Abbreviations
IL
TNFα
IBD
NOD
PBMCs
MDP
CD
SEMFs
IFNγ
IL-32γ-TG
WT
DSS
DCs
RA
sRANKL
OA
Syk
JNK
FLS
siRNA
TSLP
TLR
BLP
LPS
poly I:C
dsRNA
DAMPs
PR3
Journal List > Immune Netw > v.14(3) > 1033418
IL
TNFα
IBD
NOD
PBMCs
MDP
CD
SEMFs
IFNγ
IL-32γ-TG
WT
DSS
DCs
RA
sRANKL
OA
Syk
JNK
FLS
siRNA
TSLP
TLR
BLP
LPS
poly I:C
dsRNA
DAMPs
PR3
 | Figure 1Schematic drawing of IL-32 in mucosal epithelial cells after pathogen infection. Mucosal epithelial cells-released IL-32 stimulates monocytes to produce inflammatory mediators and also differentiates monocytes into macrophage or dendritic cell (DC) like. The macrophages and DC like cells release inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6. Inflammatory mediators-released from the macrophages and DC like cells in the inflamed area recruit and proliferate T-cells resulted in protecting the host against the pathogens and clearing the infections. However, the recruited various immune cells-produced inflammatory cytokines in the absence of endogenous immune suppressor provokes a large number of neutrophil infiltration. Mucosal tissue damages in IBD and CD occur in consequence of the neutrophil proteinases released from the infiltrated neutrophil. |
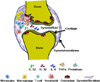 | Figure 2The effects of IL-32 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). An unknown mechanism triggers rheumatoid arthritis (RA) although anti-cytokine therapies are very effective to treat RA patients. The influx of various immune cells, monocyte, macrophage, T-cell, neutrophil, osteoclast, and synovial fibroblast cell present in synovial fluid of RA patients. These immune cells produce inflammatory cytokines such as IL-32, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα including serine proteinases from neutrophil resulted in bone resorption and joint damage in RA patients. |
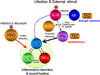 | Figure 3The regulation of IL-32 in vivo. The experiment of microarray in vitro by using A549 stable cells expressing IL-18Rβ (also known as IL-1R7) treated with IL-18 has identified IL-32 induction that is indicated by blue arrow in Fig. 3 (22). However, the regulation of IL-32 in vivo is the downstream of IFNγ. Th2 immune response is induced by IL-18 after helminth infection whereas interacellular pathogens such as virus, M. Tuberculosis M. Leprae triggers Th1 immune response through IL-12/IL-18. Th1 T-cells and natural killer cells-released IFNγ plus viral RNA are potent inducers of IL-32 through activation of acquired immunity whereas infection directly releases proteinase 3 (PR3) from neutrophils. PR3 cleaves IL-32, TNFα, and IL-1β and enhances these cytokine activities. The unrestrained innate and acquired immunity provoke local inflammation via cross induction of cytokine is involved in IL-32-related inflammatory disorders. |
IL
TNFα
IBD
NOD
PBMCs
MDP
CD
SEMFs
IFNγ
IL-32γ-TG
WT
DSS
DCs
RA
sRANKL
OA
Syk
JNK
FLS
siRNA
TSLP
TLR
BLP
LPS
poly I:C
dsRNA
DAMPs
PR3
Soohyun Kim 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0322-7935