Abstract
To characterize the genetic diversity of bovine viral diarrhea viruses (BVDV) circulating in Korea, 11 BVDV isolates were obtained from 467 field samples collected during 2005∼2006 in Korea. All of the BVDV isolates were identified as non-cytopathic (non-cp) BVDV biotypes. The 5′ noncoding region (NCR) genes of the isolates were sequenced and analyzed. In total, ten BVDV isolates were typed as BVDV-1 by comparing the genomic sequences to the 5′ NCR. One isolate (05R169) showed 98.6% nucleotide sequence identity with the BVDV-2 reference strain and was therefore typed as BVDV-2. Our results indicate that BVDV-1 is the main genotype circulating in the cattle population of Korea.
References
1). Becher P, Orlich M, Shannon AD, Horner G, Konig M, Thiel HJ. Phylogenetic analysis of pestiviruses from domestic and wild ruminants. J Gen Virol. 78:1357–1366. 1997.

2). Beer M, Wolf G, Kaaden OR. Phylogenetic analysis of the 5′-untranslated region of german BVDV type II isolates. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 49:43–47. 2002.

3). Brock KV, Redman DR, Vickers ML, Irvine NE. Quantitation of bovine viral diarrhea virus in embryo transfer flush fluids collected from a persistently infected heifer. J Vet Diagn Invest. 3:99–100. 1991.

4). Houe H. Epidemiology of bovine viral diarrhea virus. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 11:521–547. 1995.

5). Houe H. Epidemiological features and economical importance of bovine virus diarrhoea virus (BVDV) infections. Vet Microbiol. 64:89–107. 1999.

6). Jones LR, Zandomeni R, Weber EL. Genetic typing of bovine viral diarrhea virus isolates from Argentina. Vet Microbiol. 81:367–375. 2001.

7). Kim IJ, Hyun BH, Shin JH, Lee KK, Lee KW, Cho KO, Kang MI. Identification of bovine viral diarrhea virus type 2 in Korean native goat (Capra hircus). Virus Res. 121:103–106. 2006.

8). Park JS, Moon HJ, Lee BC, Hwang WS, Yoo HS, Kim DY, Park BK. Comparative analysis on the 5′-untranslated region of bovine viral diarrhea virus isolated in Korea. Res Vet Sci. 76:157–163. 2004.

9). Pellerin C, van den Hurk J, Lecomte J, Tussen P. Identification of a new group of bovine viral diarrhea virus strains associated with severe outbreaks and high mortalities. Virology. 203:260–268. 1994.

10). Ridpath JF, Bolin SR. Differentiation of types 1a, 1b and 2 bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) by PCR. Mol Cell Probes. 12:101–106. 1998.
11). Ridpath JF, Bolin SR, Dubovi EJ. Segregation of bovine viral diarrhea virus into genotypes. Virology. 205:66–74. 1994.

12). Vilcek S, Durkovic B, Kolesárová M, Greiser-Wilke I, Paton D. Genetic diversity of international bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) isolates: identification of a new BVDV-1 genetic group. Vet Res. 35:609–615. 2004.

13). Vilcek S, Durkovic B, Kolesárová M, Paton DJ. Genetic diversity of BVDV: consequences for classification and molecular epidemiology. Prev Vet Med. 72:31–35. 2005.

