Abstract
The innate immune system confers first-line defense against various pathogens including bacteria and viruses. Early detection of invading pathogens by the host depends on a limited number of specific pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that detect pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and activate signal transduction cascades that lead to activation of defense mechanisms. Among those sensors, RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) play crucial roles in the detection of viruses by recognizing intracellular viral patterns such as viral RNAs to induce type-I interferon production. The discovery of intracellular RNA sensing mechanism by RIG-I prompted the investigations to find out intracellular DNA sensors. Recently, several proteins including DAI, AIM2, IFI16, and cGAS have been suggested as DNA sensing molecules to detect DNA viruses and bacteria, suggesting there are multiple receptors for microbial DNA. In this review, we discuss the current our understanding of sensing microbial DNA and subsequent induction of immune responses.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Ronald PC, Beutler B. Plant and animal sensors of conserved microbial signatures. Science. 2010; 330:1061–4.

2). Kawai T, Akira S. The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int Immunol. 2009; 21:317–37.

3). Jun EJ, Kim YK. Activation of innate immune system during viral infection: Role of pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) in viral Infection. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009; 39:145–57.

5). Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M, et al. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5:730–7.

6). Kato H, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Yoneyama M, Yamamoto M, Matsui K, et al. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature. 2006; 441:101–5.

7). Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000; 408:740–5.

8). Spies B, Hochrein H, Vabulas M, Huster K, Busch DH, Schmitz F, et al. Vaccination with plasmid DNA activates dendritic cells via Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) but functions in TLR9-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2003; 171:5908–12.

9). Heit A, Maurer T, Hochrein H, Bauer S, Huster KM, Busch DH, et al. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 9 expression is not required for CpG DNA-aided cross-presentation of DNA-conjugated antigens but essential for cross-priming of CD8 T cells. J Immunol. 2003; 170:2802–5.

10). Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Recognition of cytosolic DNA activates an IRF3-dependent innate immune response. Immunity. 2006; 24:93–103.

11). Ishii KJ, Coban C, Kato H, Takahashi K, Torii Y, Takeshita F, et al. A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nat Immunol. 2006; 7:40–8.

12). Ishikawa H, Ma Z, Barber GN. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature. 2009; 461:788–92.

13). Ishii KJ, Kawagoe T, Koyama S, Matsui K, Kumar H, Kawai T, et al. TANK-binding kinase-1 delineates innate and adaptive immune responses to DNA vaccines. Nature. 2008; 451:725–9.

14). Miyahira AK, Shahangian A, Hwang S, Sun R, Cheng G. TANK-binding kinase-1 plays an important role during in vitro and in vivo type I IFN responses to DNA virus infections. J Immunol. 2009; 182:2248–57.
15). Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science. 2013; 339:786–91.

16). Delaloye J, Roger T, Steiner-Tardivel QG, Le Roy D, Knaup Reymond M, Akira S, et al. Innate immune sensing of modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) is mediated by TLR2-TLR6, MDA-5 and the NALP3 inflammasome. PLoS Pathog. 2009; 5:e1000480.

17). Muruve DA, Pétrilli V, Zaiss AK, White LR, Clark SA, Ross PJ, et al. The inflammasome recognizes cytosolic microbial and host DNA and triggers an innate immune response. Nature. 2008; 452:103–7.

18). Takaoka A, Wang Z, Choi MK, Yanai H, Negishi H, Ban T, et al. DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and an activator of innate immune response. Nature. 2007; 448:501–5.

19). Wang Z, Choi MK, Ban T, Yanai H, Negishi H, Lu Y, et al. Regulation of innate immune responses by DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) and other DNA-sensing molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:5477–82.

20). Ablasser A, Bauernfeind F, Hartmann G, Latz E, Fitzgerald KA, Hornung V. RIG-I-dependent sensing of poly(dA:dT) through the induction of an RNA polymerase III-transcribed RNA intermediate. Nat Immunol. 2009; 10:1065–72.

21). Chiu YH, Macmillan JB, Chen ZJ. RNA polymerase III detects cytosolic DNA and induces type I interferons through the RIG-I pathway. Cell. 2009; 138:576–91.

22). Inn KS, Lee SH, Rathbun JY, Wong LY, Toth Z, Machida K, et al. Inhibition of RIG-I-mediated signaling by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded deubiquitinase ORF64. J Virol. 2011; 85:10899–904.

23). Valentine R, Smith GL. Inhibition of the RNA polymerase III-mediated dsDNA-sensing pathway of innate immunity by vaccinia virus protein E3. J Gen Virol. 2010; 91:2221–9.

