Abstract
Noroviruses (NoV) are the major viral pathogen that causes epidemic acute gastroenteritis and outbreaks of food-borne illness. The major genotypes responsible for the epidemics of NoV are GII.4 and GII.3. However, most studies of NoV have been associated with GII.4 genotype and only few studies have been done with GII.3 genotype. Here, we selected 18 GII.3 strains, which recently circulated in Korea, and determined the partial sequences of the capsid gene. Phylogenetic analysis comparing these sequences with 29 reference strains from the GenBank database was performed using the MEGA program. All NoV GII.3 strains formed 2 distinct genetic lineages and variant groups. Lineage A showed 94.1∼97.6%, 90.2∼94.6% nucleotide identities from lineage B and variant group, respectively. Lineage B showed 90.2∼94.6% nucleotide identities from variant group. These different genetic lineages based on the phylogenetic analysis of capsid sequences imply that the circulating Korean NoV GII.3 strains have potential antigenic variation.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Glass RI, Bresee J, Jiang B, Gentsch J, Ando T, Fankhauser R, et al. Gastroenteritis viruses: an overview. Novartis Found Symp. 2001; 238:5–19.

2). Chikhi-Brachet R, Bon F, Toubiana L, Pothier P, Nicolas JC, Flahault A, et al. Virus Diversity in a Winter Epidemic of Acute Diarrhea in France. J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 40:4266–72.

3). Dey SK, Nguyen TA, Phan TG, Nishio O, Salim AF, Rahman M, et al. Molecular and epidemiological trend of norovirus associated gastroenteritis in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. J Clin Virol. 2007; 40:218–23.

4). Kapikian AZ, Wyatt RG, Dolin R, Thornhill TS, Kalica AR, Chanock RM. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1972; 10:1075–81.

5). Kaplan JE, Gary GW, Baron RC, Singh N, Schonberger LB, Feldman R, et al. Epidemiology of Norwalk gastroenteritis and the role of Norwalk virus in outbreaks of acute nonbacterial gastroenteritis. Ann Intern Med. 1982; 96:756–61.

6). Vinjé J, Hamidjaja RA, Sobsey MD. Development and application of a capsid VP1 (region D) based reverse transcription PCR assay for genotyping of genogroup I and II noroviruses. J Virol Methods. 2004; 116:109–17.

7). Ambert-Balay K, Bon F, Le Guyader F, Pothier P, Kohli E. Characterization of new recombinant noroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:5179–86.

8). Medici MC, Martinelli M, Abelli LA, Ruggeri FM, Di Bartolo I, Arcangeletti MC, et al. Molecular epidemiology of norovirus infections in sporadic cases of viral gastroenteritis among children in Northern Italy. J Med Virol. 2006; 78:1486–92.

9). Gallimore CI, Cubitt D, du Plessis N, Gray JJ. Asymptomatic and symptomatic excretion of noroviruses during a hospital outbreak of gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:2271–4.

10). Lambden PR, Caul EO, Ashley CR, Clarke IN. Sequence and genome organization of a human small round-structured (Norwalk-like) virus. Science. 1993; 259:516–9.

11). Park KS, Jeong HS, Baek KA, Lee CG, Park SM, Park JS, et al. Genetic analysis of norovirus GII.4 variants circulating in Korea in 2008. Arch Virol. 2010; 155:635–41.

12). Park JW, Lee SG, Lee YM, Jheong WH, Ryu S, Paik SY. Full sequence analysis and characterization of the South Korean Norovirus GII-4 variant CUK-3. Virol J. 2011; 8:167.

13). Jeong AY, Yun SI, Jee YM, Kang YS, Lee YM. Molecular characterization of Korean isolate of human norovirus, the Hu/NLV/Gunpo/2006/KO Strain. Korean J Microbiol. 2009; 45:105–11.
14). Kojima S, Kageyama T, Fukushi S, Hoshino FB, Shinohara M, Uchida K, et al. Genogroup-specific PCR primers for detection of Norwalk-like viruses. J Virol Methods. 2002; 100:107–14.

15). Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994; 22:4673–80.

16). Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987; 4:406–25.
17). Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007; 24:1596–9.

18). Kim SH, Cheon DS, Kim JH, Lee DH, Jheong WH, Heo YJ, et al. Outbreaks of gastroenteritis that occurred during school excursions in Korea were associated with several waterborne strains of norovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:4836–9.

