Abstract
Purpose
We investigated the change in serum total immunoglobulin E (IgE) and allergen-specific IgE according to allergic diseases and age.
Methods
Allergic markers of children under 18 years of age with allergic diseases for the last 5 years were collected from 12 hospitals nationwide. The total data was 9,710. Data about levels of serum total IgE and allergen-specific IgE to 15 common allergens were collected.
Results
In children with asthma, serum total IgE was higher in older age than in younger age until age 7 to 12 years, at which time the level was highest (paper radioimmunosorbent test, 526.7 IU/mL; UniCAP, 339.9 IU/mL). The level was lower in older age than that during younger age. This change was similar to that in children with allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis. The level was highest at ages 7 to 12 years in children with allergic rhinitis, and at age 10 to 12 years in children with atopic dermatitis. In children with both asthma and allergic rhinitis, as well as in children with all three diseases, the change in serum total IgE was similar to that of children with an isolated disease. The highest level in children with all three diseases was higher than that in children with an isolated disease. The analysis of allergen-specific IgE positivity showed that food allergens were dominant before the age of 2 years, and that aeroallergens such as house dust mites were dominant.
Figures and Tables
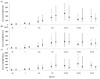 | Fig. 1The levels of serum total immunoglobulin G (IgE) according to age in children with asthma (A), allergic rhinitis (B) and atopic dermatitis (C) (■, paper radioimmunosorbent test; ●, UniCAP). |
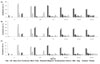 | Fig. 2Sensitization rate of 15 inhalant and food allergens according to age in children with asthma (A), allergic rhinitis (B) and atopic dermatitis (C). Dp, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; Df, Dermatophagoides farinae. |
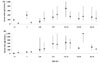 | Fig. 3The levels of serum total immunoglobulin (IgE) according to the age in patients with both asthma and allergic rhinitis (A) and patients with asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis (B) (■, paper radioimmunosorbent test; ●, UniCAP). |
References
1. Health, United States, 2005 with chartbook on trends in the health of Americans [Internet]. 2005. cited 2006 Oct 30. Hyattsville (MD): National Center for Health Statistics;Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus05.pdf.
3. Jee HM, Kim KW, Kim CS, Sohn MH, Shin DC, Kim KE. Prevalence of Asthma, Prevalence of asthma, rhinitis and eczema in Korean children using the international study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC) questionnaires. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009. 19:165–172. (Korea).
4. Ishizaka K, Ishizaka T, Terry WD. Antigenic structure of gamma-E-globulin and reaginic antibody. J Immunol. 1967. 99:849–858.
5. Johansson SG, Bennich H. Immunological studies of an atypical (myeloma) immunoglobulin. Immunology. 1967. 13:381–394.
6. Businco L, Marchetti F, Pellegrini G, Perlini R. Predictive value of cord blood IgE levels in 'atrisk' newborn babies and influence of type of feeding. Clin Allergy. 1983. 13:503–508.

7. Barbee RA, Halonen M, Lebowitz M, Burrows B. Distribution of IgE in a community population sample: correlations with age, sex, and allergen skin test reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981. 68:106–111.

8. Lindberg RE, Arroyave C. Levels of IgE in serum from normal children and allergic children as measured by an enzyme immunoassay. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986. 78(4 Pt 1):614–618.

9. Beeh KM, Ksoll M, Buhl R. Elevation of total serum immunoglobulin E is associated with asthma in nonallergic individuals. Eur Respir J. 2000. 16:609–614.

10. Burrows B, Martinez FD, Halonen M, Barbee RA, Cline MG. Association of asthma with serum IgE levels and skin-test reactivity to allergens. N Engl J Med. 1989. 320:271–277.

11. Lee SJ, Lee HC, Hong CS, Huh KB, Lee SY. A study of serum IgE levels in the healthy subjects and the patients with allergic diseases in Koreans. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982. 2:86–94.
12. Tack YJ, Kim YJ, Lee CS, Lee HC. Diagnostic significance of serum IgE level in bronchial asthma. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983. 3:23–29.
13. Hwang YS, Jung SI. A study of serum IgE levels in bronchial asthma and normal in Korea. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986. 6:8–14.
14. Gergen PJ, Arbes SJ Jr, Calatroni A, Mitchell HE, Zeldin DC. Total IgE levels and asthma prevalence in the US population: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 124:447–453.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download