Abstract
Leptin is a 16 kDa protein which consists of 167 amino acids. Leptin is considered as one of the adipokines, secreted by white adipocytes, and is the product of the obese (ob) gene. Recently, leptin is recognized as the immuno-stimulator which belongs to the same class of long chain helical cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-6. Leptin is related to the immune responses evoked by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Thus, studies of association between immunomolecules including leptin and tuberculosis may contribute to provide an essential solution regulating adverse immune responses in several mycobacterial diseases. Leptin has a multifunctional role in the secretion of acute-phase cytokines including IL-1β and tumor-necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and links to T helper 1 (Th1) immune response. Moreover, the binding of leptin to leptin receptor (LepR) is important in that this binding involves janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway. In addition, the activation of LepR mediates extra-cellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) pathways. Furthermore, many studies suggest that leptin may play a critical role in respiratory diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma as well as tuberculosis. These findings indicate that leptin is one of the important regulators for immune responses in respiratory diseases. We herein discuss the multifunctional role of leptin in mycobacterial lung disease, especially focusing on the related pathway to immune responses.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Frühbeck G, Jebb SA, Prentice AM. Leptin: physiology and pathophysiology. Clin Physiol. 1998; 18:399–419.

3). Fain JN, Leffler CW, Bahouth SW. Eicosanoids as endogenous regulators of leptin release and lipolysis by mouse adipose tissue in primary culture. J Lipid Res. 2000; 41:1689–94.

4). Babon JJ, Nicola NA. The biology and mechanism of action of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Growth Factors. 2012; 30:207–19.

6). Fernández-Riejos P, Najib S, Santos-Alvarez J, Martín-Romero C, Pérez-Pérez A, González-Yanes C, et al. Role of leptin in the activation of immune cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2010; 2010:568343.

7). Eyckerman S, Broekaert D, Verhee A, Vandekerckhove J, Tavernier J. Identification of the Y985 and Y1077 motifs as SOCS3 recruitment sites in the murine leptin receptor. FEBS Lett. 2000; 486:33–7.

8). Fantuzzi G, Faggioni R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2000; 68:437–46.
9). Hansen GH, Niels-Christiansen LL, Danielsen EM. Leptin and the obesity receptor (OB-R) in the small intestine and colon: a colocalization study. J Histochem Cytochem. 2008; 56:677–85.

10). Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. 1998; 12:57–65.

11). Zarkesh-Esfahani H, Pockley G, Metcalfe RA, Bidlingmaier M, Wu Z, Ajami A, et al. High-dose leptin activates human leukocytes via receptor expression on monocytes. J Immunol. 2001; 167:4593–9.

12). Gruen ML, Hao M, Piston DW, Hasty AH. Leptin requires canonical migratory signaling pathways for induction of monocyte and macrophage chemotaxis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007; 293:C1481–8.

13). Mattioli B, Straface E, Matarrese P, Quaranta MG, Giordani L, Malorni W, et al. Leptin as an immunological adjuvant: enhanced migratory and CD8+ T cell stimulatory capacity of human dendritic cells exposed to leptin. FASEB J. 2008; 22:2012–22.
14). Tian Z, Sun R, Wei H, Gao B. Impaired natural killer (NK) cell activity in leptin receptor deficient mice: leptin as a critical regulator in NK cell development and activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 298:297–302.

15). Feng CG, Kaviratne M, Rothfuchs AG, Cheever A, Hieny S, Young HA, et al. NK cell-derived IFN-gamma differentially regulates innate resistance and neutrophil response in T cell-deficient hosts infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 2006; 177:7086–93.
16). Lemos MP, Rhee KY, McKinney JD. Expression of the leptin receptor outside of bone marrow-derived cells regulates tuberculosis control and lung macrophage MHC expression. J Immunol. 2011; 187:3776–84.

17). Sanna V, Di Giacomo A, La Cava A, Lechler RI, Fontana S, Zappacosta S, et al. Leptin surge precedes onset of autoimmune encephalomyelitis and correlates with development of pathogenic T cell responses. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111:241–50.

18). Procaccini C, De Rosa V, Galgani M, Abanni L, Calì G, Porcellini A, et al. An oscillatory switch in mTOR kinase activity sets regulatory T cell responsiveness. Immunity. 2010; 33:929–41.

19). Faggioni R, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Leptin regulation of the immune response and the immunodeficiency of malnutrition. FASEB J. 2001; 15:2565–71.
20). Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ, Bloom SR, Lechler RI. Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature. 1998; 394:897–901.

21). Dye C, Williams BG. The population dynamics and control of tuberculosis. Science. 2010; 328:856–61.