14). Vilcek S, Herring AJ, Herring JA, Nettleton PF, Lowings JP, Paton DJ. Pestiviruses isolated from pigs, cattle and sheep can be allocated into at least three genogroups using polymerase chain reaction and restriction endonuclease analysis. Arch Virol. 136:309–323. 1994.
15). Vilcek S, Paton DJ, Durkovic B, Strojny L, Ibata G, Moussa A, Loitsch A, Rossmanith W, Vega S, Scicluna MT, Paifi V. Bovine viral diarrhoea virus genotype 1 can be separated into at least eleven genetic groups. Arch Virol. 146:99–115. 2001.
Figure 1.
Immunofluorescence of 05R169 isolate by IFA test using monoclonal antibody against BVDV in MDBK cell.
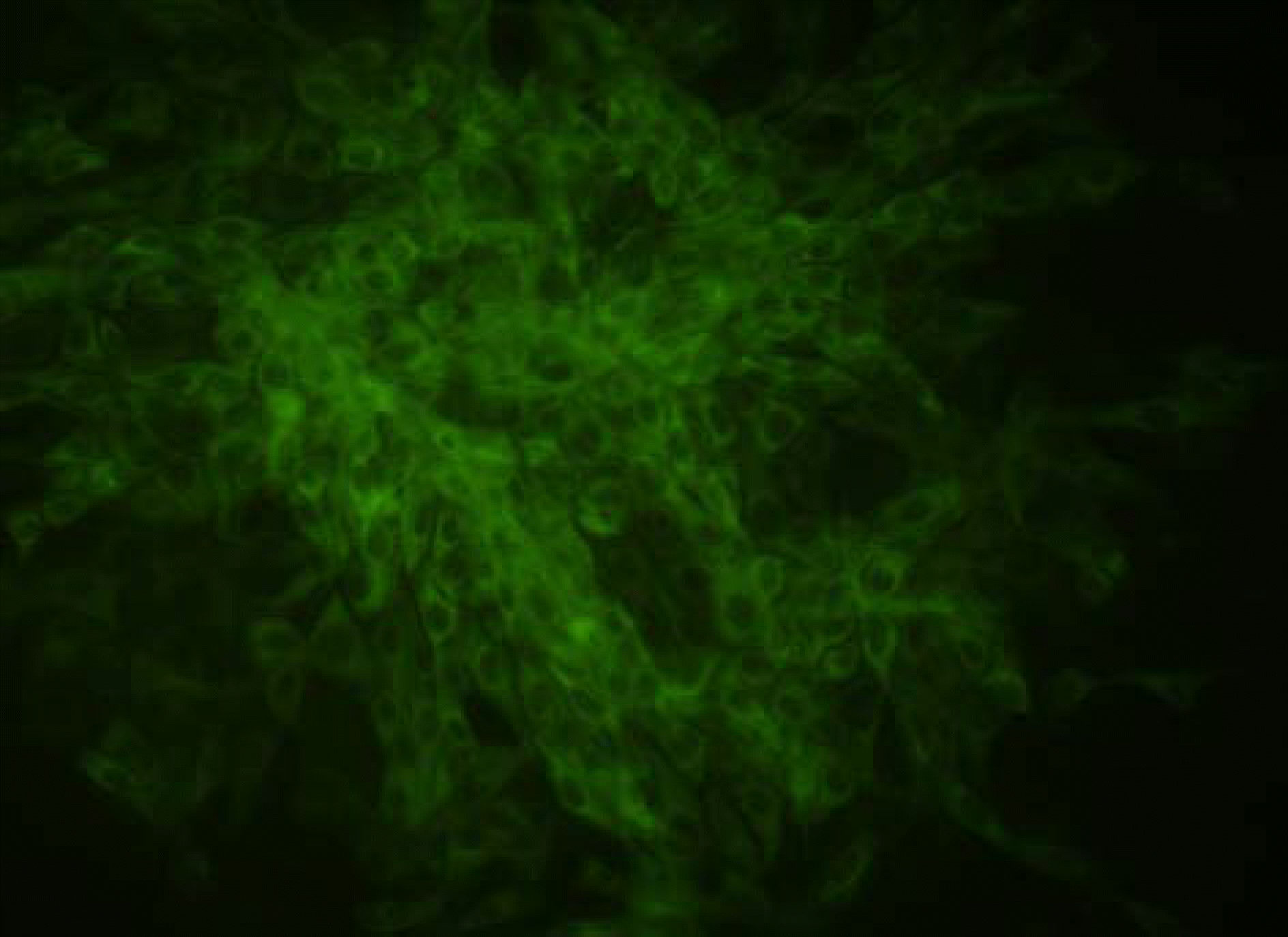
Figure 2.
RT-PCR products of BVDV isolates were detected on 1.5% agarose gel. The expected size was 288 bp. M; 100 bp DNA ladder, Lane 1; 05D26, Lane 2; 05D73, Lane 3; NADL strain, Lane 4; negative sample.
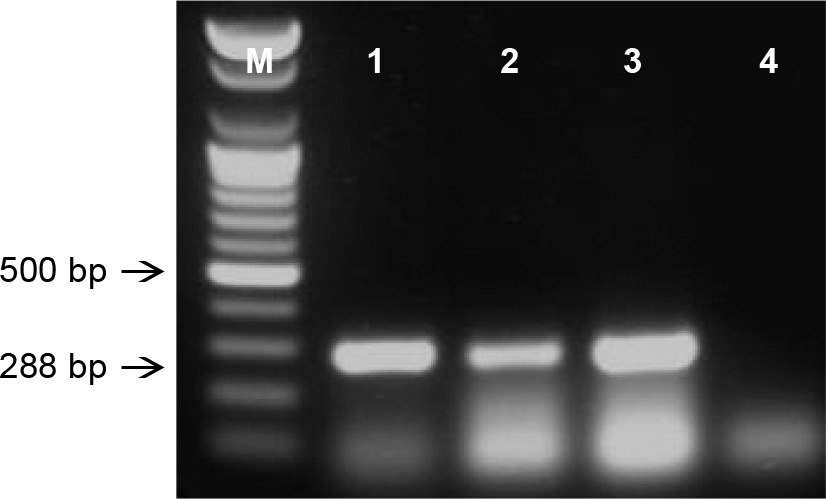
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of the 5′ non-coding regions (NCR) of BVDV strains and isolates. The tree was generated from comparative alignment of sequences from 245 bp of the 5'NCR of the BVDV genome. The multiple sequences were constructed by the neighbor joining method. Genotypes were given on the right of tree. Abbreviations: Korea (KOR), Australia (AUS), Germany (GER), Canada (CAN), Slovenia (SLO), Belgium (BEL), Japan (JPN), China (CHI), Italy (ITA), Sweden (SWE), United State of America (USA).