24). Jehl SP, Nogueira CV, Zhang X, Starnbach MN. IFNgamma inhibits the cytosolic replication of Shigella flexneri via the cytoplasmic RNA sensor RIG-I. PLoS pathog. 2012; 8:e1002809.
25). Kim T, Pazhoor S, Bao M, Zhang Z, Hanabuchi S, Facchinetti V, et al. Aspartate-glutamate-alanine-histidine box motif (DEAH)/RNA helicase A helicases sense microbial DNA in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:15181–6.

26). Zhang Z, Yuan B, Bao M, Lu N, Kim T, Liu YJ. The helicase DDX41 senses intracellular DNA mediated by the adaptor STING in dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12:959–65.

27). Yang P, An H, Liu X, Wen M, Zheng Y, Rui Y, et al. The cytosolic nucleic acid sensor LRRFIP1 mediates the production of type I interferon via a beta-catenin-dependent pathway. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:487–94.
28). Hong S, Park S, Yu JW. Pyrin domain (PYD)-containing inflammasome in innate immunity. J Bacteriol Virol. 2011; 41:133–46.

29). Hornung V, Ablasser A, Charrel-Dennis M, Bauernfeind F, Horvath G, Caffrey DR, et al. AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature. 2009; 458:514–8.

30). Fernandes-Alnemri T, Yu JW, Datta P, Wu J, Alnemri ES. AIM2 activates the inflammasome and cell death in response to cytoplasmic DNA. Nature. 2009; 458:509–13.

31). Bürckstümmer T, Baumann C, Blüml S, Dixit E, Dürnberger G, Jahn H, et al. An orthogonal proteomic-genomic screen identifies AIM2 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor for the inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2009; 10:266–72.

32). Fernandes-Alnemri T, Yu JW, Juliana C, Solorzano L, Kang S, Wu J, et al. The AIM2 inflammasome is critical for innate immunity to Francisella tularensis. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:385–93.
33). Rathinam VA, Jiang Z, Waggoner SN, Sharma S, Cole LE, Waggoner L, et al. The AIM2 inflammasome is essential for host defense against cytosolic bacteria and DNA viruses. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:395–402.

34). Unterholzner L, Keating SE, Baran M, Horan KA, Jensen SB, Sharma S, et al. IFI16 is an innate immune sensor for intracellular DNA. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:997–1004.

35). Kis-Toth K, Szanto A, Thai TH, Tsokos GC. Cytosolic DNA-activated human dendritic cells are potent activators of the adaptive immune response. J Immunology. 2011; 187:1222–34.

36). Kerur N, Veettil MV, Sharma-Walia N, Bottero V, Sadagopan S, Otageri P, et al. IFI16 acts as a nuclear pathogen sensor to induce the inflammasome in response to Kaposi Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2011; 9:363–75.

38). Woodward JJ, Iavarone AT, Portnoy DA. c-di-AMP secreted by intracellular Listeria monocytogenes activates a host type I interferon response. Science. 2010; 328:1703–5.
39). Burdette DL, Monroe KM, Sotelo-Troha K, Iwig JS, Eckert B, Hyodo M, et al. STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP. Nature. 2011; 478:515–8.

40). Parvatiyar K, Zhang Z, Teles RM, Ouyang S, Jiang Y, Iyer SS, et al. The helicase DDX41 recognizes the bacterial secondary messengers cyclic di-GMP and cyclic di-AMP to activate a type I interferon immune response. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13:1155–61.

41). Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science. 2013; 339:826–30.

