Abstract
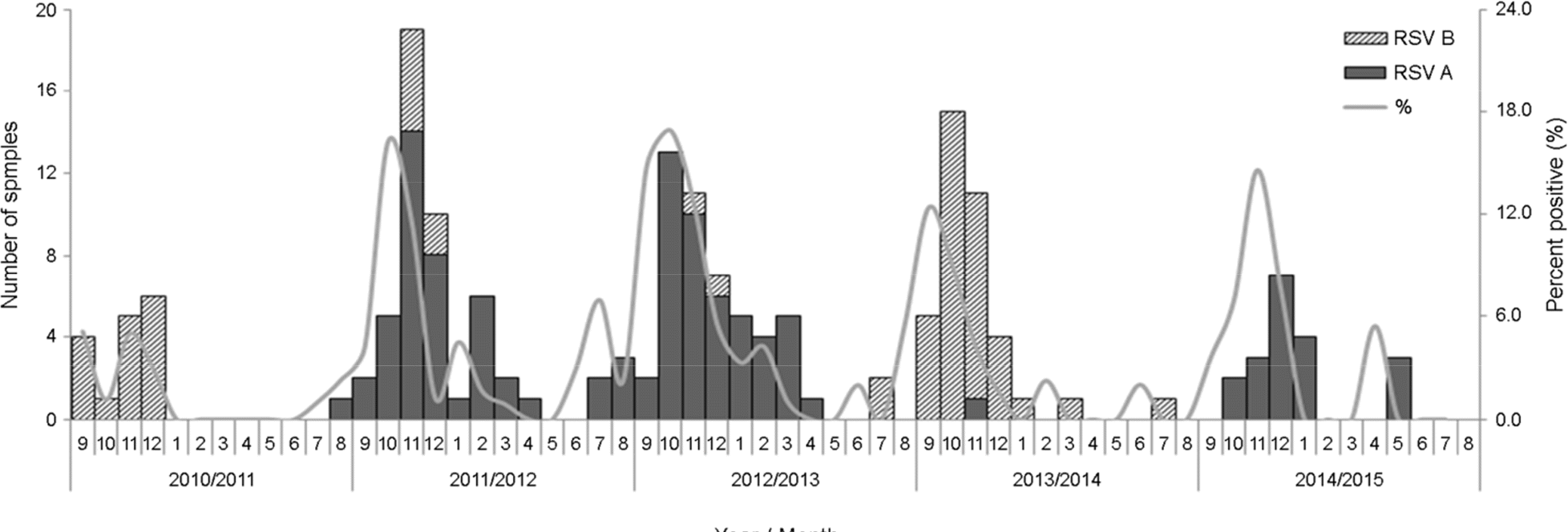
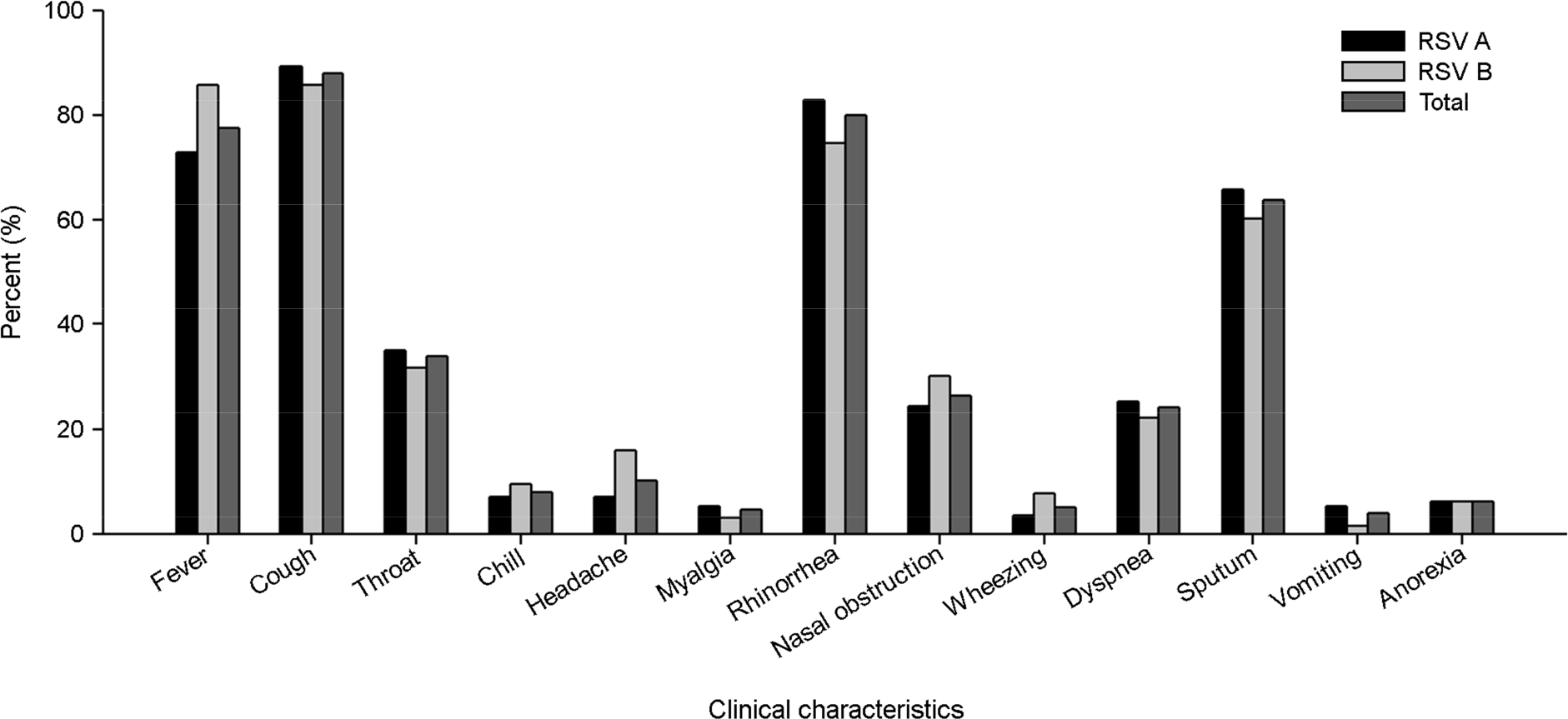
Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is known as the leading cause of respiratory tract illness in infancy and elderly children worldwide. We investigate the prevalence pattern and genetic characteristics in the second variable region G protein gene of HRSV during 5 consecutive seasons from 2010 to 2015. A total of 4,793 specimens (throat swabs) were collected from patients with acute respiratory tract. HRSV were evaluated and classified as HRSV A (n=111) or HRSV B (n=64) by real-time RT-PCR or RT-PCR. In general HRSV were detected in winter season. Coughing, fever, rhinorrhea and sputum were confirmed main symptoms in patients with HRSV. There were no significant differences in clinical characteristics or severity according to the HRSV subgroup infections. Out of 175 HRSV positive samples, 94 samples were successfully sequenced using G gene. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that 62 HRSV-A strains clustered into genotypes ON1 (n=54, 87.1%), NA1 (n=7), NA2 (n=1) and 32 HRSV-B strains clustered into three genotypes: BA4 (n=28, 87.5%), BA5 (n=2), BA6 (n=2). These results provide a better understanding of HRSV prevalence pattern and genetic characteristics.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Kim KS. Host Immune response of glycosylation patterns on Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) attachment (G) protein, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Report. 2013.
2). Le Bayon JC, Lina B, Rosa-Calatrava M, Boivin G. Recent developments with live-attenuated recombinant paramyxovirus vaccines. Rev Med Virol. 2013; 23:15–34.
3). Nair H, Nokes DJ, Gessner BD, Dherani M, Madhi SA, Singleton RJ, et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and mata-analysis. Lancet. 2010; 375:1545–55.
4). Song WK, Lee KM, Kim HT. Occurrence and clinical characteristic of patients infected with subgroups of respiratory syncytial virus. Korean Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 1999; 2:8–13.
5). Crowe JE Jr, Williams JV. Immunology of viral respiratory tract infection in infancy. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2003; 4:112–9.