19). Gong YW, Oh BY, Kim HY, Lee MY, Kim YH, Go JM, et al. Molecular epidemiologic investigation of Norovirus infections in Incheon City, Korea, from 2005 to 2007. J Bacteriol Virol. 2008; 38:249–57.

20). Jiang X, Wang J, Graham DY, Estes MK. Detection of Norwalk virus in stool by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992; 30:2529–34.

21). Burton-MacLeod JA, Kane EM, Beard RS, Hadley LA, Glass RI, Ando T. Evaluation and comparison of two commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for detection of antigenically diverse human Noroviruses in stool samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:2587–95.

Go to : 
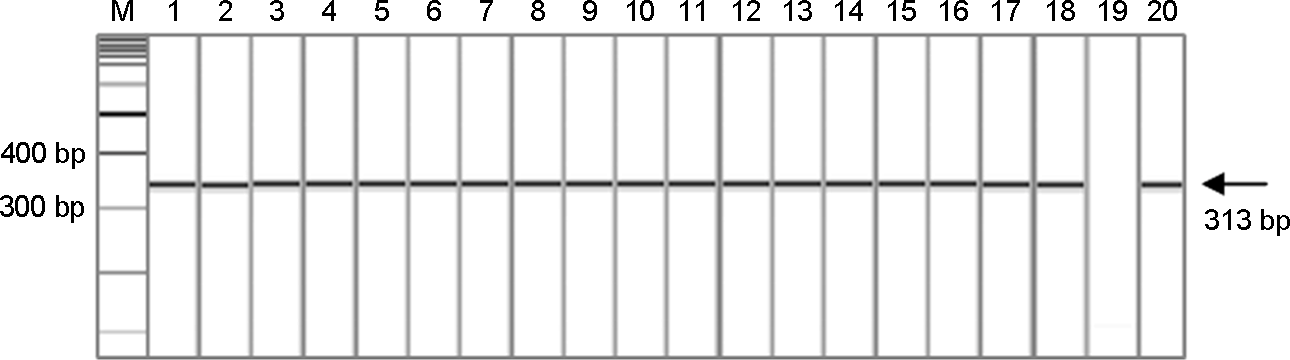 | Figure 1.Gel electrophoresis of PCR products of capsid region of 18 norovirus GII.3 isolates from patients with gastroenteritis; Lane M, 100 bp DNA ladder; Lane 1∼18, 18 norovirus GII.3 isolates; Lane 19, negative control; Lane 20, positive control. |
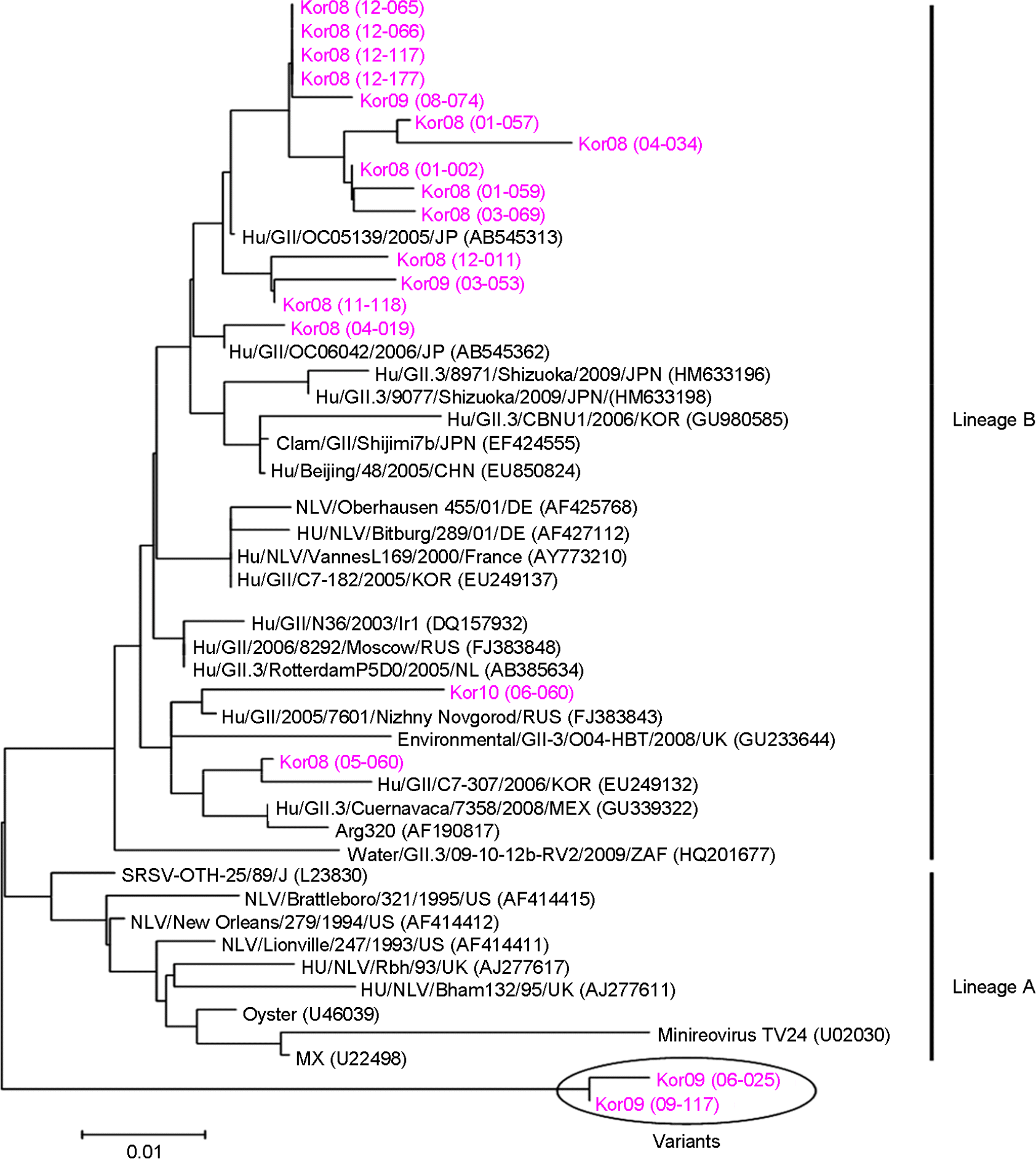 | Figure 2.Phylogenetic analysis based on a 205 bp sequence of the capsid region of Korean norovirus GII.3 strains and reference strains. Nucleotide sequences were analyzed using the neighbor-joining method. |
