1). Krauss S., Webster RG. Avian influenza virus surveillance and wild birds: past and present. Avian Dis. 2010. 54:394–8.

2). Hale BG., Randall RE., Ortin J., Jackson D. The multifunctional NS1 protein of influenza A viruses. J Gen Virol. 2008. 89:2359–76.

3). Alexander DJ. A review of avian influenza in different bird species. Vet Microbiol. 2000. 74:3–13.

4). Zhao S., Jin M., Li H., Tan Y., Wang G., Zhang R, et al. Detection of antibodies to the nonstructural protein (NS1) of avian influenza viruses allows distinction between vaccinated and infected chickens. Avian Dis. 2005. 49:488–93.

5). Banks J., Speidel EC., Harris PA., Alexander DJ. Phylogenetic analysis of influenza A viruses of H9 haemagglutinin subtype. Avian Pathol. 2000. 29:353–9.

6). Alexander DJ. Report on avian influenza in the Eastern Hemisphere during 1997-2002. Avian Dis. 2003. 47:792–7.

7). Guo YJ., Krauss S., Senne DA., Mo IP., Lo KS., Xiong XP, et al. Characterization of the pathogenicity of members of the newly established H9N2 influenza virus lineages in Asia. Virology. 2000. 267:279–88.

8). Lin YP., Shaw M., Gregory V., Cameron K., Lim W., Klimov A, et al. Avian-to-human transmission of H9N2 subtype influenza A viruses: relationship between H9N2 and H5N1 human isolates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:9654–8.

9). Lambrecht B., Steensels M., Van Borm S., Meulemans G., Van den Berg T. Development of an M2e-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for differentiating infected from vaccinated animals. Avian Dis. 2007. 51:221–6.

10). Jeong OM., Kim MC., Kang HM., Ha GW., Oh JS., Yoo JE, et al. Validation of egg yolk antibody based C-ELISA for avian influenza surveillance in breeder duck. Vet Microbiol. 2010. 144:287–92.

11). Lee HT., Jung KH., Park JH., Ha GW., Oh JS., Oh YK, et al. Detection of the avian influenza viruses nonstructural protein 1 for distinction between vaccinated and infected chickens using synthetic peptide-based ELISA. J Bacteriol Virol. 2010. 40:207–12.

