Abstract
Hantaan virus (HTNV) and Seoul virus (SEOV) have mainly been known as the cause of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Korea since HTNV has been isolated from Korean field mouse, Apodemus agrarius in 1976 and SEOV has been isolated from Rattus norvegicus in 1980. Soochong virus-1, –2, –3, –4 (SOOVs) were isolated from lung tissues of four Apodemus peninsulae captured on August 1997 at Mt. Gyebang in Hongcheon-gun, Mt. Gachil, Inje-gun, Gangwon Province, and in September 1998 at Mt. Deogyu, Muju-gun, Jeollabuk Province. Apodemus peninsulae is the second-most dominant field rodent species found throughout Korea. To determine phylogenetic analysis of SOOVs, we entirely identified nucleotide sequences of M and L segments. The length of M segment was 3,615 bp and L segment was 6,533 bp. SOOVs were diverged from HTNV by 22.7∼23.3% and SEOV by 36.3∼37.2%, in M segment. In addition, L segment was diverged from HTNV by 21.8∼22.0% and SEOV by 30.3∼30.5%. SOOVs sequence compared with Amur virus (AMRV) in M segment showed that SOOVs were different with AMRV about 14.6∼16.2% in nucleotide sequences. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis based on entire sequences of the M and L segment indicated that the SOOVs sequences present a separate lineage with HTNV, SEOV and AMRV. SOOVs constituted an individual cluster on the phylogenetic tree and they composed a phylogenic lineage separately. According to these data, SOOVs could be classified as a new hantavirus.
Go to : 
References
1). 백락주, 강주일, 송기준, 송진원, 양병국, 이용주. 1995 년 계방산에서 채집한 들쥐의 한타바이러스 감염에 대 한 혈청학적 연구. 대한바이러스학회지. 27(2):177–183. 1997.
2). 송기준, 윤형선, 고은영, 정기모, 박광숙, 이용주, 송진 원, 백락주. Isolation of Apodemus peninsulae-borne Hantanvirus and comparison of molecular biological characteristics. 대한바이러스학회지 30권 1호. 19–28. 2000.
3). 정수용, 송기준, 송진원, 문성실, 김은주, 박광숙, 기선 호, 백락주. 신종 수청바이러스와 무주바이러스의 혈 청학적 특성. 대한바이러스학회지. 35(3):249–225. 2005.
4). Avsic-Zupanc T, Xiao SY, Stojanovic R, Gligic A, van der Groen G, LeDuc JW. Characterization of Dobrava virus: a Hantavirus from Slovenia, Yugoslavia. J Med Virol. 38:132–137. 1992.

5). Baek LJ, Kariwa H, Lokugamage K, Yoshimatsu K, Arikawa J, Takashima I, Kang JI, Moon SS, Chung SY, Kim EJ, Kang HJ, Song KJ, Klein TA, Yanagihara R, Song JW. Soochong virus: An antigenically and genetically distinct hantavirus isolated from Apodemus peninsulae in Korea. J Med Virol. 78(2):290–297. 2006.
6). Elliott LH, Ksiazek TG, Rollin PE, Spiropoulou CF, Morzunov S, Monroe M, Goldsmith CS, Humphrey CD, Zaki SR, Krebs JW, et al. Isolation of the causative agent of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 51:102–108. 1994.

7). Hughes AL, Friedman R. Evolutionary diversification of protein-coding genes of hantaviruses. Mol Biol Evol. 17:1558–1568. 2000.

8). Lee HW, Baek LJ, Johnson KM. Isolation of Hantaan virus, the etiologic agent of Korean hemorrhagic fever, from wild urban rats. J Infect Dis. 146:638–644. 1982.

9). Lee PW, Amyx HL, Gajdusek DC, Yanagihara RT, Goldgaber D, Gibbs CJ Jr. New hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome-related virus in rodents in the United States. Lancet. 2:1405. 1982.
10). Lopez N, Padula P, Rossi C, Miguel S, Edelstein A, Ramirez E, Franze-Fernandez MT. Genetic characterization and phylogeny of Andes virus and variants from Argentina and Chile. Virus Res. 50:77–84. 1997.
11). Brummer-Korvenkontio M, Vaheri A, Hovi T, von Bonsdorff CH, Vuorimies J, Manni T, Penttinen K, Oker-Blom N, Lahdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica: detection of antigen in bank voles and serologic diagnosis of human infection. J Infect Dis. 141:131–134. 1980.

12). Nowak RM. Walker's mammals of the world. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University: 1499. 1999.
13). Ogino M, Yoshimatsu K, Ebihara H, Araki K, Lee BH, Okumura M, Arikawa J. Cell fusion activities of Hantaan virus envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 78:10776–10782. 2004.

14). Rollin PE, Ksiazek TG, Elliott LH, Ravkov EV, Martin ML, Morzunov S, Livingstone W, Monroe M, Glass G, Ruo S, et al. Isolation of black creek canal virus, a new hantavirus from Sigmodon hispidus in Florida. J Med Virol. 46:35–39. 1995.
15). Schmalhohn CS. Bunyaviridae: The Virus and Their Replication. Fields virology, Third Edition: 1447–1472. 1996.
16). Schmaljohn CS, Dalrymple JM. Analysis of Hantaan virus RNA: evidence for a new genus of bunyaviridae. Virology. 131:482–491. 1983.