22). Santucci N, D'Attilio L, Kovalevski L, Bozza V, Besedovsky H, del Rey A, et al. A multifaceted analysis of immune-endocrine-metabolic alterations in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e26363.

23). Wieland CW, Florquin S, Chan ED, Leemans JC, Weijer S, Verbon A, et al. Pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. Int Immunol. 2005; 17:1399–408.
24). Bruno A, Alessi M, Soresi S, Bonanno A, Riccobono L, Montalbano AM, et al. Increased leptin/leptin receptor pathway affects systemic and airway inflammation in COPD former smokers. J Inflamm Res. 2011; 4:51–9.
25). Sarraf P, Frederich RC, Turner EM, Ma G, Jaskowiak NT, Rivet DJ 3rd, et al. Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse leptin levels: potential role in inflammatory anorexia. J Exp Med. 1997; 185:171–5.

26). Tilg H, Moschen AR. Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006; 6:772–83.

27). Buyukoglan H, Gulmez I, Kelestimur F, Kart L, Oymak FS, Demir R, et al. Leptin levels in various manifestations of pulmonary tuberculosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2007; 2007:64859.

28). Myers MG Jr. Leptin receptor signaling and the regulation of mammalian physiology. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004; 59:287–304.

29). Farooqi IS, Wangensteen T, Collins S, Kimber W, Matarese G, Keogh JM, et al. Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:237–47.

30). van Crevel R, Karyadi E, Netea MG, Verhoef H, Nelwan RH, West CE, et al. Decreased plasma leptin concentrations in tuberculosis patients are associated with wasting and inflammation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:758–63.

31). Choi GE, Jo Y, Shin SJ. Current understanding of Mycobacterium abscessus infection. J Bacteriol Virol. 2012; 42:17–28.
32). Ordway D, Henao-Tamayo M, Smith E, Shanley C, Harton M, Troudt J, et al. Animal model of Mycobacterium abscessus lung infection. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 83:1502–11.
33). Mustafa T. Does leptin have a role in immunity to tuberculosis? Indian J Med Res. 2008; 128:691–3.
34). Yüksel I, Sencan M, Dökmetaş HS, Dökmetaş I, Ataseven H, Yönem O. The relation between serum leptin levels and body fat mass in patients with active lung tuberculosis. Endocr Res. 2003; 29:257–64.

35). Kim JH, Lee CT, Yoon HI, Song J, Shin WG, Lee JH. Relation of ghrelin, leptin and inflammatory markers to nutritional status in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin Nutr. 2010; 29:512–8.

36). Chan ED, Iseman MD. Slender, older women appear to be more susceptible to nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. Gend Med. 2010; 7:5–18.

37). Tasaka S, Hasegawa N, Nishimura T, Yamasawa W, Kamata H, Shinoda H, et al. Elevated serum adiponectin level in patients with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex pulmonary disease. Respiration. 2010; 79:383–7.
38). Andreas S, Anker SD, Scanlon PD, Somers VK. Neurohumoral activation as a link to systemic manifestations of chronic lung disease. Chest. 2005; 128:3618–24.

39). Takabatake N, Nakamura H, Abe S, Hino T, Saito H, Yuki H, et al. Circulating leptin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 159:1215–9.

40). Lam QL, Lu L. Role of leptin in immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007; 4:1–13.
41). Bruno A, Chanez P, Chiappara G, Siena L, Giammanco S, Gjomarkaj M, et al. Does leptin play a cytokine-like role within the airways of COPD patients? Eur Respir J. 2005; 26:398–405.

42). Baranova A, Randhawa M, Jarrar M, Younossi ZM. Adipokines and melanocortins in the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007; 7:195–205.

43). Bruno A, Pace E, Chanez P, Gras D, Vachier I, Chiappara G, et al. Leptin and leptin receptor expression in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:230–237. e1–444.