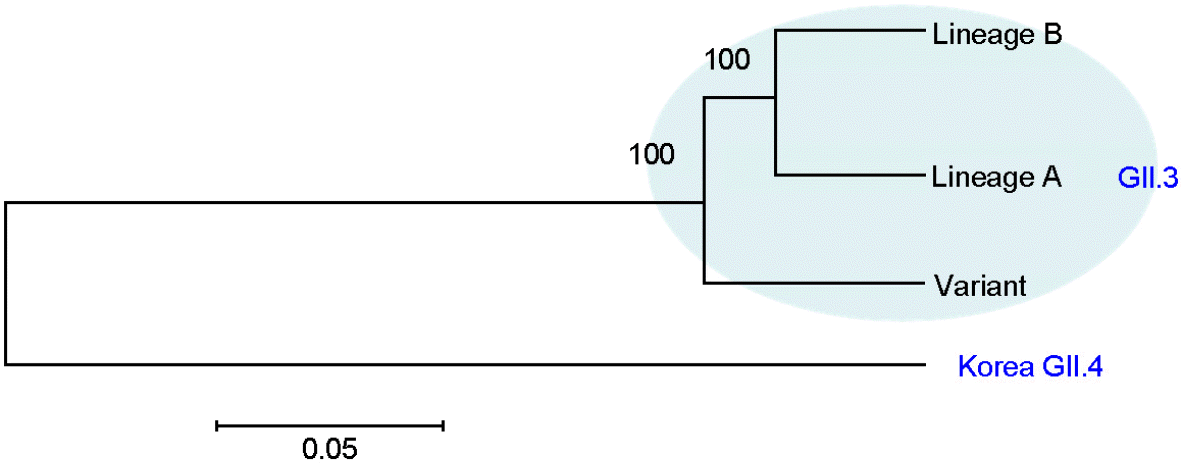 | Figure 3.Phylogenetic analysis of the capsid region of norovirus GII.3 lineages and Korea GII.4. |
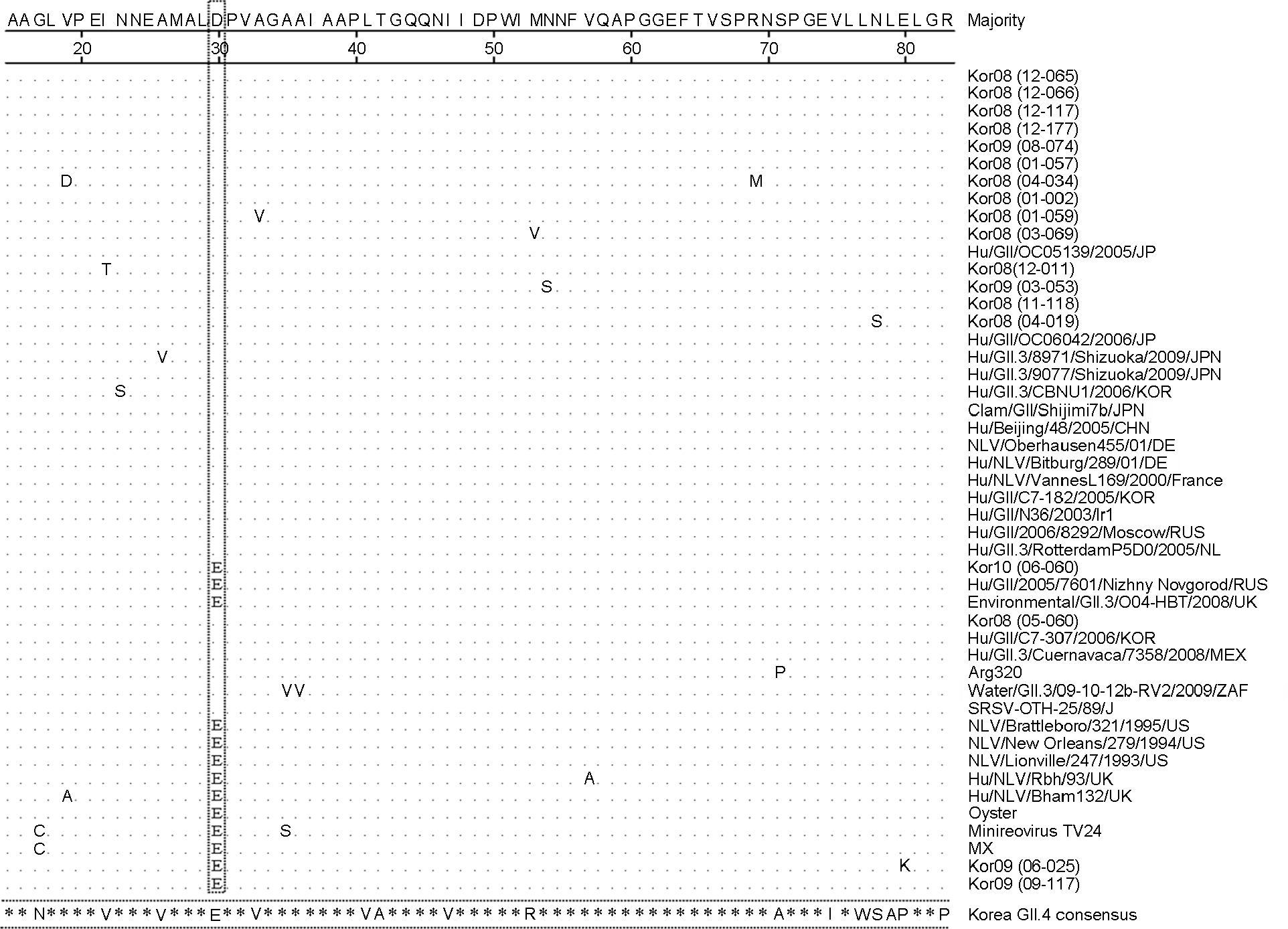 | Figure 4.Comparison of norovirus GII.3 amino acid sequences and Korea GII.4 consensus sequence in the capsid region. The box is conserved mutation site. |
Table 1.
Norovirus GII.3 strains isolated from patients' stool with acute gastroenteritis




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download