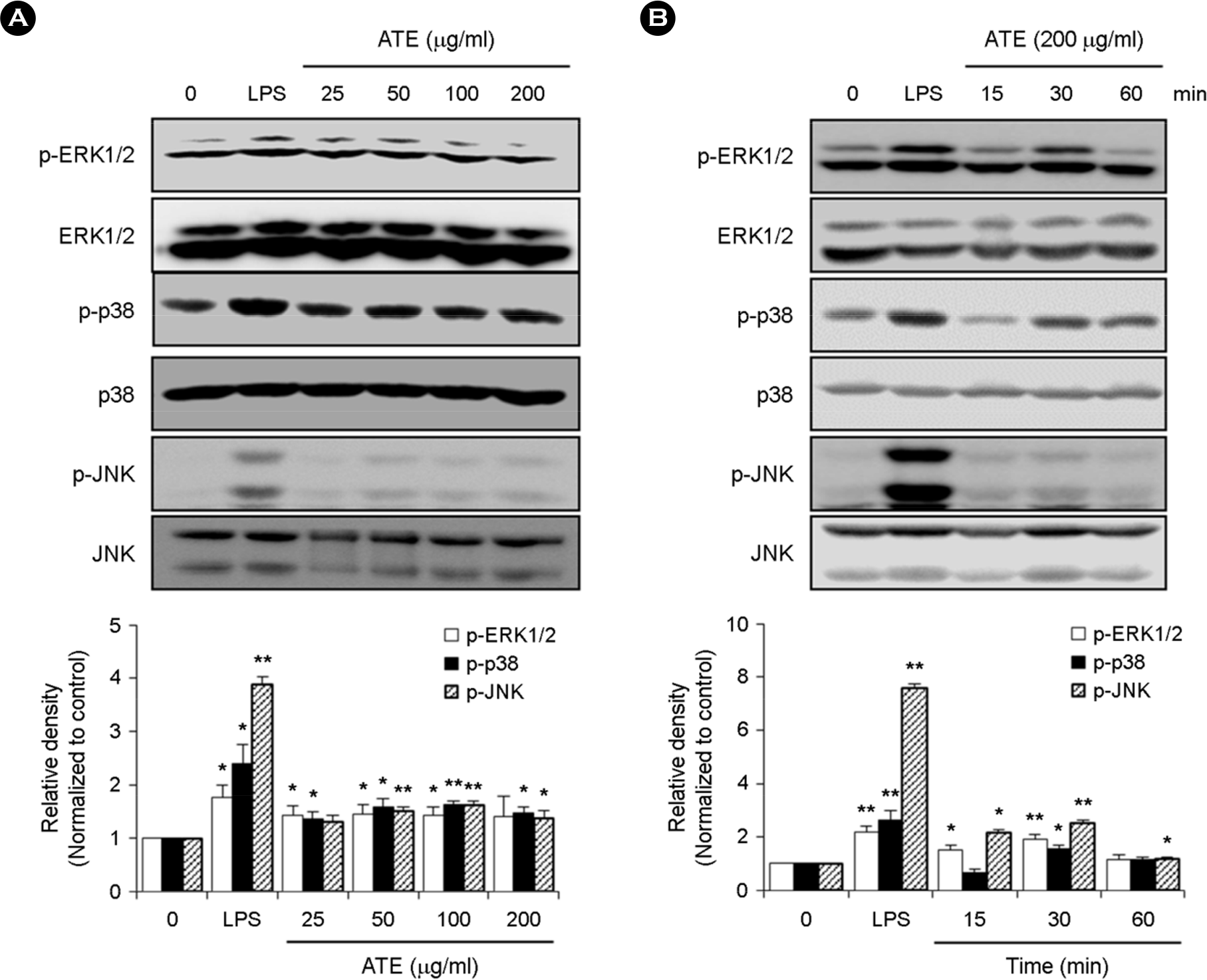 | Figure 5.Effect of ATE on the MAPK pathway in RAW264.7 cells. (A) RAW264.7 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of ATE or LPS for 30 min. The protein levels of phospho-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, phospho-p38, p38, phospho-JNK, and JNK were determined by Western blot analysis. (B) RAW264.7 cells were