Abstract
Tobacco rattle virus (TRV) is a plant pathogen belonging to the Group IV positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses. TRV causes disease in various plants (e.g., potato, tomato and tobacco), for which it was classified as a controlled quarantine virus in Korea. This study aimed to develop specific primer sets for the rapid detection of TRV. Two RT-PCR primer sets were developed for specific detection of TRV. Furthermore, nested primer sets were also developed, which is required for high sensitivity detection in plant quarantine. The RT-PCR and nested PCR products had the following sizes: set 5 (1,096→540 bp), and set 7 (878→756 bp), respectively. In addition, a modified positive-control plasmid was also developed for use as a positive control in TRV quarantine. The diagnostic system for TRV detection was verified using samples from Korean quarantine sites for the last five years (2009–2014). A total of 83 cases were detected among various import crops. This system for detection of TRV will continuously contribute to plant quarantine in the future.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Lee S, Kang EH, Heo NY, Kim SM, Kim YJ, Shin YG. Detection of Carnation necrotic fleck virus and Carnation ringspot virus using RT-PCR. Res Plant Dis. 2013; 19:36–44.
2). Lee S, Kang EH, Chu YM, Shin YG, Ahn TY. Development of PCR diagnosis system for plant quarantine seed-borne Wheat streak mosaic virus. Korean J Microbiol. 2013; 49:112–7.
3). Lee S, Shin YG. Development and practical use of RT-PCR for seed-transmitted Prune dwarf virus in quarantine. Plant Pathol J. 2014; 30:178–82.
4). Nicolaisen M, Bösze Z, Nielsen SL. Detection of Tobacco rattle virus in potato tubers using a simple RT-PCR procedure. Potato Research. 1999; 42:173–9.
5). Wei T, Lu G, Clover GRG. A multiplex RT-PCR for the detection of Potato yellow vein virus, Tobacco rattle virus and Tomato infectious chlorosis virus in potato with a plant internal amplification control. Plant Pathology. 2009; 58:203–9.
6). Pérez EE, Weingartner DP, Hiebert E, McSorley R. Tobacco rattle virus detection in potato tubers from northeast Florida by PCR and tissue blotting. Amer J of Potato Res. 2012; 77:363–8.
7). Riga E, Larsen R, Eastwell K, Guerra N, Guerra L, Crosslin JM. Rapid detection of Tobacco rattle tobravirus in Viruliferous paratrichodorus allius from greenhouse and field specimens. J Nematol. 2009; 41:60–3.
8). Kenyon DM, Handy CL, Thomas JE. Detection of Tobacco rattle virus in soil using real-time PCR. Aspects of Applied Biology. 2005; 76:77–9.
9). Yang JG, Wang FL, Chen DX, Shen LL, Qian YM, Liang ZY, et al. Development of a one-step immunocapture real-time RT-PCR assay for detection of Tobacco mosaic virus in soil. Sensors. 2012; 12:16685–94.
10). Xu H, Nie J. Molecular detection and identification of potato isolates of Tobacco rattle virus. Canadian J Plant Pathol. 2006; 28:271–9.
11). Holeva R, Phillips MS, Neilson R, Brown DJF, Young V, Boutsika K, et al. Real-time PCR detection and quantification of vector trichodorid nematodes and Tobacco rattle virus. Mol Cell Probes. 2006; 20:203–11.
12). Mumford RA, Walsh K, Barker I, Boonham N. Detection of Potato mop top virus and Tobacco rattle virus using a multiplex real-time fluorescent reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay. Phytopathology. 2000; 90:448–53.
13). Shin YG, Rho JY. Development of a PCR diagnostic system for Iris yellow spot tospovirus in quarantine. Plant Pathol J. 2014; 30:440–4.
14). Animal, Plant and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Agency. List of plant quarantine viruses in Korea newly revised in 2013. Res Plant Dis. 2013; 19:67–75.
15). Shin YG. An advanced quarantine system for the inspection of seed-borne viruses in Korea. 2009.
16). Lee S, Kang EH, Shin YG, Lee SH. Development of RT-PCR and nested PCR for detecting four quarantine plant viruses belonging to Nepovirus. Res Plant Dis. 2013; 19:220–5.