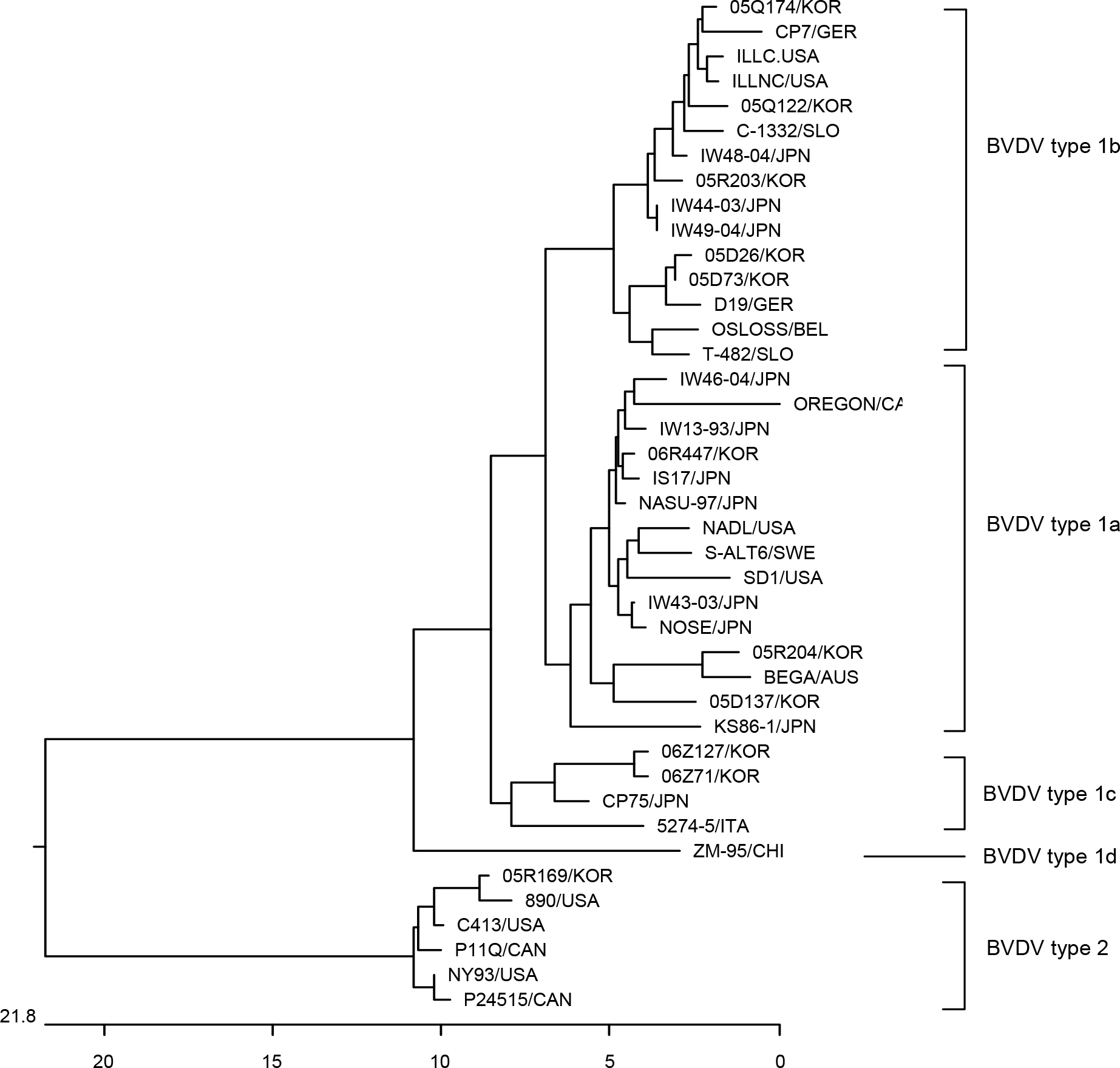
Table 1.
Bovine viral diarrhea viruses isolated from cattle in Korea and GenBank accession numbers of their 5'NCR nucleotide sequences
| Virus isolate | Source of sample | Isolated province | Breed | Biotype | Genotype | Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05D26 | Tissue homogenate | Chungbuk | K∗ | NCP† | 1b | DQ973172 |
| 05D73 | Tissue homogenate | Gyeonggi | H | NCP | 1b | DQ973173 |
| 05Q122 | Aborted fetus | Chungnam | H | NCP | 1b | DQ973175 |
| 05D137 | Aborted fetus | Jeonbuk | K | NCP | 1a | DQ973174 |
| 05Q174 | Tissue homogenate | Gangwon | H | NCP | 1b | DQ973176 |
| 05R169 | Blood plasma | Chungnam | H | NCP | 2 | DQ973177 |
| 05R203 | Blood plasma | Gyeongnam | K | NCP | 1b | DQ973178 |
| 05R204 | Blood plasma | Gyeongbuk | H | NCP | 1a | DQ973179 |
| 06R447 | Blood plasma | Gangwon | K | NCP | 1a | DQ973180 |
| 06Z71 | Blood plasma | Chungnam | K | NCP | 1c | DQ973181 |
| 06Z127 | Blood plasma | Chungnam | K | NCP | 1c | DQ973182 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download