Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) establishes a latent infection in greater than 90% of the world's adult population and associates with various tumors. EBV primarily infects epithelial cells and B cell in vivo. Mechanism of EBV infection in B cells is known to involve binding of EBV glycoprotein gp350 to CD21 on B cell surface. Epithelial cells are infected with EBV even though most of epithelial cells do not express CD21. Recently, integrin αvβ5, αvβ6 and αvβ8 on epithelial cells were reported to facilitate EBV infection by interacting with gHgL complex. We examined the expression profile of integrins known to be expressed on epithelial cells. Integrin αvβ5 and αvβ6, but not αvβ8 were detected in a gastric epithelial cell line, AGS. We then tested whether siRNAs specific to β6 can inhibit EBV infection of epithelial cells. One among the four tested siRNAs significantly reduced β6 expression and suppressed transfer infection of EBV to AGS cells. Our data suggest that siRNAs to integrins might be useful to control EBV infection to epithelial cells.
Figures and Tables
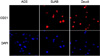 | Figure 1Detection of CD21 expression in AGS cells by immunofluorescence assay. AGS cells were stained with the anti-CD21 antibody and the Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody. The cells were then incubated DAPI to stain nuclei. BJAB and Daudi cells were used as positive controls for CD21 expression (200× magnification). |
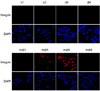 | Figure 2Detection of integrin expression in AGS cells by immunofluorescence assay. The cells were incubated with integrin α1, α2, α6, β4, αvβ3, or αvβ8 specific antibodies and then with the Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody. The cells were then incubated with DAPI to stain nuclei (200× magnification). |
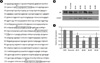 | Figure 3The effect of siRNAs on the expression of β6. (A) Sequence of integrin β6 (NCBI accession no. NM_000888). The sequences of four siRNAs used to down-regulate integrin β6 are marked with boxes and numbers. (B) Expression of β6 was analyzed by Western blot in the cells transfected with each siRNA. BJAB cells were used as a negative control. (C) Similar Western blot experiments shown in (B) were repeated three times. The relative expression levels of β6 following each siRNA treatment compared with that of scrambled control siRNA treatment are shown as mean ± SD. **p < 0.01 |
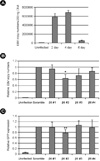 | Figure 4The effect of β6 siRNA on EBV infection. (A) AGS cells were co-cultured with lytic cycle induced B95-8 cells for 24 h. After removing B95-8 cells by PBS wash, the infected AGS cells were then cultured for 2, 4, and 6 days further. The efficiency of transfer infection was assayed by QPCR for EBNA-1 sequence as described in the Methods. siRNA treated AGS cells were transfer infected with lytic cycle induced B95-8 cells (B) or B95-8 EBfaV-GFP cells (C). (B) EBV copy numbers were analyzed by QPCR for EBNA-1 sequence. (C) EBV infection was measured by FACS analysis of GFP expressing cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 |
Notes
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) (2009-0074118) and by grants from the Gyeonggi Regional Research Center (GRRC) of the Catholic University of Korea [(GRRC Catholic 2012-B05), RNA-based development of biopharmaceutical lead molecules].
References
1. Klein E. The complexity of the Epstein-Barr virus infection in humans. Pathol Oncol Res. 1998. 4:3–7.

2. Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Epstein-Barr virus. Fields Virology. 1996. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;2397–2446.
3. Shibata D, Weiss LM. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1992. 140:769–774.
5. Niedobitek G, Agathanggelou A, Herbst H, Whitehead L, Wright DH, Young LS. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in infectious mononucleosis: virus latency, replication and phenotype of EBV-infected cells. J Pathol. 1997. 182:151–159.

7. Li Q, Spriggs MK, Kovats S, Turk SM, Comeau MR, Nepom B, et al. Epstein-Barr virus uses HLA class II as a cofactor for infection of B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1997. 71:4657–4662.

8. Borza CM, Morgan AJ, Turk SM, Hutt-Fletcher LM. Use of gHgL for attachment of Epstein-Barr virus to epithelial cells compromises infection. J Virol. 2004. 78:5007–5014.

9. Molesworth SJ, Lake CM, Borza CM, Turk SM, Hutt-Fletcher LM. Epstein-Barr virus gH is essential for penetration of B cells but also plays a role in attachment of virus to epithelial cells. J Virol. 2000. 74:6324–6332.

10. Chesnokova LS, Nishimura SL, Hutt-Fletcher LM. Fusion of epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus proteins is triggered by binding of viral glycoproteins gHgL to integrins alphavbeta6 or alphavbeta8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. 106:20464–20469.

11. Chesnokova LS, Hutt-Fletcher LM. Fusion of Epstein-Barr virus with epithelial cells can be triggered by αvβ5 in addition to αvβ6 and αvβ8, and integrin binding triggers a conformational change in glycoproteins gHgL. J Virol. 2011. 85:13214–13223.

14. Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002. 110:673–687.
15. Seo NS, Zeng CQ, Hyser JM, Utama B, Crawford SE, Kim KJ, et al. Integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 are receptors for the rotavirus enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. 105:8811–8818.
16. Fang IM, Yang CH, Yang CM, Chen MS. Overexpression of integrin alpha6 and beta4 enhances adhesion and proliferation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells on layers of porcine Bruch's membrane. Exp Eye Res. 2009. 88:12–21.

17. Yoshiyama H, Imai S, Shimizu N, Takada K. Epstein-Barr virus infection of human gastric carcinoma cells: implication of the existence of a new virus receptor different from CD21. J Virol. 1997. 71:5688–5691.

18. Speck P, Kline KA, Cheresh P, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus lacking latent membrane protein 2 immortalizes B cells with efficiency indistinguishable from that of wild-type virus. J Gen Virol. 1999. 80:2193–2203.

19. Seo JS, Cho NY, Kim HR, Tsurumi T, Jang YS, Lee WK, et al. Cell cycle arrest and lytic induction of EBV-transformed B lymphoblastoid cells by a histone deacetylase inhibitor, Trichostatin A. Oncol Rep. 2008. 19:93–98.

20. Fingeroth JD, Weis JJ, Tedder TF, Strominger JL, Biro PA, Fearon DT. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984. 81:4510–4514.

21. Shannon-Lowe CD, Neuhierl B, Baldwin G, Rickinson AB, Delecluse HJ. Resting B cells as a transfer vehicle for Epstein-Barr virus infection of epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. 103:7065–7070.

22. Shimizu N, Yoshiyama H, Takada K. Clonal propagation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants in EBV-negative Akata cells. J Virol. 1996. 70:7260–7263.

23. Kieff E. Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. Fundamental Virology. 1996. New York: Raven Press;1109–1162.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download