Abbreviations
PrPc
PrPSc
IKK
SEAP
HEK
HEK 293E
mRFP
Syk
Pyk2
Journal List > Immune Netw > v.13(4) > 1033380
PrPc
PrPSc
IKK
SEAP
HEK
HEK 293E
mRFP
Syk
Pyk2
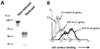 | Figure 1Preparation of soluble recombinant human PrPC-Fc and its binding to monocytes. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified soluble recombinant PrPC-Fc protein. Soluble PrPC-Fc consists of amino acids 21-229 of human PrPC fused with the Fc portion of human IgG1. Protein samples were separated on a 4~20% gradient SDS-PAGE gel with or without reducing condition. The molecular weight of soluble PrPC-Fc is 55~65 kDa in reducing condition and 120~140 kDa in non-reducing condition. (B) Human primary monocytes were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min and blocked with 5% normal goat serum for 30 min. They were then incubated with control Fc or with soluble PrPC-Fc at the indicated concentrations, followed by labeling with FITC-conjugated anti-human IgG. Flow cytometric analysis shows the specific binding of soluble PrPC-Fc to monocytes in a dose-dependent manner. |
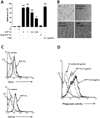 | Figure 2Differentiation of monocytes into macrophage-like cells following soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. (A) THP-1 cells were treated with soluble PrPC-Fc, heat-denatured (at 95℃ for 30 min) PrPC-Fc, or control Fc at the indicated concentrations for 30 min, and adherent cells were counted. Cell adherence was expressed as a percentage of the total number of cultured cells. The assay was performed in triplicate. Bar graphs represent the mean±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in comparison with untreated control. *p <0.05; **p<0.01. (B) Phase-contrast images of THP-1 cells treated with soluble PrPC-Fc, control Fc, or PMA for 48 h (200×magnification). (C) Primary monocytes were cultured with soluble PrPC-Fc or control Fc for 24 h followed by labeling with anti-CD1a-FITC or anti-CD11b-FITC and flow cytometric analysis. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. (D) Primary monocytes were cultured for 48 h in the presence of soluble PrPC-Fc or control Fc and then incubated for 6 h with E. coli labeled with RFP. Flow cytometric data indicate the amount of phagocytosis of E. coli by monocytes. The data are representative of two independent experiments. |
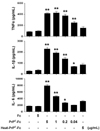 | Figure 3Cytokine production from monocytes stimulated by soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. Primary monocytes were cultured with soluble PrPC-Fc, heat-denatured PrPC-Fc, or control Fc at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. The culture supernatant was collected, and the concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 were determined with the Quantikine Assay Kit. The assay was performed in triplicate. Bar graphs represent the mean±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in comparison with untreated control. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. The data are representative of four independent experiments. |
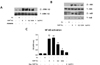 | Figure 4Activation of the ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways in THP-1 cells stimulated by soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. (A) THP-1 cells were treated with soluble PrPC-Fc or control Fc at the indicated concentrations for 15 min. For inhibition of ERK signaling, PD98059 (20µM) was added to the THP-1 culture 1 h before soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. Western blotting was performed with cell lysates to detect phosphorylated ERK-1/2 and total ERK-1/2. (B) THP-1 cells were treated with soluble PrPC-Fc or control Fc at the indicated concentrations for 15 min. Western blotting was performed with cell lysates to detect phosphorylated IKK, total IKK, phosphorylated IκB, and total IκB. (C) THP-1 Blue™ cells, which secret SEAP upon NF-κB activation, were treated with soluble PrPC-Fc, heat-denatured PrPC-Fc, or control Fc at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. Secreted SEAP in the culture supernatant was quantified by a colorimetric assay as described in Materials and Methods, and the OD at 655 nm was measured with a microplate reader. The assay was performed in triplicate. Bar graphs represent the mean±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in comparison with untreated control. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. |
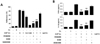 | Figure 5Role of ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways in monocyte cell adherence and cytokine production induced by soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. (A) THP-1 cells were treated with soluble PrPC-Fc or control Fc at the indicated concentrations for 30 min, and adherent cells were counted. Specific signaling inhibitors such as PD98059 (20µM), SN50 (10µM), or SB203580 (10µM) were added to the THP-1 culture 1 h before soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. Cell adherence is expressed as a percentage of the total number of cultured cells. The assay was performed in triplicate. Bar graphs represent the mean±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in comparison with soluble PrPC-Fc (1µg/ml)-treated cells. **p<0.01. (B) Primary monocytes were treated with 1µg/ml soluble PrPC-Fc or Fc control for 36 h. Specific signaling inhibitors such as PD98059 (20µM), SN50 (10µM), or SB203580 (10µM) were added to the monocyte culture 1 h before soluble PrPC-Fc treatment. The concentrations of TNF-α and IL-1β in the culture supernatant were determined with the Quantikine Assay Kit. The assay was performed in triplicate. Bar graphs represent the mean±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in comparison with soluble PrPC-Fc-treated cells. **p<0.01. The data are representative of two independent experiments. |
PrPc
PrPSc
IKK
SEAP
HEK
HEK 293E
mRFP
Syk
Pyk2
Eui-Cheol Shin 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6308-9503