Abstract
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS) and Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF) are tick-borne diseases belonging to the family Bunyaviridae. Since SFTS was first reported in China in 2009, the virus was isolated and confirmed in 2011, with additional reports of SFTSV expanding its geographic range from China to South Korea and Japan. CCHFV has the widest geographic distribution of any tick-borne virus, encompassing around 30 countries from eastern China through Asia, the Middle East, and southeastern Europe to Africa. During the past decade, CCHFV has emerged in new areas of Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia and has increased in endemic areas. Migratory birds are considered to play a role in dispersing CCHFV vectors, and the virus. This review summarises SFTSV and CCHFV, highlighting the role of migratory birds in the transmission of tick-borne disease.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Palomar AM, Santibáñez P, Mazuelas D, Roncero L, Santibáñez S, Portillo A, et al. Role of birds in dispersal of etiologic agents of tick-borne zoonoses, Spain, 2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:1188–91.

2). Lindeborg M, Barboutis C, Ehrenborg C, Fransson T, Jaenson TG, Lindgren PE, et al. Migratory birds, ticks, and crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:2095–7.

3). Choi CY, Kang CW, Kim EM, Lee S, Moon KH, Oh MR, et al. Ticks collected from migratory birds, including a new record of Haemaphysalis formosensis, on Jeju Island, Korea. Exp Appl Acarol. 2013.
4). Waldenström J, Lundkvist A, Falk KI, Garpmo U, Bergström S, Lindegren G, et al. Migrating birds and tickborne encephalitis virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007; 13:1215–8.

5). Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1523–32.
6). Niu G, Li J, Liang M, Jiang X, Jiang M, Yin H, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus among domesticated animals, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:756–63.

7). Ko S, Kang JG, Kim SY, Kim HC, Klein TA, Chong ST, et al. Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks from southern Korea. J Vet Sci. 2010; 11:197–203.

8). Moon BC, Jeong JH, Choi YJ, Kim JE, Seo HJ, Shin EH, et al. Detection and identification of the Spotted Fever Group Rickettsial agents from Haemaphysalis ticks in Jeju Island, Korea. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009; 39:317–27.
9). Oh JY, Moon BC, Bae BK, Shin EH, Ko YH, Kim YJ, et al. Genetic identification and phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma and Ehrlichia species in Haemaphysalis longicornis collected from Jeju Island, Korea. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009; 39:257–67.
10). Chong ST, Kim HC, Lee IY, Kollars TM Jr, Sancho AR, Sames WJ, et al. Seasonal distribution of ticks in four habitats near the demilitarized zone, Gyeonggi-do (Province), Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2013; 51:319–25.

11). Kang JG, Kim HC, Choi CY, Nam HY, Chae HY, Chong ST, et al. Molecular detection of Anaplasma, Bartonella, and Borrelia species in ticks collected from migratory birds from Hong-do Island, Republic of Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013; 13:215–25.
12). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Turdus naumanni and Turdus pallidus. http://www.iucnredlist.org.
13). www.birdskorea.org
14). East Asia/Australasia Flyway - BirdLife International.
15). Deng B, Zhang S, Geng Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Yao W, et al. Cytokine and chemokine levels in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. PLoS ONE. 2012; 7:e41365.

16). Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim NH, et al. Severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19.

17). Wu Y, Gao GF. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus expands its borders. Emerging Microbes & Infections. 2013; 2:e36.

18). Prevention of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2013. http://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/intro/CdcKrIntro0201.jsp?menuIds=HOME001-MNU0005-MNU0011&fid=21&q_type=&q_value=&cid=21368&pageNum=.
19). Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987; 4:406–25.
20). Oh WS, Heo ST, Kim SH, Choi WJ, Han MG, Kim JY. Plasma exchange and ribavirin for rapidly progressive severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Int J Infect Dis. 2013. S1201–9712.