Go to : 
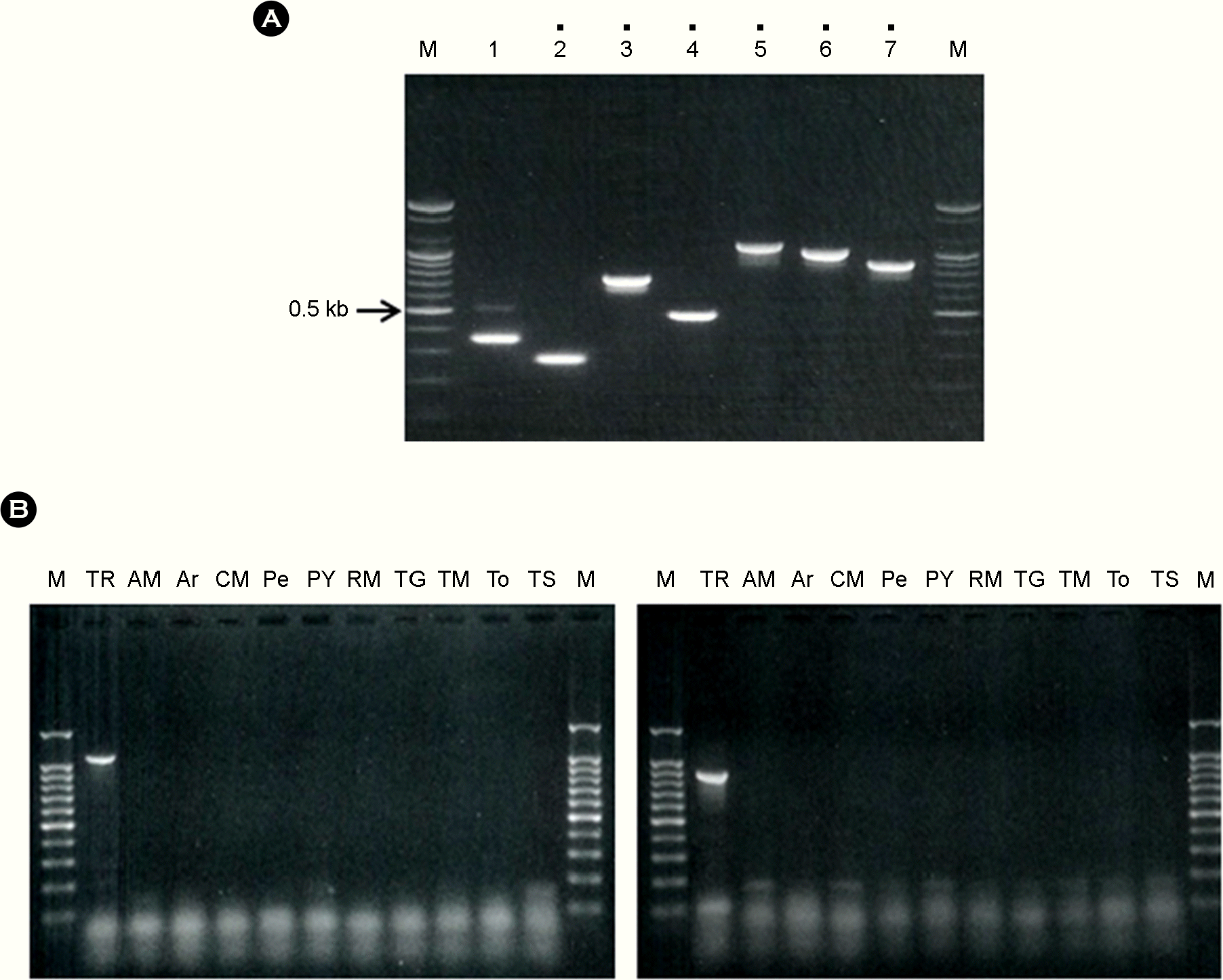 | Figure 2.Results of selection of TRV RT-PCR primer sets. Panel (A), First selection of specific RT-PCR primer sets for the detection of TRV. M, 100 bp step DNA Ladder maker (Genepia, Korea); dot, selected PCR primer set; Lane number, primer set for detection of TRV. Panel (B), Second selection of specific RT-PCR primer sets for the detection of TRV. Lane M, 100 bp step DNA Ladder maker (Genepia); lane AM, Alfalfa mosaic virus; lane Ar, Arabis mosaic virus; lane CM, Cucumber mosaic virus; lane Pe, Pepper mottle virus; lane PY, Potato virus Y; lane RM, Ribgrass mosaic virus; lane TG, Tobacco mild-green mosaic virus; lane TM, Tobacco mosaic virus; lane To, Tomato mosaic virus; lane TS, Tomato spotted wilt virus.