6). Kim YJ, Kim DW, Lee WJ, Yun MR, Lee HY, Lee HS, et al. Rapid replacement of human respiratory syncytial virus A with the ON1 genotype having 72 nucleotide duplication in G gene. Infect Genet Evol. 2014; 26:103–12.

7). Ren L, Xiao Q, Zhou L, Xia Q, Liu E. Molecular characterization of human respiratory syncytial virus subtype B: A novel genotype of subtype B circulating in China. J Med Virol. 2015; 87:1–9.

8). Cui G, Zhu R, Qian Y, Deng J, Zhao L, Sun Y, et al. Genetic variation in attachment glycoprotein genes of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroups A and B in children in recent five consecutive years. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e75020.

9). Lee HS. Current development of vaccines for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Public Health Weekly Report, KCDC. 2012; 48:917–21.
10). de-Paris F, Beck C, de Souza Nunes L, Machado AB, Paiva RM, da Silva Menezes D, et al. Evaluation of respiratory syncytial virus group A and B genotypes among nosocomial and community-acquired pediatric infections in southern Brazil. Virol J. 2014; 11:36.

11). Agoti CN, Mayieka LM, Otieno JR, Ahmed JA, Fields BS, Waiboci LW, et al. Examining strain diversity and phylogeography in relation to an unusual epidemic pattern of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in a long-term refugee camp in Kenya. BMC Infect Dis. 2014; 14:178.

12). Yoon GH, Kim YH. The clinical characteristics in infantile bronchiolitis and pneumonia according to respiratory syncytial virus subgroups: experience of single tertiary medical center from 2010 to 2012. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:84–9.

13). Choi EH, Lee HJ. Genetic diversity and molecular epidemiology of the G protein of subgroups A and B of respiratory syncytial viruses isolated over 9 consecutive epidemics in Korea. J Infect Dis. 2000; 181:1547–56.

14). Kang SY, Hong CR, Kang HM, Cho EY, Lee HJ, Choi EH, et al. Clinical and Epidemiological characteristics of Human Metapneumovirus Infects, in comparison with respiratory syncytial virus A and B. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2013; 20:168–77.
15). Jung HD, Cheong HM. Prevalence of respiratory viruses in patients causing acute respiratory infections. Public Health Weekly Report. 2014; 7:805–12.
16). Shobugawa Y, Saito R, Sano Y, Zaraket H, Suzuki Y, Kumaki A, et al. Emerging genotypes of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup A among patients in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:2475–82.

