INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Mice
Immunization
Flow cytometry
ELISPOT and ELISA analysis
Data analysis
RESULTS
Papain immunization recruits circulating basophils to the draining LN via IL-3
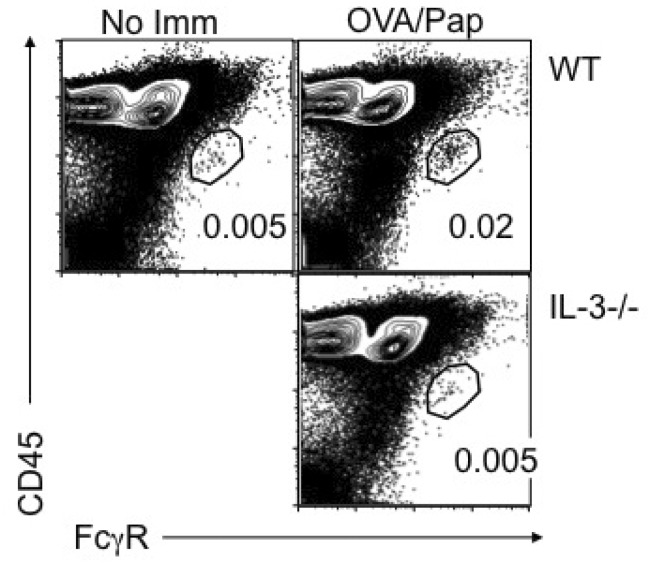 | Figure 1Papain immunization-mediated basophil LN recruitment requires IL-3. Groups of BALB/c and IL-3-/- mice were immunized with 100 µg OVA protein plus 50 µg papain. Draining cervical LN was collected 4 days post immunization. LN cells were examined for the existence of FcεRhigh CD45intermediate basophils. WT mice without immunization were included as negative controls. Data shown are representative of three repeated experiments. |
IL-3 plays no role in papain-induced Th2 immune responses
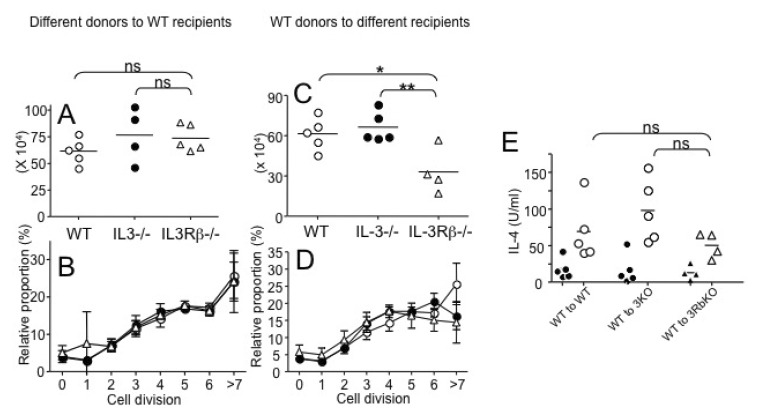 | Figure 2Roles of IL-3 and IL-3R during papain-induced Th2 immunity. (A, B) CD4 T cells were isolated from WT, IL-3-/-, and IL-3Rβ-/- DO11.10 mice, labeled with CFSE, and transferred into BALB/c recipients (3×106 cells per recipients). The recipients were then immunized with 100 µg OVA protein plus 50 µg papain into the ear pinnae. (A) Seven days post immunization, draining cervical LN cells were harvested. Total KJ1.26+ CD4 T cells were enumerated by FACS analysis. (B) CFSE dilution of KJ1.26+ CD4 T cells was also examined. (C~E) CD4 T cells were isolated from WT DO11.10 mice, labeled with CFSE, and transferred into WT, IL-3-/-, and IL-3Rβ-/- recipients (3×106 cells per recipients). (C) Total KL1.26+ CD4 T cells were enumerated as described above. (D) CFSE dilution was determined as described above. (E) Cervical LN cells were restimulated with OVA323-339 peptide for 24 hours and IL-4 production was determined by ELISA. Filled symbols are without peptide stimulation. Each symbol represents individually tested mouse. Similar results were obtained from two independent experiments. *p<0.05; **p<0.05;0.01. |
IL-3-independent Th2 immune responses after nonviable parasite Ag injection
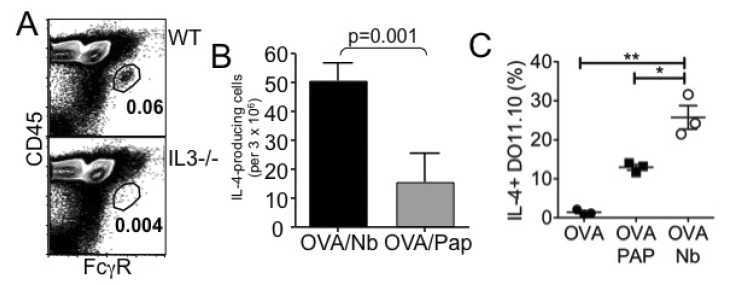 | Figure 3Nonviable N. brasiliensis immunization induces Th2 immunity. (A) WT or IL-3-/- mice were immunized with 100 µg OVA protein plus 500 dead L3 Nb parasites into the ear pinnae. Four days post injection, cervical draining LN was harvested and basophil recruitment was examined by FACS analysis. (B) Seven days post injection, cervical LN cells were harvested and in vitro stimulated with OVA peptide for 24 hours. IL-4-producing cells were determined by ELISPOT analysis as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Draining LN cells were in vitro stimulated with OVA peptide for 48 hours. Cells were stained for KJ1.26, CD4, and IL-4. DO11.10 CD4 T cell expression of intracellular IL-4 was determined by intracellular cytokine staining as described in Materials and Methods. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. |