42). Yoshida H, Okabe Y, Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Nagata S. Lethal anemia caused by interferon-beta produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:49–56.
Go to : 
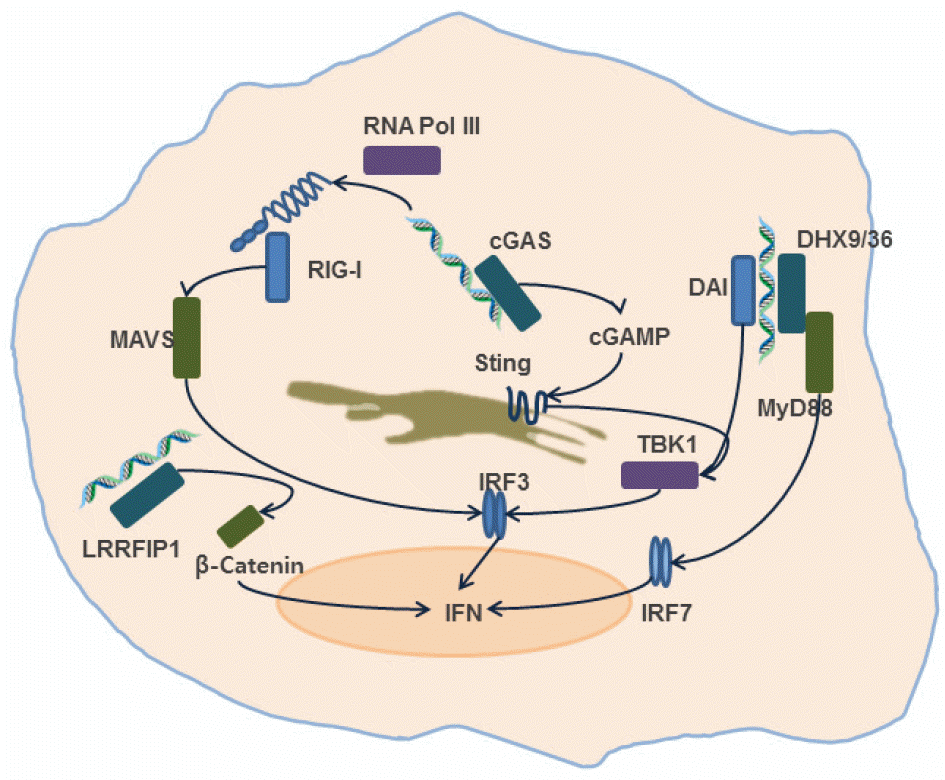 | Figure 1.
Induction of type-I interferon by intracellular DNA sensors. It has been shown that intracellular DNA sensors including DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI), RNA polymerase III (RNA Pol III), Leucine rich repeat interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1), Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), (DExD/H)-box helicase 9/36 (DHX9/36) can induce type-I interferon production upon recognition of pathogen-derived DNA. |
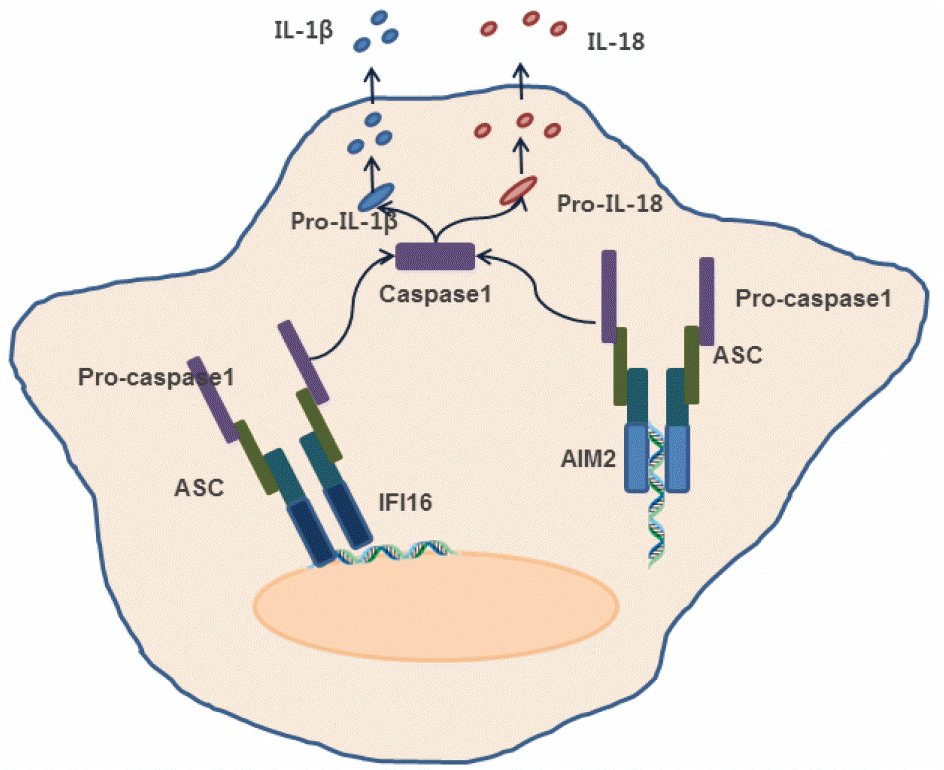 | Figure 2.
Activation of inflammasome signaling by intracellular DNA sensors. Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) and gamma-interferon-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) activate inflammasome signaling pathway leading to caspase-1 activation upon recognition of pathogen-derived DNA. |
Table 1.
List of cytosolic DNA sensors.
| DNA sensors | Related pathogens | Ligand | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type-I interferon induction |
DAI1 RNA Pol III2 DHX9/DHX363 DDX414 LRRFIP15 cGAS6 |
HSV1a HSV1, Adenovirus, EBVb, L. pneumophiliac HSV1 HSV1, Adenovirus VSVd, L. monocytogenese HSV1 |
dsDNA dsDNA CpG DNA dsDNA dsDNA, dsRNA dsDNA |
| Inflammasome activation |
AIM27 IFI168 |
F. tulalensisf, L. monocytogenes, VVg, mCMVh HSV1, KSHVi |
dsDNA dsDNA |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download