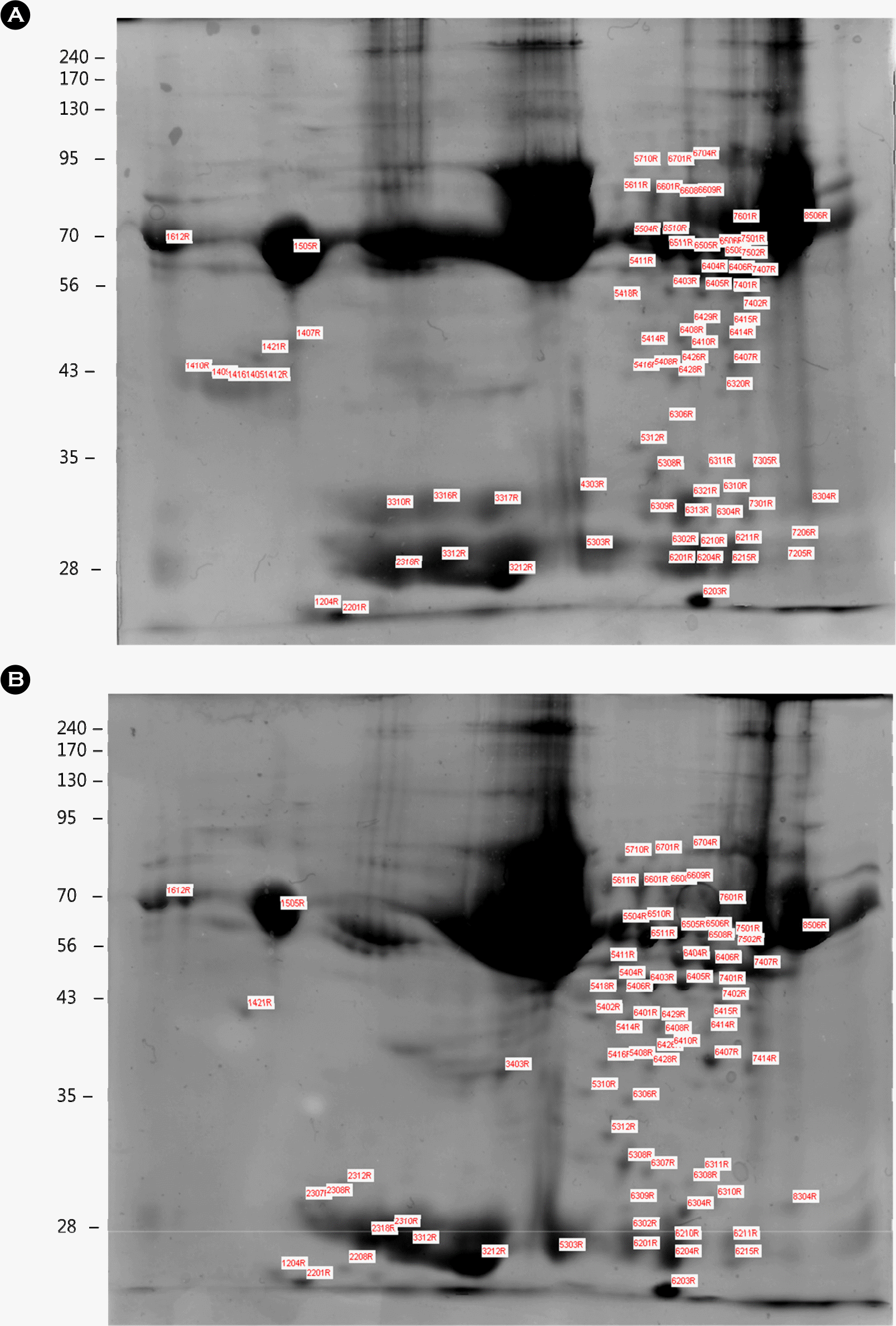
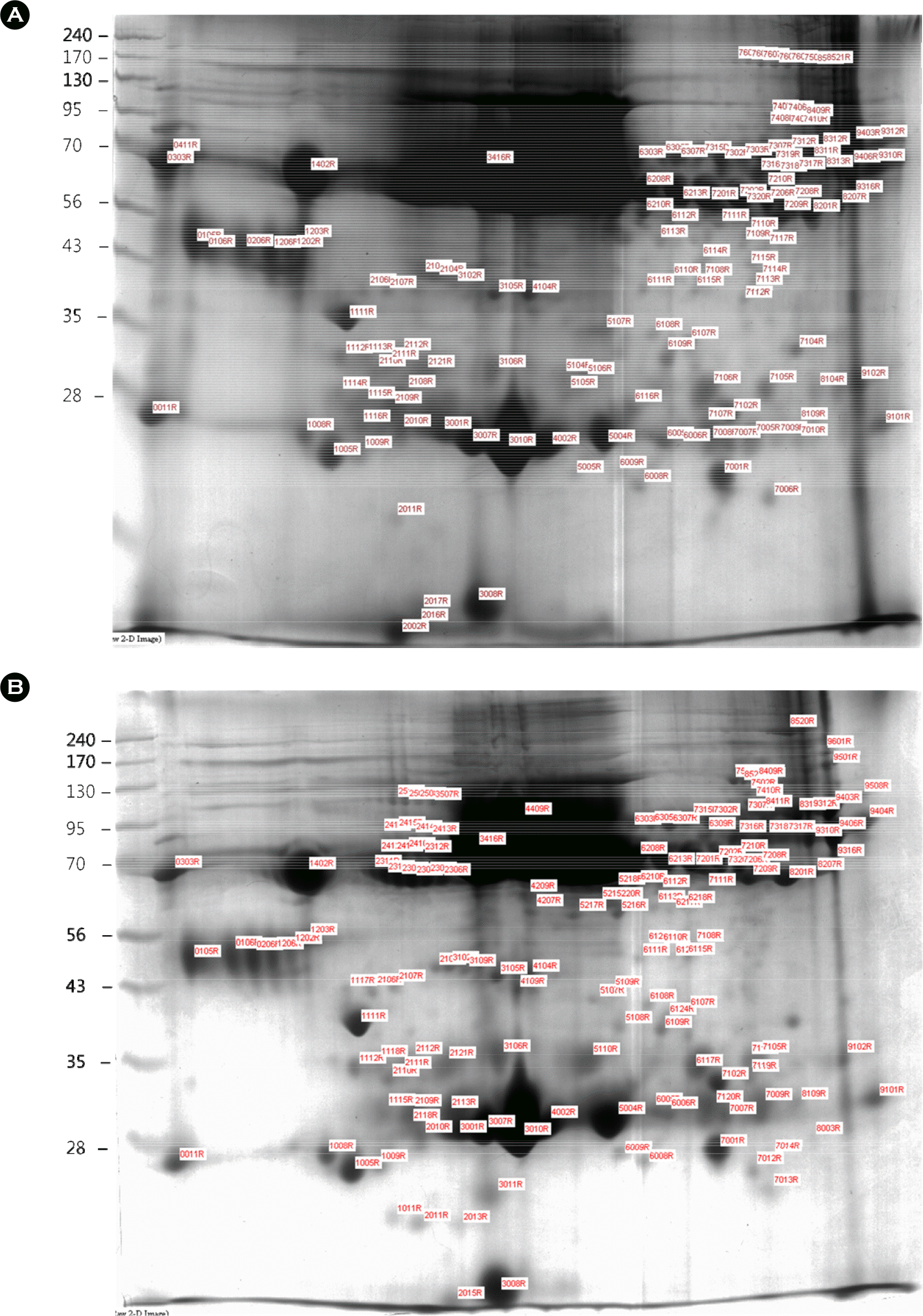
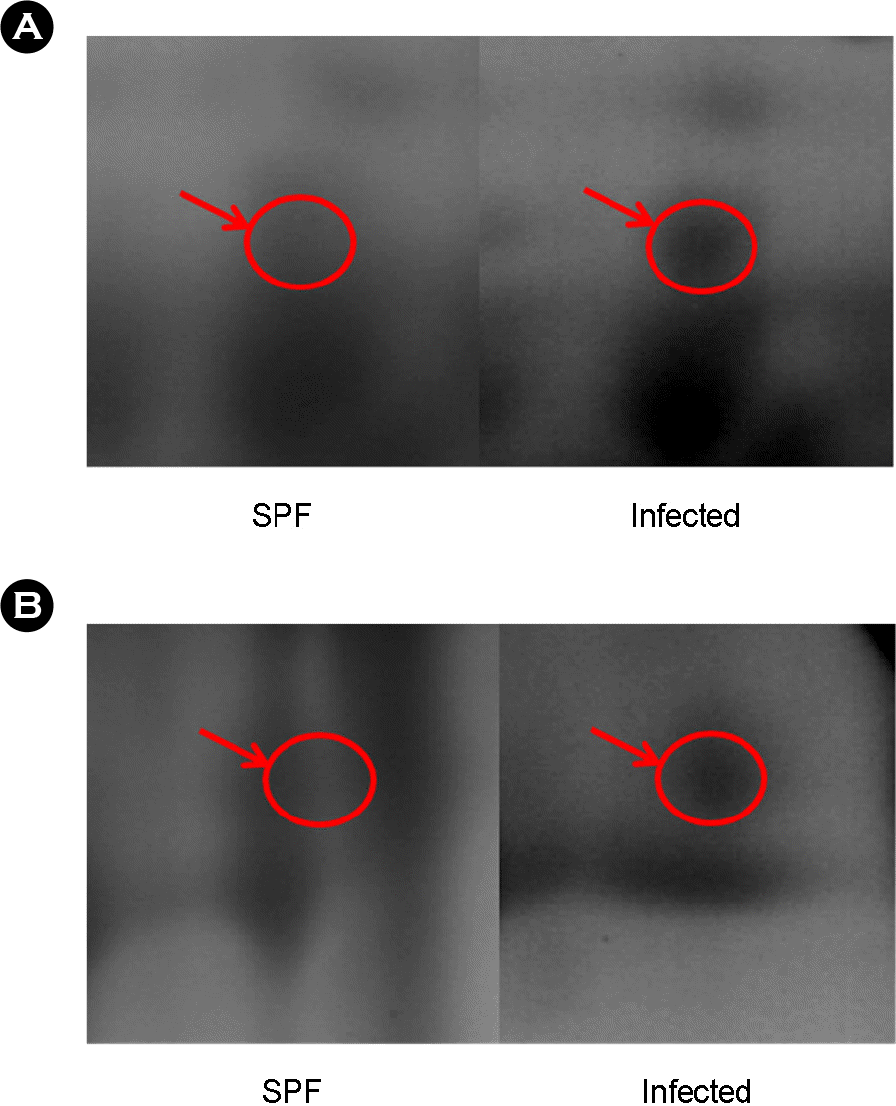
12). Huang SY., Lin JH., Chen YH., Chuang CK., Chiu YF., Chen MY, et al. Analysis of chicken serum proteome and differential protein expression during development in single-comb White Leghorn hens. Proteomics. 2006. 6:2217–24.