Go to : 
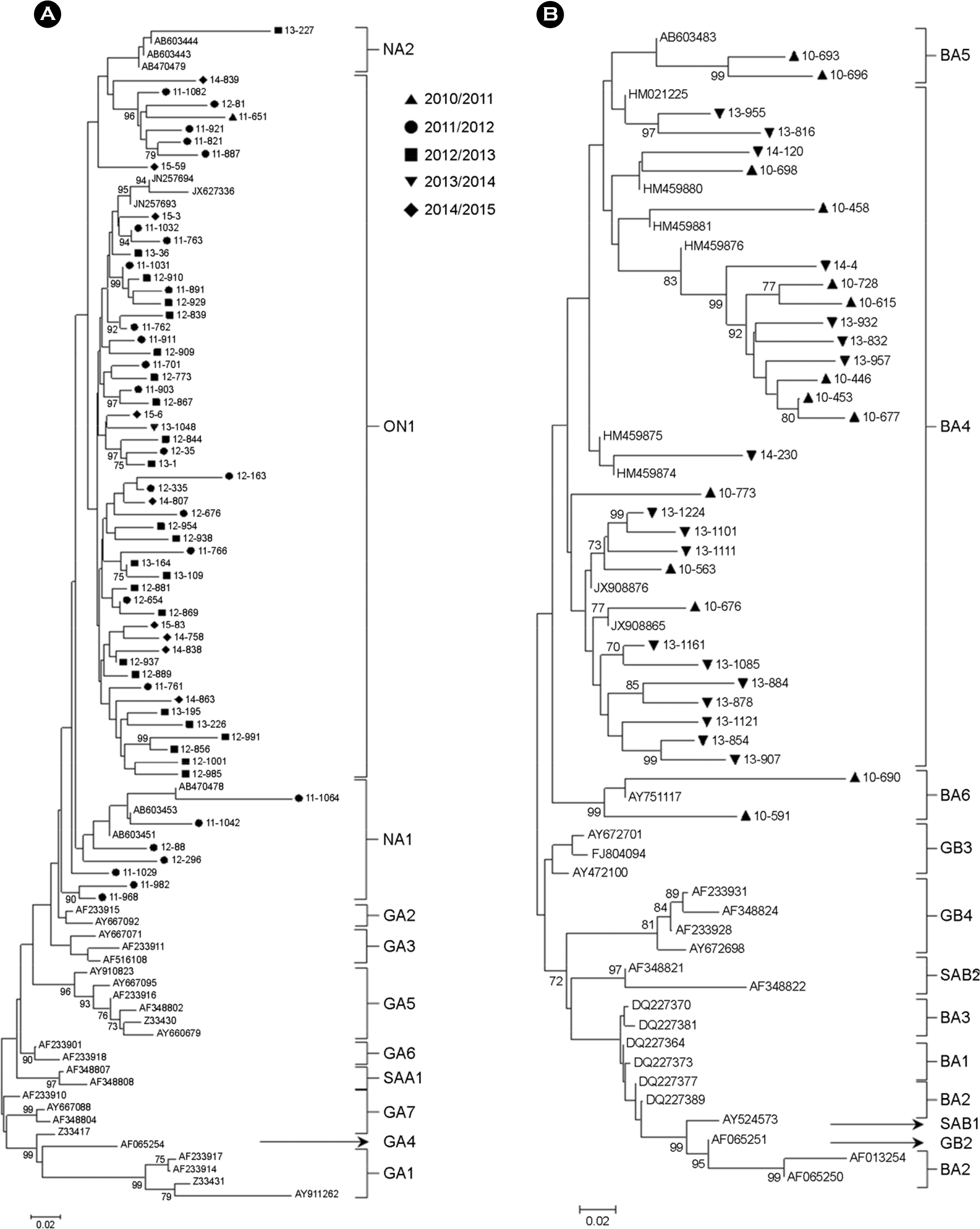 | Figure 3.Phylogenetic trees for HRSV-A (A) and HRSV-B (B) based on the second variable region of the G protein. The nucleotide sequences were aligned using Clustal W. Trees using the neighbor-joining method with Mega 4. The scale bars show the proportions of nucleotide substitutions, and the numbers at the branches are bootstrap values determined for 500 iterations. Only bootstrap values with |
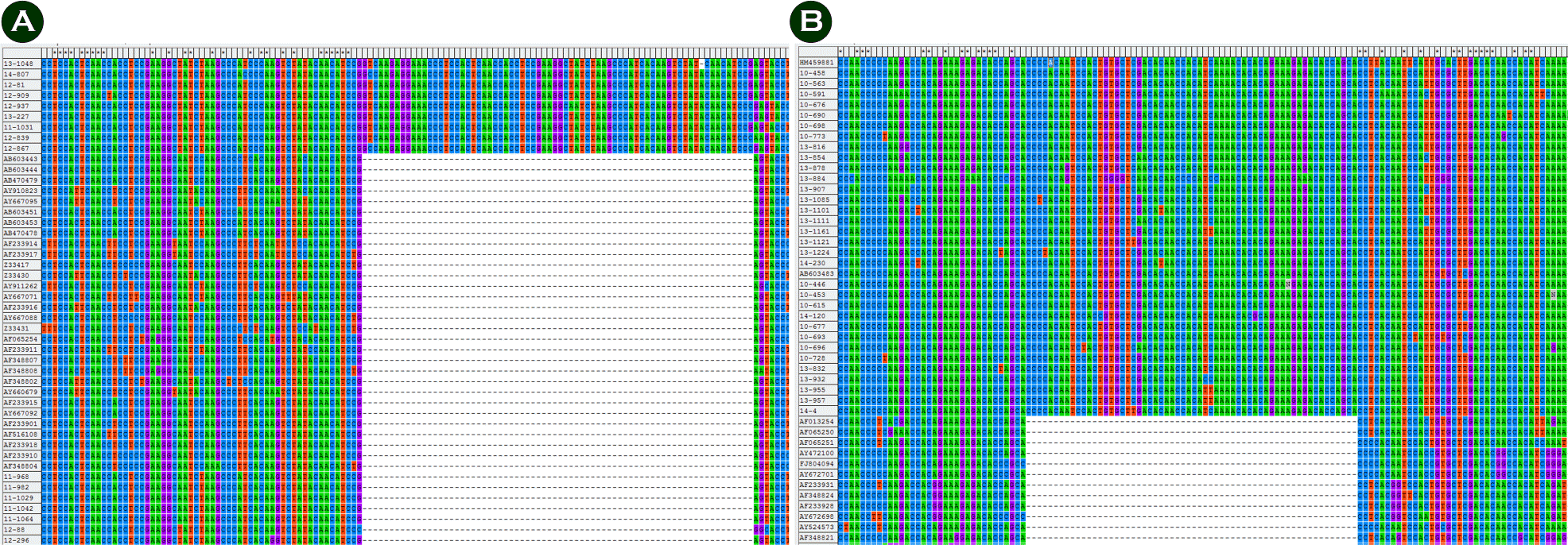 | Figure 4.(A) Nucleotide characteristics of ON1 genotype and (B) nucleotide characteristics of BA genotype. |
Table 1.
Detection of RSV from 2011/2012 to 2014/2015 seasons
| Season | No. of tested | No. of total positive | Positive rate (%) | No. of positive (%)∗ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSV A | RSV B | ||||
| 2010/2011 | 1,142 | 17 | 1.5 | 1 (5.9) | 16 (94.1) |
| 2011/2012 | 1,120 | 51 | 4.6 | 44 (86.3) | 7 (13.7) |
| 2012/2013 | 1,105 | 50 | 4.5 | 46 (92.0) | 4 (8.00) |
| 2013/2014 | 813 | 38 | 4.8 | 1 (2.6) | 37 (97.4) |
| 2014/2015 | 613 | 19 | 3.1 | 19 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) |
Table 2.
HRSV genotype distributions from 2011/2012 to 2014/2015 seasons




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download