Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus coagulase serotype I to VIII isolated from clinical samples could be classified into two groups, methicillin-sensitive S. aurues (MSSA) and methicilln-resistant S. aurues (MRSA), by antibiotics susceptibility and existence of mecA which is a gene related with methicillin resistance. Coagulase serotype I, VI, and VIII were MSSA which showed different antimicrobial susceptibility. Coagluase serotype II-V and VII were MRSA in which mecA and SCCmec were detected. To analyze Sau1 restriction and modification (R-M) complex types by coagulase type and SCCmec type, sau1hsdR, sau1hsdM and sau1hsdS genes involved in Sau1 R-M complex were detected by PCR, we found five complex types such as M1, R2M2, R2M2, R2M2S1, and R2M2S2. Coagulase serotype I, VI, and VIII of MSSA were M1, R2M2 and R2M2, respectively. SCCmec type II and coagulase serotype II, SCCmec type III and coagulase serotype III, SCCmec type IV and coagulase serotype V, and SCCmec type IV and coagulase serotype IV, VII of MRSA were Sau1 R-M complex type R2M2S1, R2M2, R2M2, and R2M2S2, respectively. Taken together, correlation between Sau1 R-M complex types and coagulase or SCCmec types of S. aureus was found.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Archer GL., Mayhall CG. Comparison of epidemiologic markers used in investigation of an outbreak of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1983. 18:395–9.
2). Bouvet A., Fournier JM., Audurier A., Branger C., Orsoni A., Girard C. Epidemiological markers for epidemic strain and carrier isolates in an outbreak of nosocomial oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. 28:1338–41.
3). Daum RS., Ito T., Hiramatsu K., Hussain F., Mongkolrattanothai K., Jamklang M, et al. A novel methicillin-resistance cassette in community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates of diverse genetic backgrounds. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:1344–7.
4). Diep BA., Carleton HA., Chang RF., Sensabaugh GF., Perdreau Remington F. Roles of 34 virulence genes in the evolution of hospital-and community-associated strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 2006. 193:1495–503.
5). Kilic A., Li H., Stratton CW., Tang YW. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns and staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec types of, as well as Panton-Valentine leukocidin occurrence among, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from children and adults in middle Tennessee. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:4436–40.
7). Cha EK., Chang KS., Hwang SM. Correlation between staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type and coagulase serotype of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009. 39:71–8.
8). Tomasz A., Nachman S., Leaf H. Stable classes of phenotypic expression in methicillin-resistamt clinical isolates of Staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991. 35:124–9.
9). Durand G., Bes M., Meugnier H., Enright MC., Forey F., Liassine N, et al. Detection of new methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones containing the toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene responsible for hospital- and community-acquired infections in France. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:847–53.
10). Johnson WM., Tyler SD., Ewan EP., Ashton FE., Pollard DR., Rozee KR. Detection of genes for enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991. 29:426–30.
11). Kanemitsu K., Yamamoto H., Takemura H., Kaku M., Shimada J. Relatedness between the coagulase gene 3′-end region and coagulase serotypes among Staphylococcus aureus strains. Microbiol Immunol. 2001. 45:23–7.
12). Watanabe S., Ito T., Takeuchi F., Endo M., Okuno E., Hiramatsu K. Structural comparison of ten serotypes of staphylocoagulases in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2005. 187:3698–707.
13). Hwang SM., Kim TU. Changes in coagulase serotype of Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Busan, 1994-2005. Korean J Microbiol. 2007. 43:346–50.
14). Lee M., Chong Y. Characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from wounds in Korean patients. J Infect Chemother. 1996. 2:130–5.
15). Lindsay JA., Holden MT. Staphylococcus aureus: superbug, super genome? Trends Microbiol. 2004. 12:378–85.
16). Lindsay JA., Moore CE., Day NP., Peacock SJ., Witney AA., Stabler RA, et al. Microarrays reveal that each of the ten dominant lineages of Staphylococcus aureus has unique combinations of surface associated and regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 2006. 188:669–76.
17). Murray NE. Type I restriction systems. sophisticated molecular machines (a legacy of Bertani and Weigle). Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2000. 64:412–34.

18). Waldron DE., Lindsay JA. Sau1: a novel lineage-specific type I restriction-modification system that blocks horizontal gene transfer into Staphylococcus aureus and between S. aureus isolates of different lineages. J Bacteriol. 2006. 188:5578–85.
19). Périchon B., Courvalin P. VanA-type vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. 53:4580–7.