treated with ATE for 15, 30, and 60 min. The protein levels of phospho-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, phospho-p38, p38, phospho-JNK, and JNK were determined by Western blot analysis. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 vs. control. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


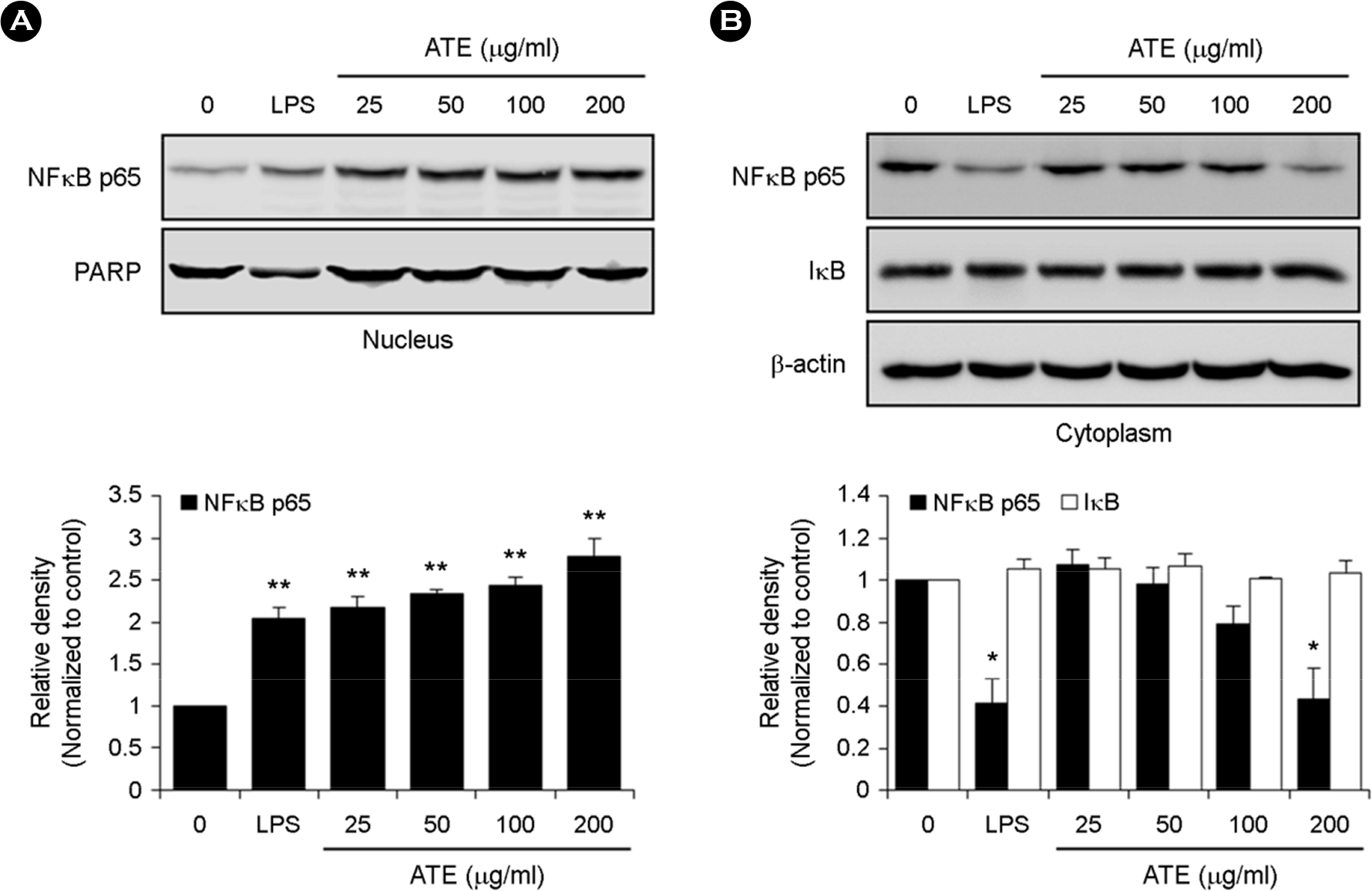
 XML Download
XML Download