|
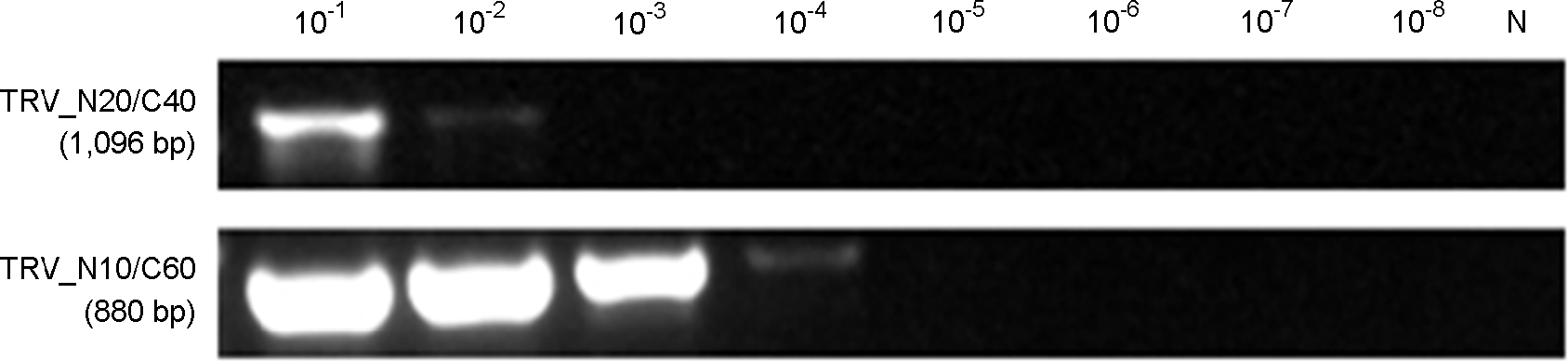
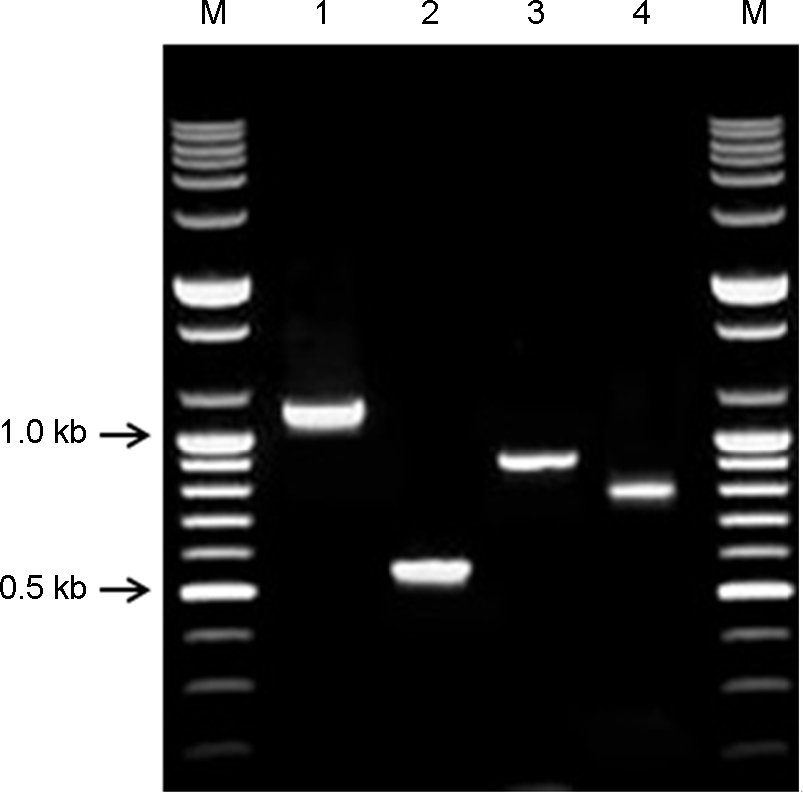 | Figure 4.Result of selected RT-PCR and nested-PCR products for the detection of TRV. Lane M, 100 bp step DNA Ladder; lane 1, final selected primer set #5 (1,096 bp); lane 2, nested-PCR product from primer set #5 (543 bp); lane 3, final selected primer set #7 (880 bp); lane 4, nested-PCR product from primer set #7 (760 bp). |