21). Lindeborg M, Barboutis C, Ehrenborg C, Fransson T, Jaenson TG, Lindgren PE, et al. Migratory Birds, Ticks, and Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:2095–7.

22). Palomar AM, Portillo A, Santibáñez P, Mazuelas D, Arizaga J, Crespo A, et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in ticks from migratory birds, Morocco. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:260–3.
23). Ergonul O. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus: new outbreaks, new discoveries. Curr Opin Virol. 2012; 2:215–20.

24). Hoogstraal H. The epidemiology of tick-borne Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Asia, Europe, and Africa. J Med Entomol. 1979; 15:307–417.
25). Anagnostou V, Papa A. Evolution of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus. Infect Genet Evol. 2009; 9:948–54.

26). Jameson LJ, Morgan PJ, Medlock JM, Watola G, Vaux AG. Importation of Hyalomma marginatum, vector of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus, into the United Kingdom by migratory birds. Ticks Tick borne Dis. 2012; 3:95–9.
27). Hoogstraal H, Kaiser MN, Traylor MA, Gaber S, Guindy E. Ticks (Ixodoidea) on birds migrating from Africa to Europe and Asia. Bull World Health Organ. 1961; 24:197–212.
28). Lee SH, Nam KW, Jeong JY, Yoo SJ, Koh YS, Lee S, et al. The Effects of Climate Change and Globalization on Mosquito Vectors: Evidence from Jeju Island, South Korea on the Potential for Asian Tiger Mosquito (Aedes albopictus) Influxes and Survival from Vietnam Rather Than Japan. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8:e68512.
Go to : 
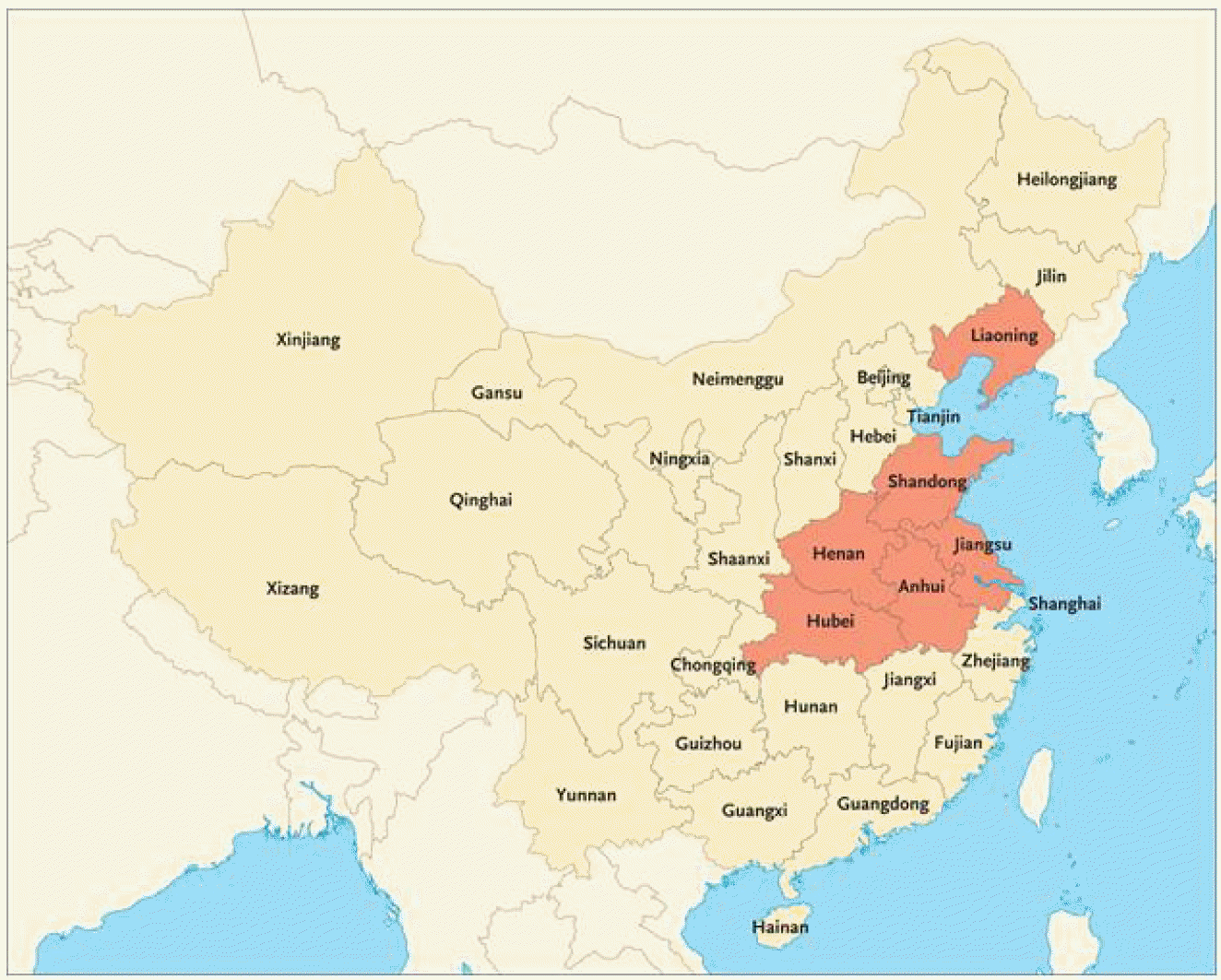 | Figure 1.
Geographic Distribution of SFTS in China. Since March 2010, SFTSV was isolated from patients are shown in red. SFTS has been reported in at least 13 provinces in the central, eastern, and northeastern regions of the People's Republic of China. Most patients are farmers living in wooded, hilly, or mountainous areas, and the epidemic season is from March through November, with the peak incidence usually in June and July (5). |
