Abstract
Purpose
Pediatric asthma is the most common chronic disease in children. It negatively affects the health-related quality of life (QoL) in children with this disease and of their caregivers. This study evaluated the relationship between clinical disease severity and the QoL of patients with asthma and their caregivers.
Methods
The study included 247 patients with asthma and their caregivers. The patients and caregivers completed the Korean Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire and the Korean Pediatric Asthma Caregivers Quality of Life Questionnaire, respectively, during clinic visits. The results were expressed as the mean score for each domain. All items were rated from 1 to 5: 1, low QoL; and 5, satisfactory QoL.
Results
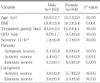
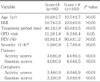
The emotion and activity QoL scores of boys were significantly higher than those of girls (P=0.001). The QoL of both patients and their caregivers was correlated more with the patients' subjective symptom scores than with the clinical severity of asthma or with lung function.
Conclusion
The QoL of patients with asthma and their caregivers decreased as asthmatic symptoms became worse. Controlling asthma symptoms is important for improving the QoL of both patients and their caregivers. Patients and their caregivers need to be evaluated and counseled during asthma treatment to improve their QoL.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:343–350.

2. Clark NM, Feldman CH, Evans D, Levison MJ, Wasilewski Y, Mellins RB. The impact of health education on frequency and cost of health care use by low income children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986. 78(1 Pt 1):108–115.

3. Rachelefsky GS. Improving patient adherence: the asthma template. Pediatr Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2007. 20:146–156.

4. Bender BG. Overcoming barriers to nonadherence in asthma treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 109:6 Suppl. S554–S559.

6. Ungar WJ, Mirabelli C, Cousins M, Boydell KM. A qualitative analysis of a dyad approach to health-related quality of life measurement in children with asthma. Soc Sci Med. 2006. 63:2354–2366.

7. 2006 Revision: GINA report, global strategy for asthma management and prevention. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). [unknown copyright year]. cited 2010 Oct 8. [unknown place]: Global Initiative for Asthma;Available from: http://www.ginasthma.org/Guidelines/guidelines-archived-2006-revision.html.
8. Bacharier LB, Strunk RC, Mauger D, White D, Lemanske RF Jr, Sorkness CA. Classifying asthma severity in children: mismatch between symptoms, medication use, and lung function. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 170:426–432.
9. Yang E, Kim W, Kwon BC, Choi SY, Sohn MH, Kim KE. Relationship among pulmonary function, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and atopy in children with clinically stable asthma. Lung. 2006. 184:73–79.

10. Cha JK, Oh JW, Hong SJ, Lee HR, Lee MI, Kim KE, et al. Development and multicenter study on Korean pediatric asthma caregiver's quality of life questionnaire (KPACQLQ). J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 20:480–491.
11. Cha JK, Oh JW, Hong SJ, Lee HR, Lee MI, Kim KE, et al. Development and multicenter study on Korean pediatric asthma quality of life questionnaire (KPAQLQ). J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 20:492–508.
12. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Ferrie PJ, Griffith LE. Measuring quality of life in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993. 147:832–838.

13. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Epstein RS, Ferrie PJ, Jaeschke R, Hiller TK. Evaluation of impairment of health related quality of life in asthma: development of a questionnaire for use in clinical trials. Thorax. 1992. 47:76–83.

14. Rowe BH, Oxman AD. Performance of an asthma quality of life questionnaire in an outpatient setting. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993. 148:675–681.

15. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Ferrie PJ, Griffith LE, Townsend M. Measuring quality of life in children with asthma. Qual Life Res. 1996. 5:35–46.

16. Juniper EF, Johnston PR, Borkhoff CM, Guyatt GH, Boulet LP, Haukioja A. Quality of life in asthma clinical trials: comparison of salmeterol and salbutamol. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:66–70.

17. Mrazek DA. Psychiatric complications of pediatric asthma. Ann Allergy. 1992. 69:285–290.
18. Kim NH, Seol EI, Jeon GH, Lee GH, Cho MG, Son C. The psychological recognition of asthmatic children from parents' views. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1997. 40:1725–1730.
19. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Willan A, Griffith LE. Determining a minimal important change in a disease-specific Quality of Life Questionnaire. J Clin Epidemiol. 1994. 47:81–87.

20. Malo JL, Boulet LP, Dewitte JD, Cartier A, L'Archevêque J, Côté J, et al. Quality of life of subjects with occupational asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993. 91:1121–1127.

21. Juniper EF. The value of quality of life in asthma. Eur Respir Rev. 1997. 7:333–337.
22. Josie KL, Greenley RN, Drotar D. Health-related quality-of-life measures for children with asthma: reliability and validity of the Children's Health Survey for Asthma and the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 3.0 Asthma Module. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007. 98:218–224.

23. Zandieh F, Moin M, Movahedi M. Assessment of quality of life in Iranian asthmatic children, young adults and their caregivers. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006. 5:79–83.
24. Raat H, Bueving HJ, de Jongste JC, Grol MH, Juniper EF, van der Wouden JC. Responsiveness, longitudinal- and cross-sectional construct validity of the Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (PAQLQ) in Dutch children with asthma. Qual Life Res. 2005. 14:265–272.

25. Rho HJ, Park MS, Park CW, Yun YY, Park JW, Hong CS, et al. Factors influencing quality of life of asthmatic patients in Korea. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 20:209–221.
26. Kim UC, Hong CS, Lee JG, Park YS. Factors influencing health and quality of life among allergy and asthma patients: with specific focus on self-efficacy, social support and health management. Korean J Psychol Soc Issues. 2005. 11:143–181.
27. Jung JY, Son JY, Hong SJ, Lee YW, Sin YS, Park JW, et al. Comparison of the patient's global self-assessment scoring method with the quality of life questionnaire for adult Korean asthmatics. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 28:134–142.
28. van der Molen T, Sears MR, de Graaff CS, Postma DS, Meyboom-de Jong B. Quality of life during formoterol treatment: comparison between asthma-specific and generic questionnaires. Canadian and the Dutch Formoterol Investigators. Eur Respir J. 1998. 12:30–34.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download