Abstract
Cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies against influenza A viruses have received attention for their potentials for prophylactic and therapeutic. These antibodies usually bind to relatively conserved stem domains of influenza hemagglutinin, one of surface glycoproteins responsible for viral binding to sialic acid-tagged cellular receptors and for membrane fusion to initiate a release process of viral genomes inside cells. Recently, a similar approach extended to influenza B viruses, which causing annual epidemics only in the human population, and some of human monoclonal antibodies exhibited promising efficacies against two antigenically diverged lineages of influenza B viruses. Moreover, one of these broadly neutralizing antibodies protected mice against both of influenza A and B challenges. Appropriate immunization may selectively enhance the efficacy of these antibodies, and this strategy may lead individuals to be prepared with broad immune responses against various influenza viruses.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
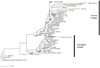
Phylogenetic analysis of influenza B HAs. 571 submitted HA sequences (collapsed from total 1,142 sequences available from National Center for Biotechnology Information) of influenza B viruses since 1940 were analyzed for their genetic distances. To compare phylogenetic lines between sequences, the neighbor-joining method was applied for a clustering algorithm. F84 distance was adopted for nucleotide distances for each coding sequence. The number in the parentheses represents the number of isolates.
References
1. Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E, Brammer L, Bridges CB, Cox NJ, et al. Influenza-associated hospitalizations in the United States. JAMA. 2004. 292:1333–1340.

2. Rota PA, Wallis TR, Harmon MW, Rota JS, Kendal AP, Nerome K. Cocirculation of two distinct evolutionary lineages of influenza type B virus since 1983. Virology. 1990. 175:59–68.

3. Ambrose CS, Levin MJ. The rationale for quadrivalent influenza vaccines. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2012. 8:81–88.

4. Ekiert DC, Wilson IA. Broadly neutralizing antibodies against influenza virus and prospects for universal therapies. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. 2:134–141.

5. Dreyfus C, Laursen NS, Kwaks T, Zuijdgeest D, Khayat R, Ekiert DC, et al. Highly conserved protective epitopes on influenza B viruses. Science. 2012. 337:1343–1348.

6. Ekiert DC, Bhabha G, Elsliger MA, Friesen RH, Jongeneelen M, Throsby M, et al. Antibody recognition of a highly conserved influenza virus epitope. Science. 2009. 324:246–251.

7. Ekiert DC, Friesen RH, Bhabha G, Kwaks T, Jongeneelen M, Yu W, et al. A highly conserved neutralizing epitope on group 2 influenza A viruses. Science. 2011. 333:843–850.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download