17). Shi X, Elliott RM. Golgi localization of Hantaan virus glycoproteins requires coexpression of G1 and G2. Virology. 300:31–38. 2002.

18). Song JW, Baek LJ, Gajdusek DC, Yanagihara R, Gavrilovskaya I, Luft BJ, Mackow ER, Hjelle B. Isolation of pathogenic hantavirus from white-footed mouse (Peromyscus leucopus). Lancet. 344:1637. 1994.

19). Song JW, Song KJ, Baek LJ, Frost B, Poncz M, Park K. In vivo characterization of the integrin beta3 as a receptor for Hantaan virus cellular entry. Exp Mol Med. 37:121–127. 2005.
20). Yashina L, Mishin V, Zdanovskaya N, Schmaljohn C, Ivanov L. A newly discovered variant of a hantavirus in Apodemus peninsulae, far Eastern Russia. Emerg Infect Dis. 7:912–913. 2001.
Go to : 
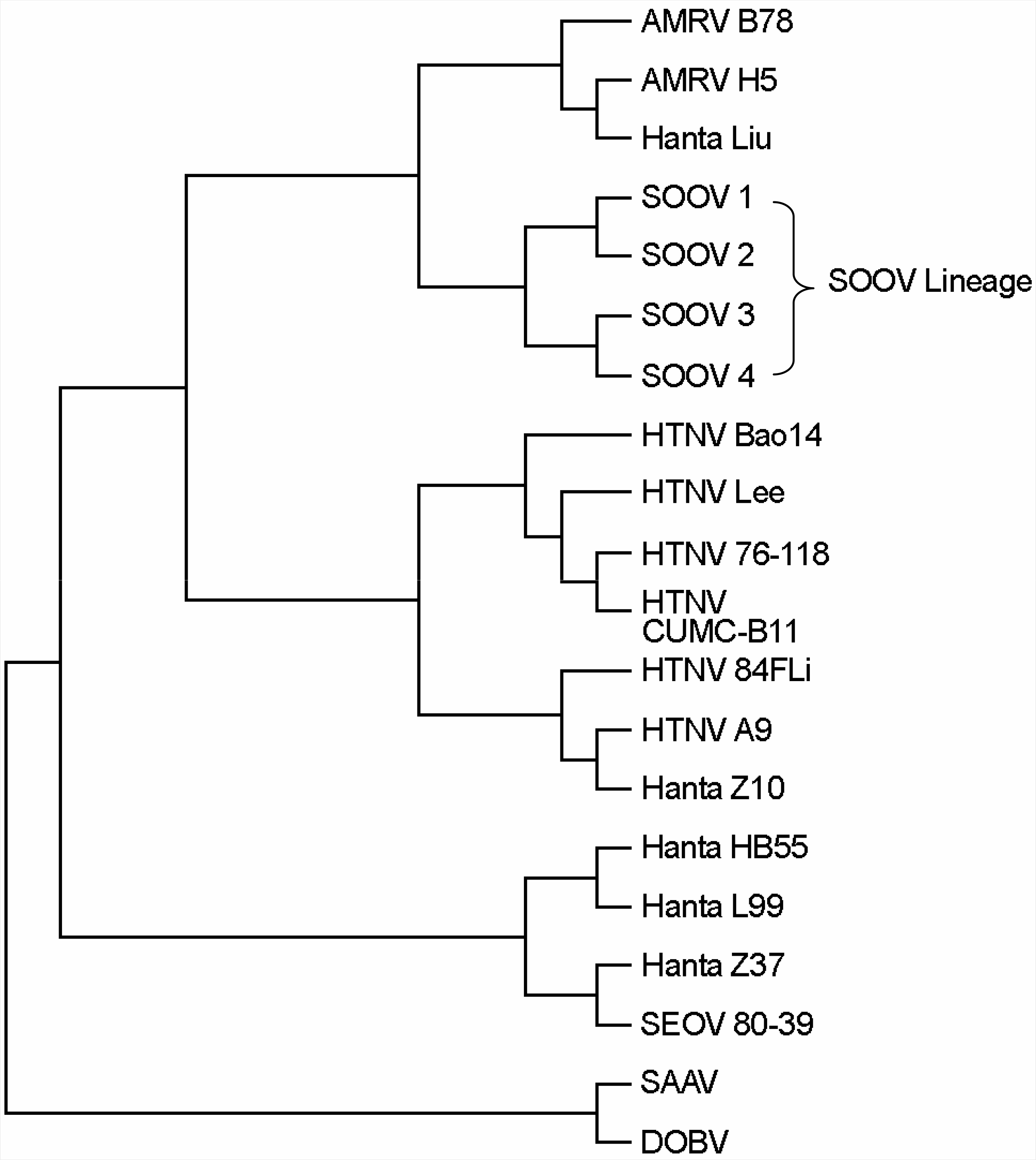 | Figure 1.Phylogenetic tree of the hantavirus entire M segments. (AMRV: amur virus, SOOV: soochong virus, HTNV: hantaan virus, SEOV: seoul virus, SAAV: saaremaa virus, DOBV: dobrava virus) |
