Abstract
Purpose
Interleukin (IL)-33, a member of the IL-1 cytokine family, is considered to be important for innate-type mucosal immunity of the lung and also has been suggested to induce Th2-type immune responses. We aimed to investigate if IL-33 is involved in airway inflammation due to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in young children.
Methods
Thirty-eight infants (≤24 months of age) admitted with their first episode of RSV bronchiolitis were enrolled in the study. Atopy was defined by having at least 1 allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE), positive result to skin prick test, or high serum IgE levels. The patients were assessed to have severe symptoms when they had ≥2 of the following clinical findings: hypoxemia (<92% oxygen saturation), rapid breathing (and/or lower chest wall indrawing), and >7 days of hospital stay. The levels of IL-33 and the IL-33 receptor (sST2) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in nasal secretion samples collected from the patients on admission and compared with 20 age-matched controls. We also investigated the levels of IL-33 and sST2 in relation to the atopic status and symptom severity of the patients.
Figures and Tables
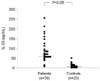 | Fig. 1Interleukin (IL)-33 levels in nasal secretion of the patients with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis were significantly increased compared to the control levels. |
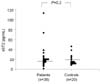 | Fig. 2Interleukin (IL)-33 receptor (sST2) levels showed no significant difference between the patients with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis and controls. |
References
1. Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005. 23:479–490.

2. Oboki K, Ohno T, Kajiwara N, Arae K, Morita H, Ishii A, et al. IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of innate rather than acquired immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. 107:18581–18586.

3. Chow JY, Wong CK, Cheung PF, Lam CW. Intracellular signaling mechanisms regulating the activation of human eosinophils by the novel Th2 cytokine IL-33: implications for allergic inflammation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. 7:26–34.

4. Pecaric-Petkovic T, Didichenko SA, Kaempfer S, Spiegl N, Dahinden CA. Human basophils and eosinophils are the direct target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member IL-33. Blood. 2009. 113:1526–1534.

5. Suzukawa M, Koketsu R, Iikura M, Nakae S, Matsumoto K, Nagase H, et al. Interleukin-33 enhances adhesion, CD11b expression and survival in human eosinophils. Lab Invest. 2008. 88:1245–1253.

6. Oboki K, Nakae S, Matsumoto K, Saito H. IL-33 and Airway Inflammation. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011. 3:81–88.

7. Stolarski B, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Kewin P, Xu D, Liew FY. IL-33 exacerbates eosinophil-mediated airway inflammation. J Immunol. 2010. 185:3472–3480.

8. Iwahana H, Hayakawa M, Kuroiwa K, Tago K, Yanagisawa K, Noji S, et al. Molecular cloning of the chicken ST2 gene and a novel variant form of the ST2 gene product, ST2LV. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. 1681:1–14.

9. Tago K, Noda T, Hayakawa M, Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Yashiro T, et al. Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of a variant form of the human ST2 gene product, ST2V. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. 285:1377–1383.

10. Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Ito-Kosaka A, Kuroiwa K, Tago K, Komatsu N, et al. Different promoter usage and multiple transcription initiation sites of the interleukin-1 receptor-related human ST2 gene in UT-7 and TM12 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1999. 264:397–406.

11. Oboki K, Ohno T, Kajiwara N, Saito H, Nakae S. IL-33 and IL-33 receptors in host defense and diseases. Allergol Int. 2010. 59:143–160.

12. Walzl G, Matthews S, Kendall S, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Coyle AJ, Openshaw PJ, et al. Inhibition of T1/ST2 during respiratory syncytial virus infection prevents T helper cell type 2 (Th2)- but not Th1-driven immunopathology. J Exp Med. 2001. 193:785–792.

13. Mathisen M, Strand TA, Sharma BN, Chandyo RK, Valentiner-Branth P, Basnet S, et al. Clinical presentation and severity of viral community-acquired pneumonia in young Nepalese children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2010. 29:e1–e6.

14. Kin Key N, Araujo-Neto CA, Nascimento-Carvalho CM. Severity of childhood community-acquired pneumonia and chest radiographic findings. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2009. 44:249–252.

15. Yagami A, Orihara K, Morita H, Futamura K, Hashimoto N, Matsumoto K, et al. IL-33 mediates inflammatory responses in human lung tissue cells. J Immunol. 2010. 185:5743–5750.

16. Kondo Y, Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, Futatsugi-Yumikura S, Morimoto M, Hayashi N, et al. Administration of IL-33 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia in the lungs in the absence of adaptive immune system. Int Immunol. 2008. 20:791–800.

17. Lloyd CM. IL-33 family members and asthma - bridging innate and adaptive immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010. 22:800–806.

18. Prefontaine D, Lajoie-Kadoch S, Foley S, Audusseau S, Olivenstein R, Halayko AJ, et al. Increased expression of IL-33 in severe asthma: evidence of expression by airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol. 2009. 183:5094–5103.

19. Prefontaine D, Nadigel J, Chouiali F, Audusseau S, Semlali A, Chakir J, et al. Increased IL-33 expression by epithelial cells in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 125:752–754.

20. Kropf P, Herath S, Klemenz R, Muller I. Signaling through the T1/ST2 molecule is not necessary for Th2 differentiation but is important for the regulation of type 1 responses in nonhealing Leishmania major infection. Infect Immun. 2003. 71:1961–1971.

21. Hazlett LD, McClellan SA, Barrett RP, Huang X, Zhang Y, Wu M, et al. IL-33 shifts macrophage polarization, promoting resistance against Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. 51:1524–1532.

22. Garlanda C, Anders HJ, Mantovani A. TIR8/SIGIRR: an IL-1R/TLR family member with regulatory functions in inflammation and T cell polarization. Trends Immunol. 2009. 30:439–446.

23. Oshikawa K, Yanagisawa K, Tominaga S, Sugiyama Y. Expression and function of the ST2 gene in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002. 32:1520–1526.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download