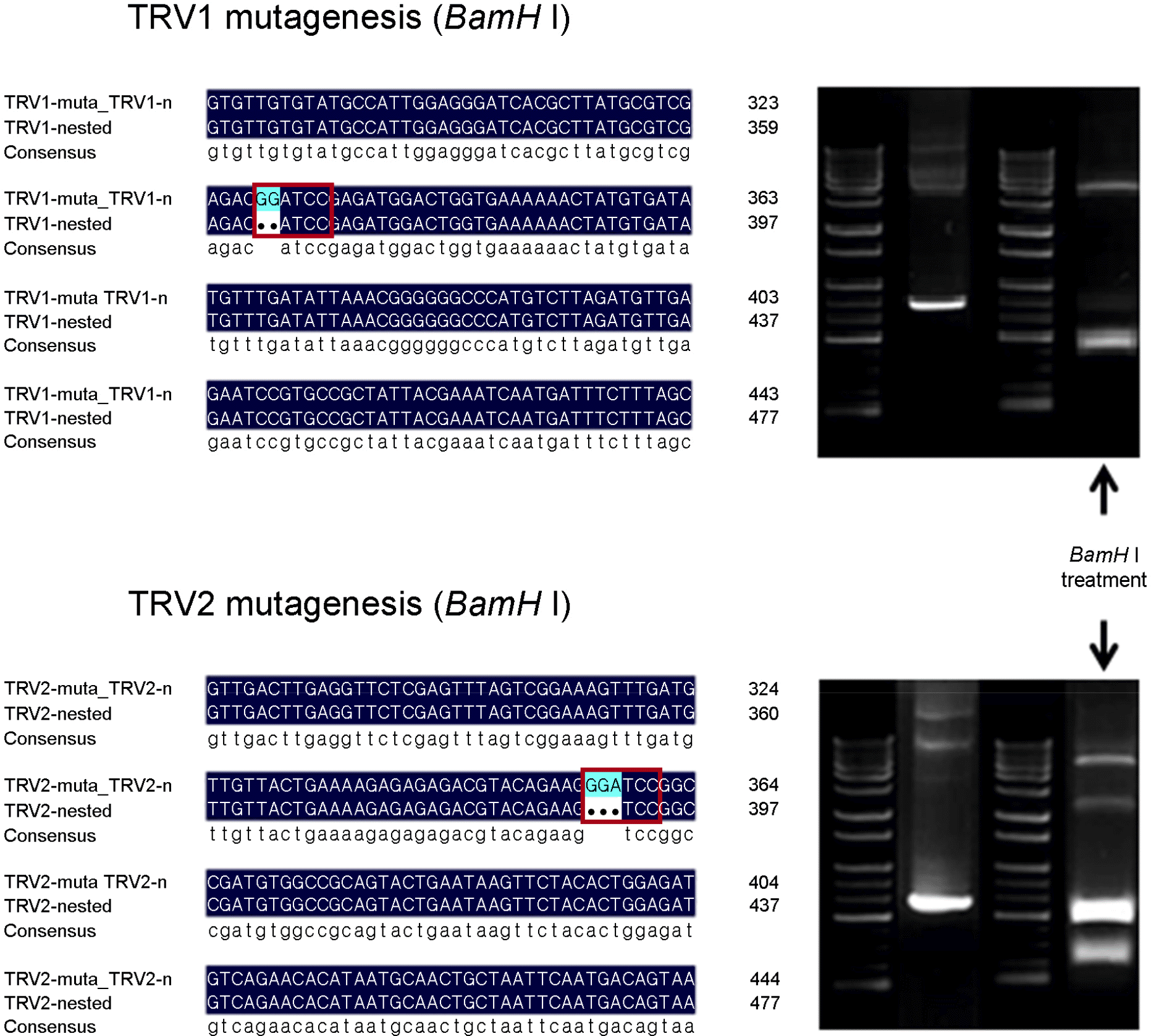 | Figure 5.
BamH I sequence insertion of the TRV genetically modified-positive control plasmids. |
Table 1.
RT-PCR amplification sets and product size for the detection of TRV
Table 2.
Final selection of RT-PCR and nested primer sets for the detection of TRV
Table 3.
Results of detection for TRV from plant quarantine sites in 2009–2014




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download