20). DeLeo FR., Chambers HF. Reemergence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the genomics era. J Clin Invest. 2009. 119:2464–74.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA fragment amplified from the SCCmec (locus A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H) by PCR with specific primers. Lane M: the marker (100 bp plus DNA ladder), lane C: S. aureus (ATCC25923), the molecular size of locus A to H are 495 bp, 284 bp, 209 bp, 342 bp, 243 bp, 414 bp, 381 bp and 303 bp, respectively. |
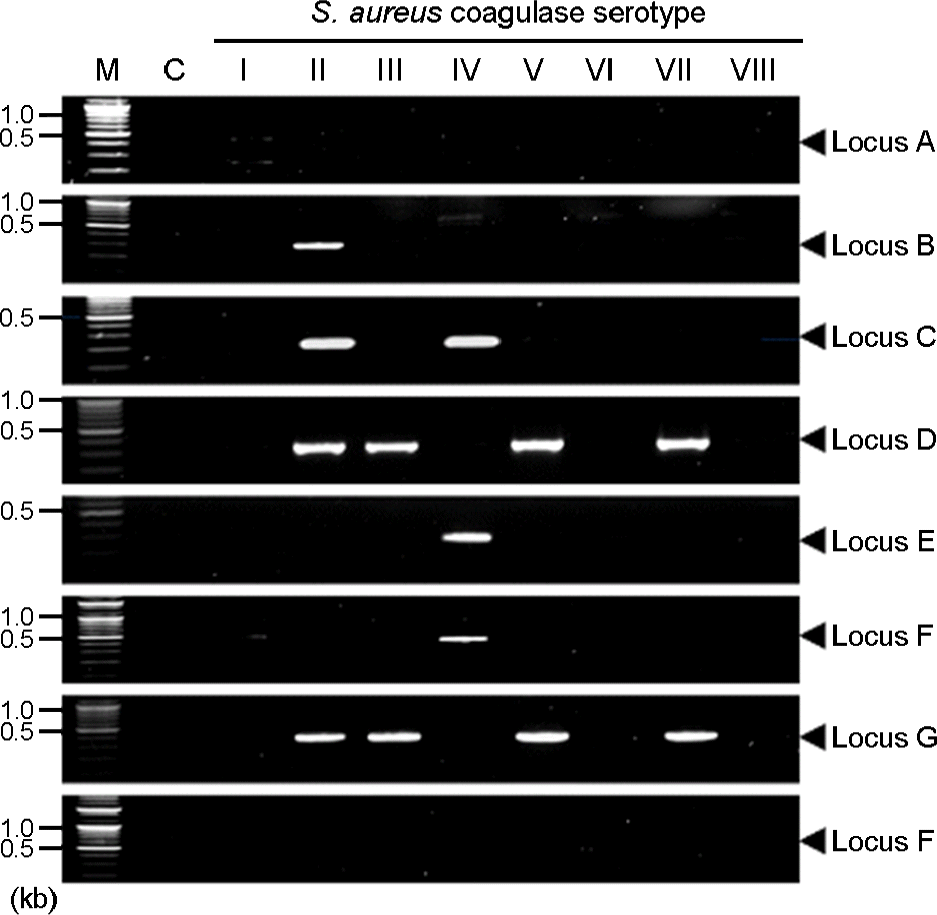
 | Figure 2.Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA fragment amplified from the Sau1 (hsdM, hsdR, hsdS) gene by PCR with specific primers. Lane M, 100 bp plus DNA ladder marker, lane C: S. aureus (ATCC25943), the molecular size of hsdM1, M2, S1, S2, R1 and R2 are 1,577 bp, 1,535 bp, 2,810 bp, 258 bp, 327 bp and 1,220 bp, respectively. |
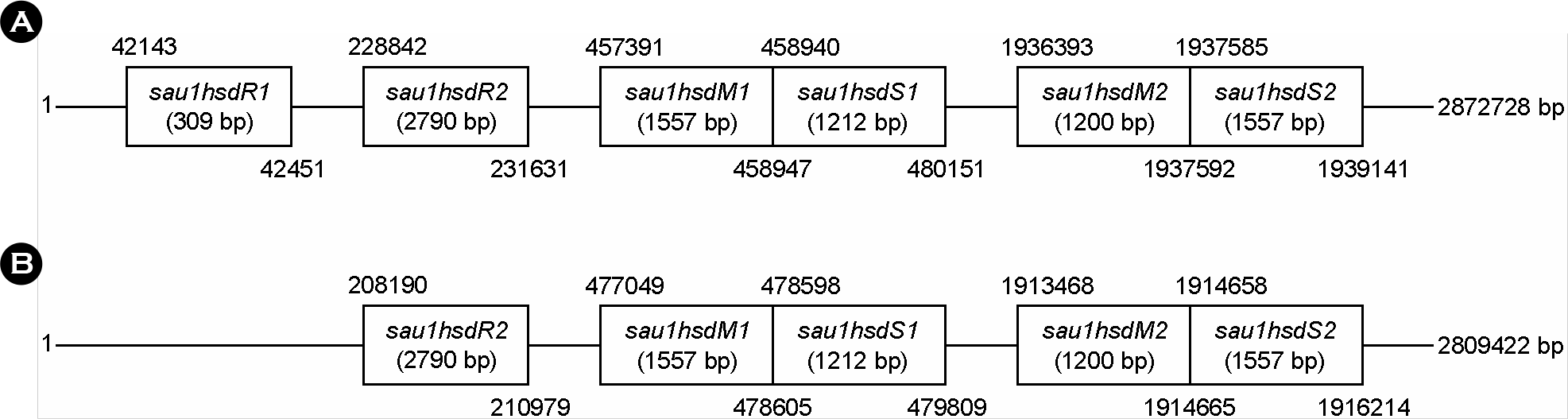 | Figure 3.Genetic maps of type 1 Restriction and Modification system of S. aureus (A). S. aureus (USA_TCH1516) strain, (B). S. aureus (COL) strain. |
Table 1.
Primers and predicted sizes of PCR products for SCCmec type and Sau1 R-M complex genes
Table 2.
CLSI disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility of S. aureus isolates according to coagulase types




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download