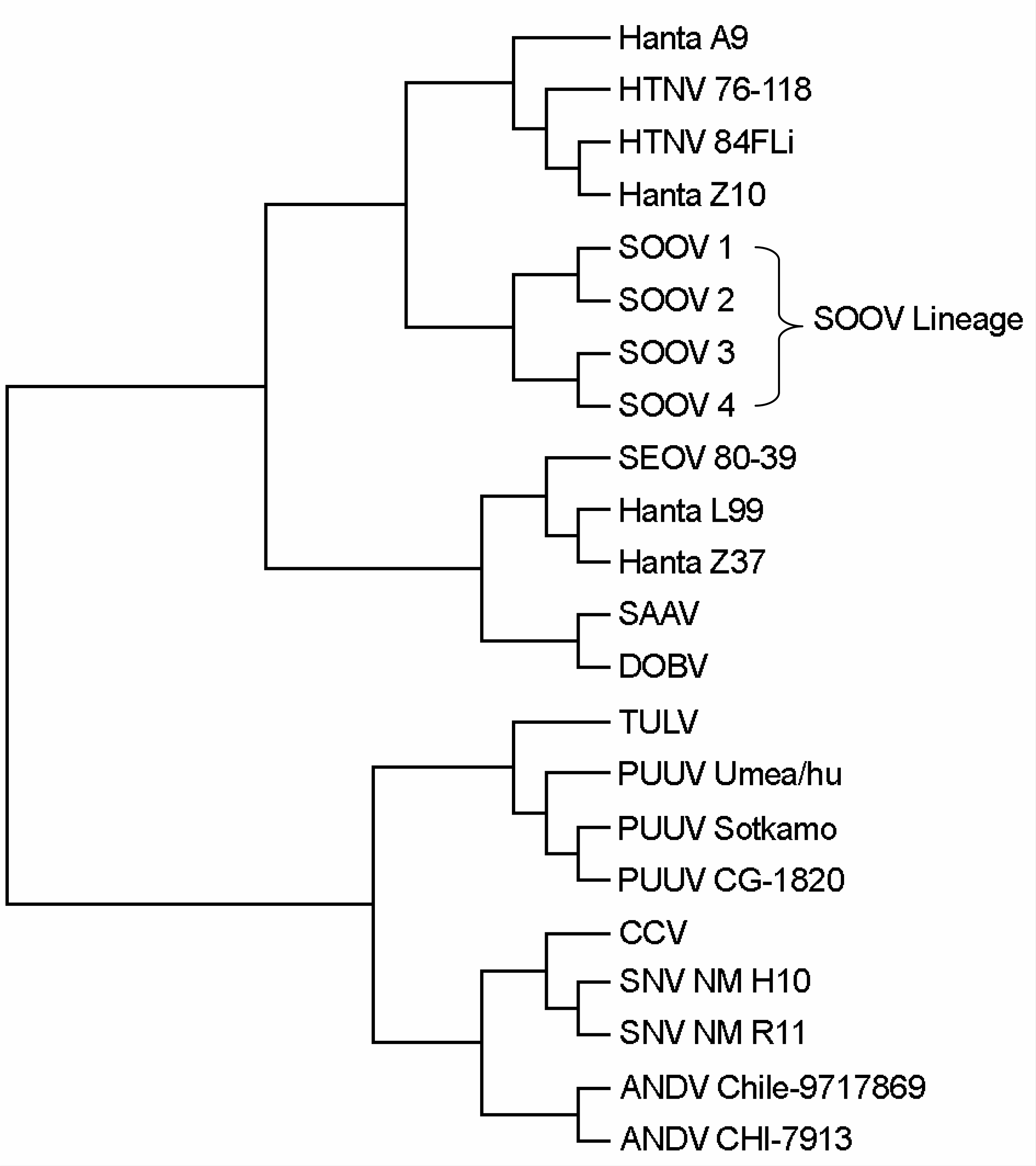 | Figure 2.Phylogenetic tree of the hantavirus entire L segments. (AMRV: amur virus, SOOV: soochong virus, HTNV: hantaan virus, SEOV: seoul virus, SAAV: saaremaa virus, DOBV: dobrava virus, TULV: tula virus, PUUV: puumala virus, CCV: creek canal virus, SNV: sin nombre virus, ANDV: andes virus) |
Table 1.
Oligonucleotide primers of M segment for PCR amplification
Table 2.
Oligonucleotide primers of L segment for PCR amplification
Table 3.
GenBank accession code of Soochong viruses
Table 4.
Percent similarity and divergency based on the nucleotide sequences of M segments
Table 5.
Percent similarity and divergency based on the nucleotide sequences of L segments




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download