Abstract
A 29-month-old boy presented with fever, dyspnea, and paleness. He was initially diagnosed with pneumonia and severe sepsis. Although he was treated with intravenous antibiotics and high dose methylprednisolone, dyspnea and paleness recurred two times. Under suspicion of pulmonary hemosiderosis, we performed video-assisted thoracoscopic lung biopsy and bronchoalveolar lavage on him and found hemosiderin-laden macrophages in both specimens. Despite thorough history and laboratory examination, we could not find any pathologic or serologic evidence for primary and secondary causes of pulmonary hemosiderosis except for one that indicating Heiner's syndrome. After taking oral prednisolone he showed improvement of anemia and dyspnea, which was maintained by milk avoidance. Based on the history and the existence of immunoglobulin G antibodies against milk components, we are considering it as the case of Heiner's syndrome.
Figures and Tables
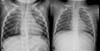 | Fig. 1(A) Chest X-ray done at the first day in our hospital shows mild haziness in the right lung and suspicious haziness in the lower lobe of left lung. (B) Chest X-ray done at the 8th day reveals improvement of both lung haziness. |
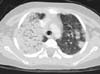 | Fig. 2Chest computed tomography done at the second day of the first admission. There is an extensive consolidation in the right lung and are multiple patchy consolidations in the left lung. |
 | Fig. 3Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cytology shows numerous hemosiderin-laden macrophages, many polymorphonuclear leukocytes, lymphocytes and some bronchial epithelial cells. (Prussian blue stain, ×400) |
References
1. You SK, Kim KS, Kim YJ, Koh YY. Two cases of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1988. 31:1209–1216.
2. Kjellman B, Elinder G, Garwicz S, Svan H. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis in Swedish children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984. 73:584–588.

3. Ohga S, Takahashi K, Miyazaki S, Kato H, Ueda K. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis in Japan: 39 possible cases from a survey questionnaire. Eur J Pediatr. 1995. 154:994–995.

4. Lim CS, Park SK, Park W, Lee SJ, Jung CZ. A case of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1996. 39:136–141.
5. Kwon YS, Kim JH, Lim DH, Kim SK, Chung SW, Son BK. A case of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis improved with steroid inhalation. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1998. 41:1153–1156.
6. Park JS, Pyun BY, Kim YT. A case of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis: long term follow-up. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 1999. 9:226–232.
7. Kwak GY, Lee NY, Lee MH, Lee SY, Chung SY, Kang JH, et al. A case of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis with seasonal recurrence. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:256–260.

8. Kiper N, Gocmen A, Ozcelik U, Dilber E, Anadol D. Long-term clinical course of patients with idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis (1979-1994): prolonged survival with low-dose corticosteroid therapy. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1999. 27:180–184.

9. Nuesslein TG, Teig N, Rieger CH. Pulmonary haemosiderosis in infants and children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2006. 7:45–48.

10. Kabra SK, Bhargava S, Lodha R, Satyavani A, Walia M. Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis: clinical profile and follow up of 26 children. Indian Pediatr. 2007. 44:333–338.
11. Ioachimescu OC, Stoller JK. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: diagnosing it and finding the cause. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008. 75:258–280.

12. Moissidis I, Chaidaroon D, Vichyanond P, Bahna SL. Milk-induced pulmonary disease in infants (Heiner syndrome). Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005. 16:545–552.

13. Mansoor DK, Sharma HP. Clinical presentations of food allergy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2011. 58:315–326.

14. Fiocchi A, Brozek J, Schünemann H, Bahna SL, von Berg A, Beyer K, et al. World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow's Milk Allergy (DRACMA) Guidelines. World Allergy Organ J. 2010. 3:57–161.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download