Abstract
Purpose
Pandemic influenza viruses have caused significant morbidity and mortality. Pandemic influenza A (H1N1) was detected in April 2009 and caused worldwide outbreak. We investigated the differences in clinical characteristics and courses between pandemic and seasonal influenzas.
Methods
We reviewed the medical records of pediatric patients, (≤18 years) with influenza hospitalized to Gachon University Gil Medical Center from the 1 April 2009 to the 31 August 2011.
Results
Two hundred twenty-six patients with pandemic influenza and 118 patients with seasonal influenza were included. Age, sex, and proportion of underlying diseases were similar between the two groups. Hypoxemia, shortness of breath, and tachypnea were more common in pandemic influenza.(P<0.05) Oxygen supplementation and radiologically confirmed pneumonia were more common in pandemic influenza.(P<0.005) However, there were no significant differences in the mean duration of hospitalization, proportion of patients admitted to the intensive care unit, need for mechanical ventilation, and death.
Figures and Tables
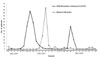 | Fig. 1Epidemiologic curve of date of hospitalization of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) and seasonal influenza. |
Table 1
Demographics and Underlying Diseases of Hospitalized Pediatric Patients with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) and Seasonal Influenza

Table 2
Clinical Characteristics of Hospitalized Pediatric Patients with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) and Seasonal Influenza

Values are presented as number (%).
*Hypoxemia was defined as an oxygen saturation of less than 94% while the patient was breathing room air. †Tachypnea was defined by age, >60/min (birth to 3 mo), >50/min (3 mo to 1 yr), >40/min (1 to <3 yr), >35/min (3 to <6 yr), >30/min (6 to <12 yr) and >20/min (≥12 yr) (Data were derived from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)30). ‡Exclude adverse effect of antiviral drug. §One patient with seasonal influenza had underlying seizure disorder.
References
1. Glezen WP. Feigin RD, Cherry J, Demmler-Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, editors. Influenza viruses. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 2009. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2395–2413.

2. Kim WJ. Novel influenza A/H1N1 pandemic: current status and prospects. J Korean Med Assoc. 2009. 52:787–794.

3. Halasa NB. Update on the 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010. 22:83–87.

4. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korean influenza surveillance report,2009-2010. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2010. 3:833–841.
5. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Analysis of reported pandemic influenza (A/H1N1 2009) virus infections in Korea--from April, 2009 through August, 2010. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2010. 3:637–642.
6. Libster R, Bugna J, Coviello S, Hijano DR, Dunaiewsky M, Reynoso N, et al. Pediatric hospitalizations associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Argentina. N Engl J Med. 2010. 362:45–55.

7. Hawkes M, Schuh S, Ipp M, Bitnun A, Richardson SE, Parkin PC, et al. Natural history of pandemic H1N1 2009 influenza infection in healthy pediatric outpatients. Acad Pediatr. 2011. 11:66–74.

8. Kumar S, Havens PL, Chusid MJ, Willoughby RE Jr, Simpson P, Henrickson KJ. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics of children hospitalized with 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2010. 29:591–594.

9. O'Riordan S, Barton M, Yau Y, Read SE, Allen U, Tran D. Risk factors and outcomes among children admitted to hospital with pandemic H1N1 influenza. CMAJ. 2010. 182:39–44.
10. Chiu SS, Chan KH, Wong WH, Chan EL, Peiris JS. Age-matched comparison of children hospitalized for 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza with those hospitalized for seasonal H1N1 and H3N2. PLoS One. 2011. 6:e21837.
11. Belongia EA, Irving SA, Waring SC, Coleman LA, Meece JK, Vandermause M, et al. Clinical characteristics and 30-day outcomes for influenza A 2009 (H1N1), 2008-2009 (H1N1), and 2007-2008 (H3N2) infections. JAMA. 2010. 304:1091–1098.

12. Tamma PD, Turnbull AE, Milstone AM, Cosgrove SE, Valsamakis A, Budd A, et al. Clinical outcomes of seasonal influenza and pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in pediatric inpatients. BMC Pediatr. 2010. 10:72.