Basophil depletion did not affect Th2 immune responses
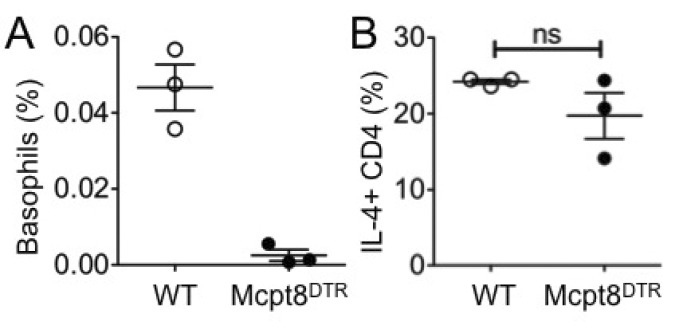 | Figure 4Th2 immune responses after basophil depletion. DO11.10 CD4 T cells were transferred into either WT or Mcpt8DTR mice. The recipients were injected with DT and immunized with OVA plus dead Nb. (A) Circulating basophils in the blood of the recipients were examined 7 days post immunization. (B) OVA specific IL-4-production was determined using draining LN cells harvested 7 days post immunization followed by in vitro 48 hours stimulation with OVA peptide. The proportion of IL-4 producing DO11.10 T cells was determined by FACS analysis. Each symbol represents individually tested mouse. WT, wild type; ns, not significant. |
Basophils are not major antigen presenting cells in the draining LN
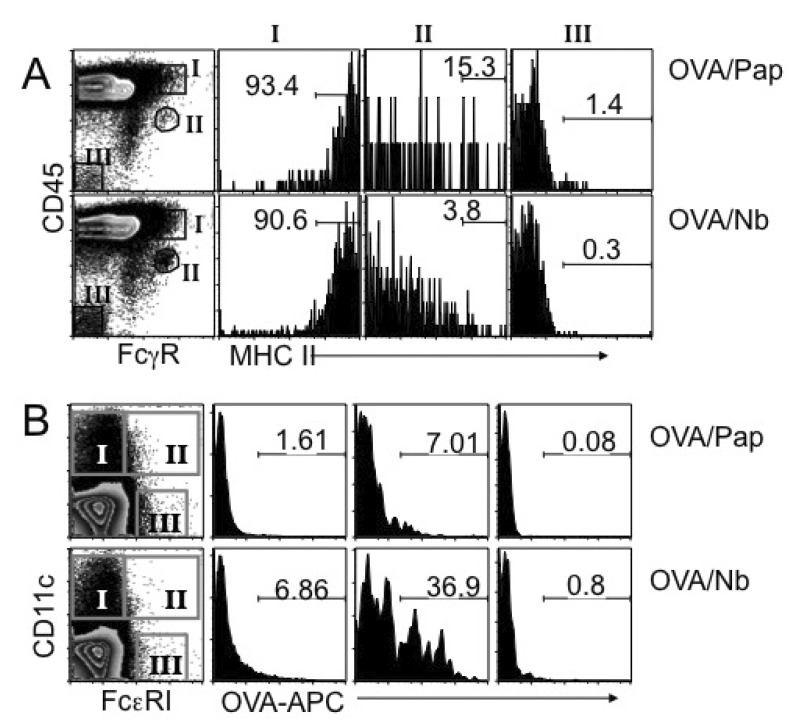 | Figure 5MHC II expression and Ag uptake of LN cells. (A) BALB/c mice were immunized with OVA plus papain or OVA plus dead Nb as indicated. Four days post immunization, draining LN cells were harvested, and stained for FcγR and CD45. MHC II expression on basophils (population II), FcγR/CD45high cells (population I) and non-lymphoid parenchymal cells (population III) were then examined. Shown are the proportions of MHC IIhigh cells among the indicated populations. (B) BALB/c mice were immunized with allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated OVA protein plus papain or dead Nb as described above. Four days later draining LN cells were harvested, and stained for CD11c and FcεRI. Ag uptake of conventional CD11c+ DC (population I), FcεRI/CD11c+ inflammatory DC (population II), and FcεRI+ CD11c- basophils (population III) was examined by FACS analysis. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results. |
IL-4 but not IL-25 or TSLP is essential to generate dead Nb-induced Th2 immunity
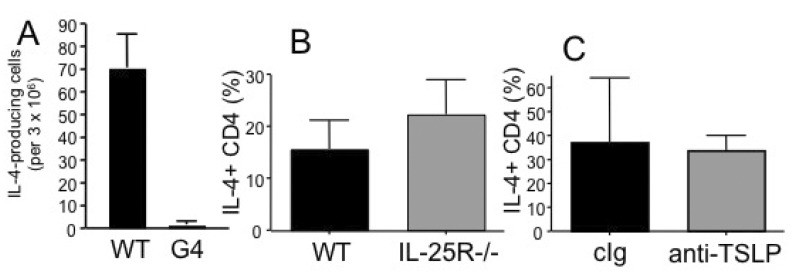 | Figure 6Roles of cytokine in dead Nb induced Th2 immunity. DO11.10 CD4 T cells were transferred into WT or IL-4-/- G4/G4 (A) or IL-25R-deficient (B) recipients. The recipients were immunized with OVA plus dead Nb as described above and IL-4-producing CD4 T cells were enumerated by ELISPOT assay as described above. (C) WT recipients of DO11.10 CD4 T cells were injected with neutralizing anti-TSLP mAb at days 0 and 4 of immunization. IL-4 production was examined as described above. Shown are the mean±STD of 3~4 individually tested recipients. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download