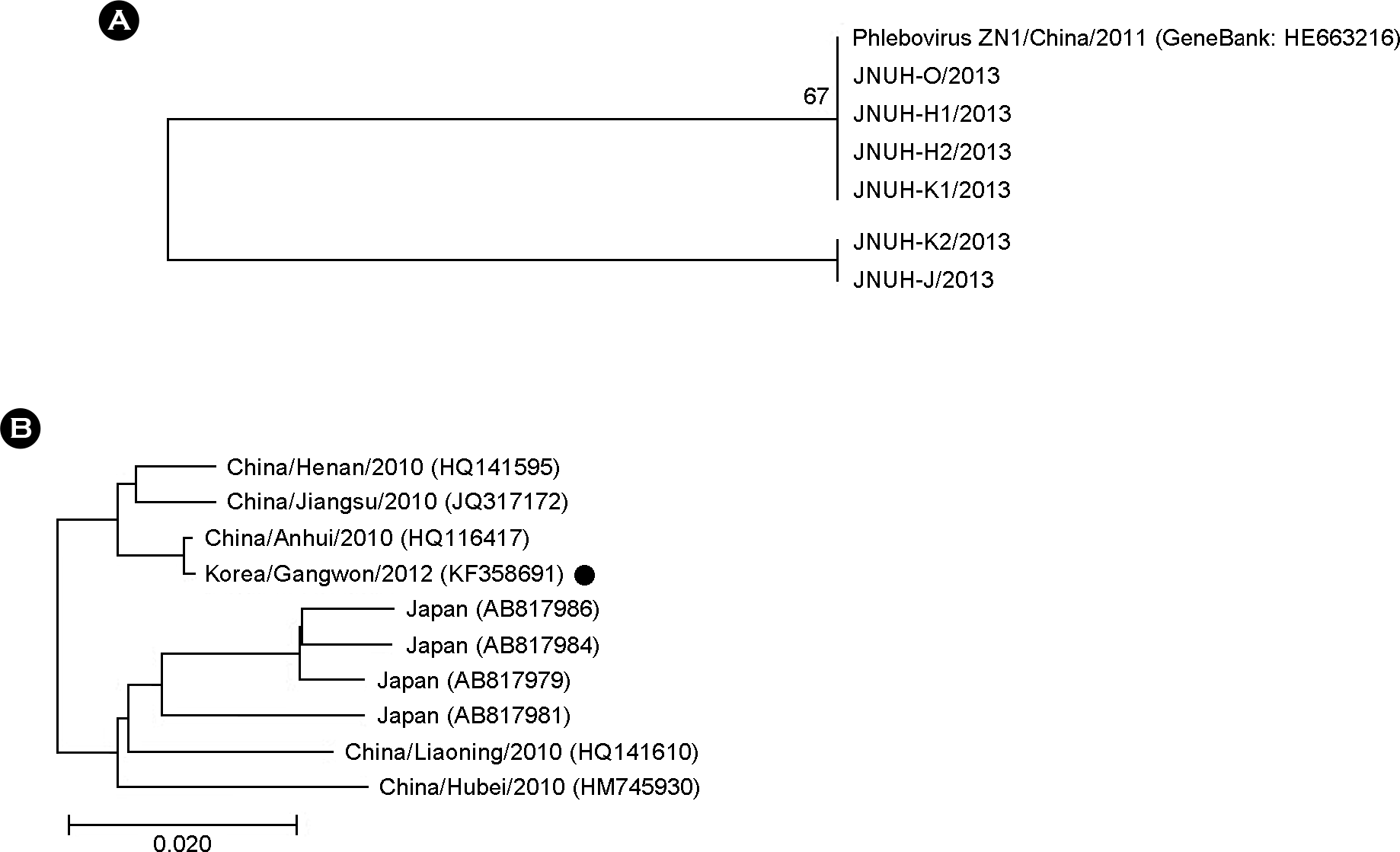 | Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of S segment of isolates obtained from SFTS patient in Jeu Island in 2013 and phylogenetic tree of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene of an isolate obtained from a SFTS patient in South Korea in 2012 (B). The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA4 (19). JNUH-O/2013, JNUH-H1/2013, JNUH-H2/2013, JNUH-K1/2013, JNUH-K2 /2013, and JNUH-J/2013, were isolated from SFTS patient in Jeju Island in 2013 respectively, and Phlebovirus ZN1/China/2011 (GeneBank: HE663216), which were isolated from China in 2011 (A) and phylogenetic tree for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene sequences of the large segment of an isolate obtained from a SFTS patient in South Korea (black dot) compared with representative SFTSV strains from China and Japan (B) (16). |
 | Figure 3.
Bird species. Typical feeding sites of Hyalomma marginatum nymphs on an Oenanthe oenanthe (26). |
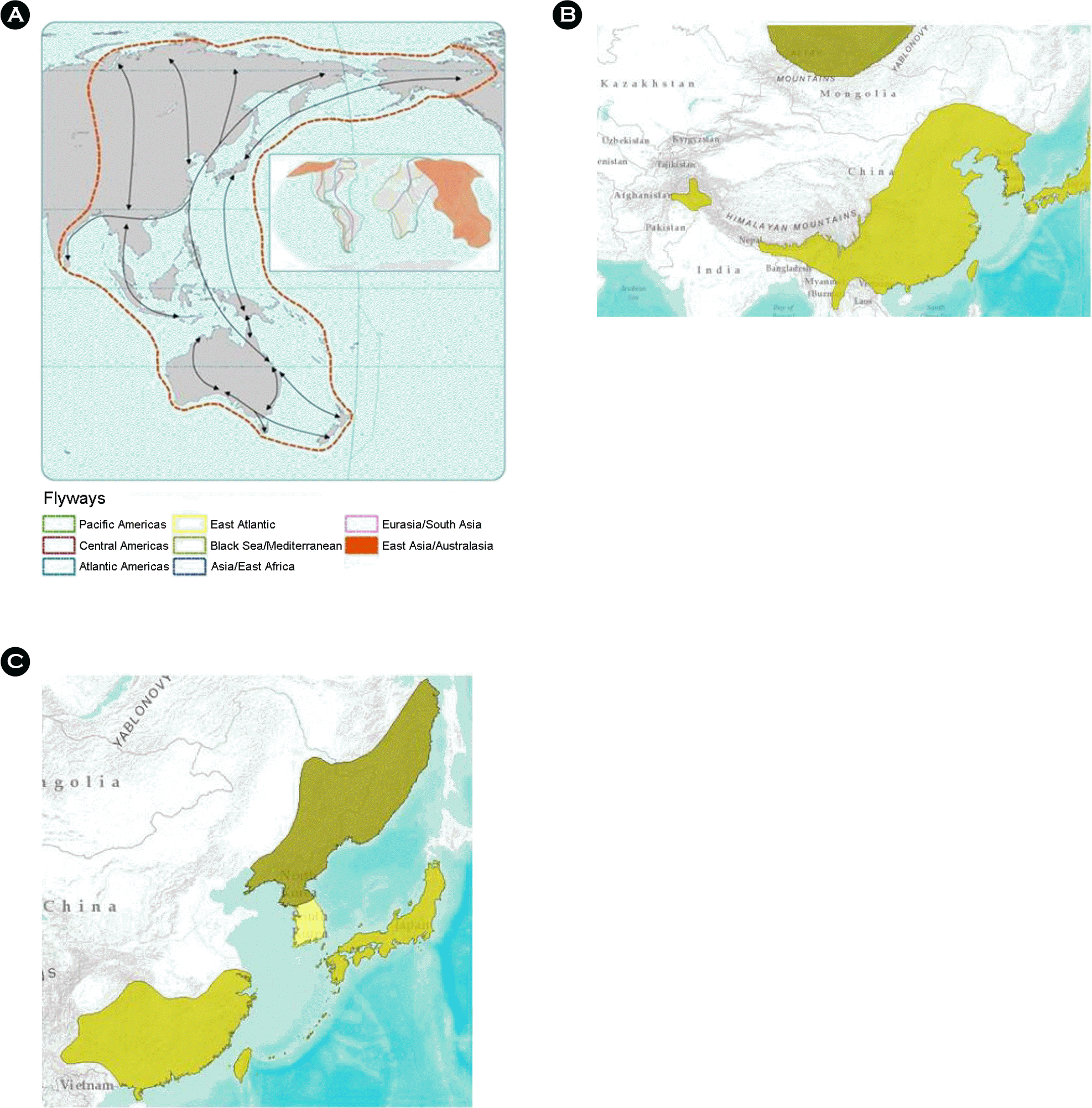 | Figure 4.
Migratory birds Flyway (A), Turdus naumanni (B), and Turdus pallidus (C) distribution map of the world. Recent research has identified eight such pathways: the East Atlantic, the Mediterranean/Black Sea, the East Asia/East Africa, the Central Asia, the East Asia/Australasia, and three flyways in the Americas and the Neotropics (A) (14). Native of T. naumanni are Bangladesh, Bhutan, Canada, China, Hong Kong, India, Japan, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Taiwan, Province of China, Thailand, and Viet Nam and Vagrant of T. naumanni are Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Faroe Islands, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, Israel, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Montenegro, Netherlands, Northern Mariana Islands, Norway, Oman, Poland, Saudi Arabia, Northern Mariana Islands, Norway, Oman, Poland, Saudi Arabia Serbia (Serbia), Slovenia, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, and United States (B) (12). Native of Turdus pallidus are Hong Kong, Japan, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Philippines Taiwan, and Province of China and Vagrant of T. pallidus are China and Germany (C) (12). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download