13. Kim SH, Park CH, Huh K, Shim GH, Kim HB, You SJ, et al. Comparison of clinical manifestation and laboratory findings between H1N1 and influenza B infection. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012. 22:64–70.

14. Kang TG, Kim MJ, Kim BG, An HS, Yun HJ, Choi EJ, et al. Comparisons of clinical features among influenza A (H1N1) and seasonal influenza A and B during 2009 to 2010 at a single institution. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011. 21:269–276.

15. Munster VJ, de Wit E, van den Brand JM, Herfst S, Schrauwen EJ, Bestebroer TM, et al. Pathogenesis and transmission of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza virus in ferrets. Science. 2009. 325:481–483.

16. Maines TR, Jayaraman A, Belser JA, Wadford DA, Pappas C, Zeng H, et al. Transmission and pathogenesis of swine-origin 2009 A (H1N1) influenza viruses in ferrets and mice. Science. 2009. 325:484–487.

17. Chan MC, Chan RW, Yu WC, Ho CC, Yuen KM, Fong JH, et al. Tropism and innate host responses of the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus in ex vivo and in vitro cultures of human conjunctiva and respiratory tract. Am J Pathol. 2010. 176:1828–1840.

18. Gordon A, Saborio S, Videa E, Lopez R, Kuan G, Balmaseda A, et al. Clinical attack rate and presentation of pandemic H1N1 influenza versus seasonal influenza A and B in a pediatric cohort in Nicaragua. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. 50:1462–1467.

19. Khandaker G, Lester-Smith D, Zurynski Y, Elliott EJ, Booy R. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 and seasonal influenza A (H3N2) in Children's Hospital, Australia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011. 17:1960–1962.

20. Kim WJ. Pandemic influenza (H1N1 2009): experience and lessons. Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:61–63.

21. Perez-Padilla R, de la Rosa-Zamboni D, Ponce de Leon S, Hernandez M, Quinones-Falconi F, Bautista E, et al. Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:680–689.

22. Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, Schmitz AM, Benoit SR, Louie J, et al. Hospitalized patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza in the United States, April-June 2009. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:1935–1944.

23. Hedrick JA, Barzilai A, Behre U, Henderson FW, Hammond J, Reilly L, et al. Zanamivir for treatment of symptomatic influenza A and B infection in children five to twelve years of age: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000. 19:410–417.

24. Whitley RJ, Hayden FG, Reisinger KS, Young N, Dutkowski R, Ipe D, et al. Oral oseltamivir treatment of influenza in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001. 20:127–133.

25. Higuera Iglesias AL, Kudo K, Manabe T, Corcho Berdugo AE, Corrales Baeza A, Alfaro Ramos L, et al. Reducing occurrence and severity of pneumonia due to pandemic H1N1 2009 by early oseltamivir administration: a retrospective study in Mexico. PLoS One. 2011. 6:e21838.

26. Yang SG, Cao B, Liang LR, Li XL, Xiao YH, Cao ZX, et al. Antiviral therapy and outcomes of patients with pneumonia caused by influenza A pandemic (H1N1) virus. PLoS One. 2012. 7:e29652.

27. Itoh Y, Shinya K, Kiso M, Watanabe T, Sakoda Y, Hatta M, et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of new swine-origin H1N1 influenza viruses. Nature. 2009. 460:1021–1025.

28. Ko JH, Kim JH, Kang JH, Kim JH, Eun BW, Kim KH, et al. Characteristics of hospitalized children with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1): a multicenter study in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. 27:408–415.

29. Lee HJ, Min SJ, Choi JH, Kang EK. Clinical characteristics of hospitalized pediatric patients with 2009 novel influenza A infection. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2010. 20:130–137.
30. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. 2009-2010 Influenza season triage algorithm for children (≤18 years) with influenza-like illness. [c2012]. cited 2009 Oct 16. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/clinicians/pdf/childalgorithm2.pdf.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download