Go to : 
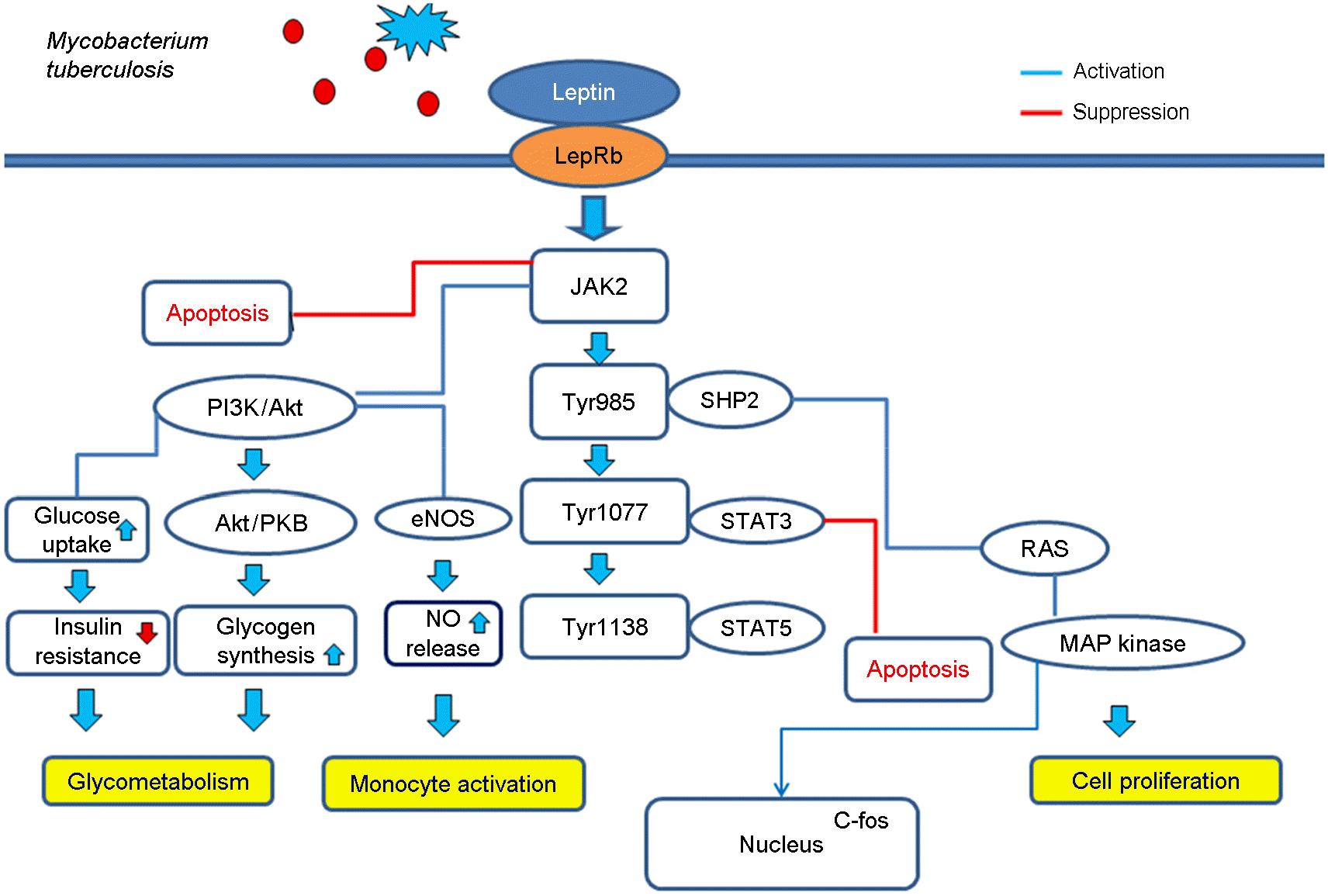 | Figure 1.
Leptin and Leptin receptor (LepR) pathway. JAK2 associates with the receptor via the box1 motif. The long isoform leptin (L) receptor (LepRb) contains four important tyrosine residues (Tyr974, Tyr985, Tyr1077 and Tyr1138). These phosphorylated tyrosine residues provide docking sites for signalling proteins with SH2 domains. Most importantly, Tyr1138 recruits the transcription factor STAT3, which is subsequently phosphorylated by JAK2, dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus. The ERK members of the MAPK family are components of the well-defined Ras/Raf/MAPK signalling cascade and have become activated by leptin. Stimulation of the PI3K pathway by leptin represents a key cascade to exert several different effects of the hormone at multiple sites. JAK, Janus kinase; PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT/PKB, protein kinase B; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; STAT, Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription; NO, nitric oxide; MAP, Mitogen-activated protein. |
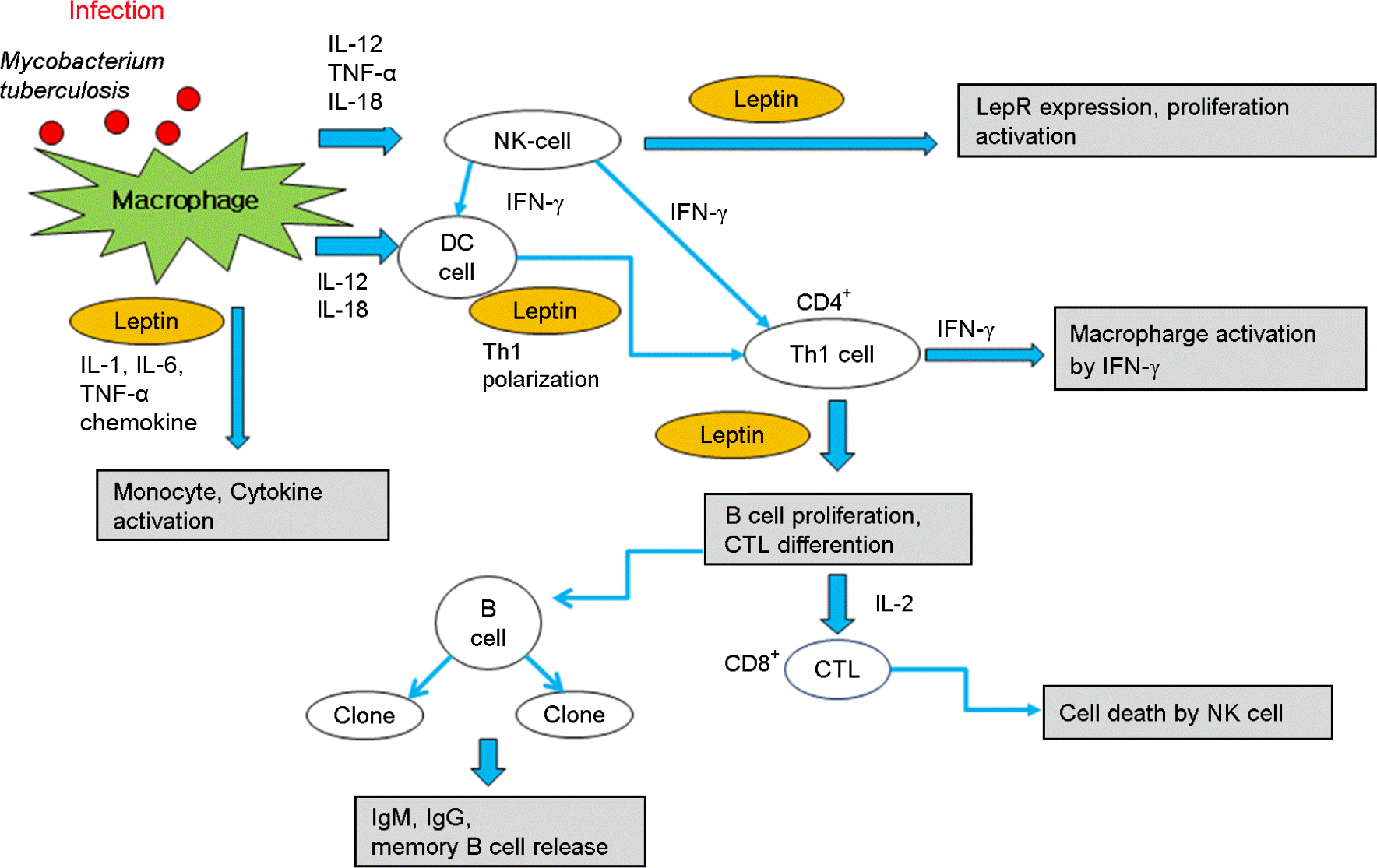 | Figure 2.
Effect of leptin on immune cell differentiation and immune responses. Leptin affects both innate and adaptive immunity. In innate immunity, leptin modulates the activity and function of neutrophils by increasing chemotaxis and the secretion of oxygen radicals through direct and indirect mechanisms. In mice, leptin seems to activate neutrophils directly. In humans, the action of leptin seems to be mediated by TNF-α secreted by monocytes. Leptin increases phagocytosis by monocytes/macrophages and enhances the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators of the acute-phase response and the expression of adhesion molecules. On NK cells, leptin increases cytotoxic ability and the secretion of perforin and IL-2. In adaptive immunity, leptin affects the generation, maturation and survival of thymic T cells by reducing their rate of apoptosis. On naive T-cell responses, leptin increases proliferation and IL-2 secretion through the activation of MAPK and PI3K pathways. On memory T cells, leptin promotes the switch towards Th1-cell immune responses by increasing IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion, the production of IgG2a by B cells and delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses. This process is then sustained by an autocrine loop of leptin secretion by Th1 cells. Finally, leptin has anti-apoptotic effects on mature T cells and on haematopoietic precursors. |
Table 1.
Effect of leptin on immune system
Table 2.
Effect of leptin on respiratory disease




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download