13). Mann K. The chicken egg white proteome. Proteomics. 2007. 7:3558–68.

14). Mann K. Proteomic analysis of the chicken egg vitelline membrane. Proteomics. 2008. 8:2322–32.

15). Mann K., Mann M. The chicken egg yolk plasma and granule proteomes. Proteomics. 2008. 8:178–91.

16). Cheung KJ., Tilleman K., Deforce D., Colle I., Van Vlierberghe H. The HCV serum proteome: a search for fibrosis protein markers. J Viral Hepat. 2009. 16:418–29.

17). Shevchenko A., Wilm M., Vorm O., Mann M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem. 1996. 68:850–8.
18). Basler CF., Aguilar PV. Progress in identifying virulence determinants of the 1918 H1N1 and the Southeast Asian H5N1 influenza A viruses. Antiviral Res. 2008. 79:166–78.

19). Toro H., van Ginkel FW., Tang DC., Schemera B., Rodning S., Newton J. Avian Influenza Vaccination in Chickens and Pigs with Replication-Competent Adenovirus-Free Human Recombinant Adenovirus 5. Avian Dis. 2010. 54:224–31.

20). Giansanti F., Rossi P., Massucci MT., Botti D., Antonini G., Valenti P, et al. Antiviral activity of ovotransferrin discloses an evolutionary strategy for the defensive activities of lactoferrin. Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. 80:125–30.

21). Martin-Mateo MC., Planas J. Conalbumin and serum iron transport in birds. I. Study in the chicken (Gallus domesticus). Rev Esp Fisiol. 1965. 21:1–7.
22). Keung WM., Azari P. Structure and function of ovotransferrin. II. Iron-transferring activity of iron-binding fragments of ovotransferrin with chicken embryo red cells. J Biol Chem. 1982. 257:1184–8.

23). Oratore A., D'Andrea G., D'Alessandro AM., Moreton K., Williams J. Binding and iron delivering of monoferric ovotransferrins to chick-embryo red blood cells (CERBC). Biochem Int. 1990. 22:111–8.
24). Valenti P., Antonini G. Lactoferrin: an important host defence against microbial and viral attack. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. 62:2576–87.
25). Cooke NE., David EV. Serum vitamin D-binding protein is a third member of the albumin and alpha fetoprotein gene family. J Clin Invest. 1985. 76:2420–4.

26). White P., Cooke N. The multifunctional properties and characteristics of vitamin D-binding protein. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 11:320–7.

27). Cooke NE., Haddad JG. Vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin). Endocr Rev. 1989. 10:294–307.

28). Dundon WG., Maniero S., Toffan A., Capua I., Cattoli G. Appearance of serum antibodies against the avian influenza nonstructural 1 protein in experimentally infected chickens and turkeys. Avian Dis. 2007. 51:209–12.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download